Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: 5T117: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease (2816–2821)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Pathologic T cell-B cell interactions are hallmark features of many autoimmune diseases. PD-1hi CXCR5- T peripheral helper (Tph) cells are B cell-helper T cells that are highly expanded in the joints of seropositive RA patients and in the circulation of SLE patients. Like T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, Tph cells produce IL-21 and stimulate B cell differentiation into plasmablasts in vitro. B cell helper-function is often considered dependent on the transcription factor Bcl6, a master regulator of Tfh-cells. However, Tph cells do not express high levels of Bcl6, which suggests that transcription factors other than Bcl6 may control IL-21 production and B cell-helper function in human CD4+ T cells. Here we evaluated the role of the transcription factor MAF in controlling T cell help to B cells.
Methods: MAF expression in human CD4+ T cell subsets was determined by RNA-seq and flow cytometry. To evaluate the role of MAF, we disrupted the gene encoding MAF by nucleofection of a CRISRP/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex in primary CD4+ T cells and in sorted Tph cells. Expression of IL-21 and other cytokines was determined by RT-PCR and ELISA. B cell-helper function of CRISPR-treated T cells was evaluated by co-culturing sorted T cell subsets from SLE or control donors with memory B cells plus SEB. Plasmablast formation was determined by flow cytometry.
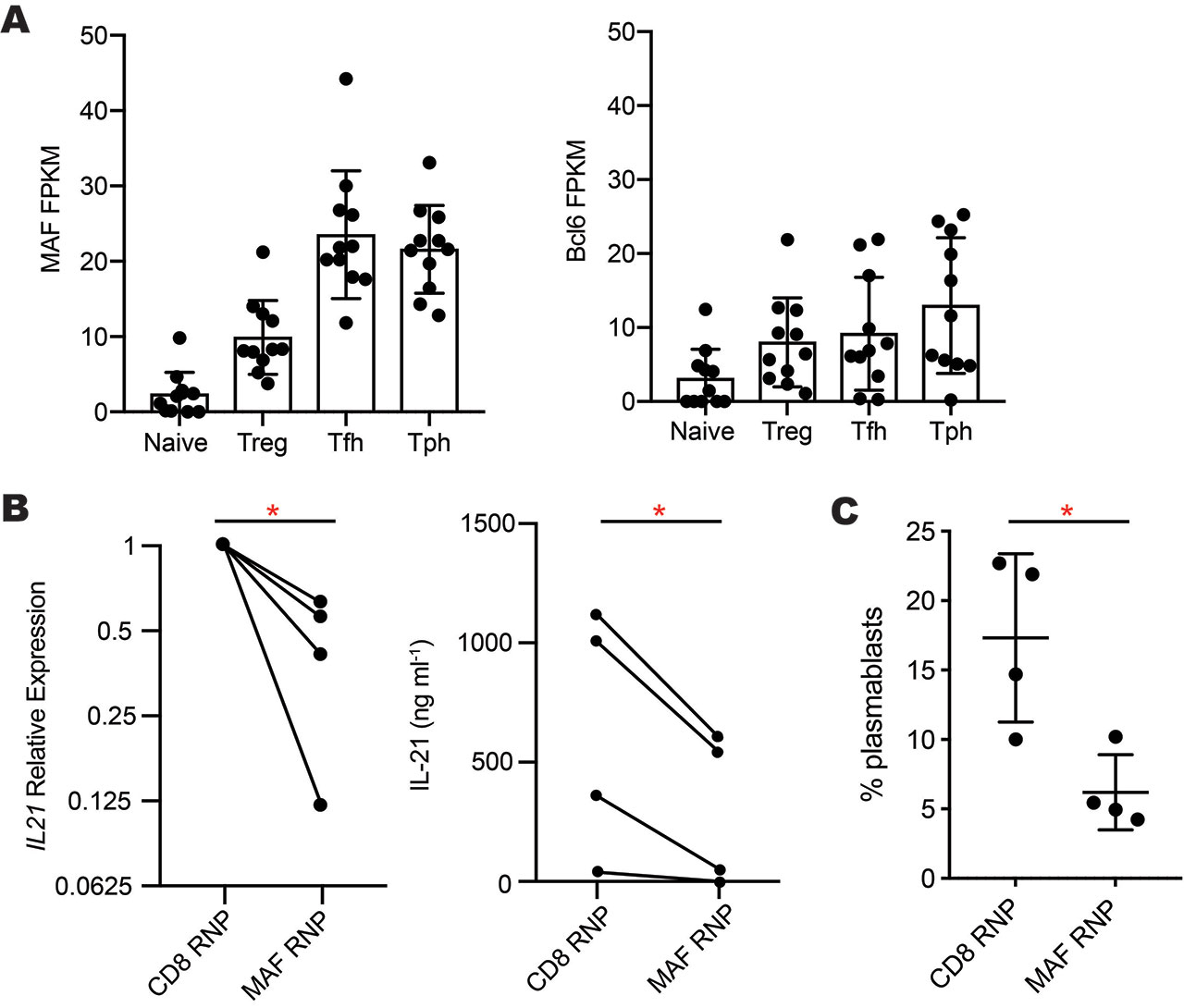
Results: RNA-seq analyses of CD4+ T cell subsets revealed high expression of MAF, but not BCL6, in both Tph cells and Tfh cells sorted from blood of RA and SLE patients (Fig. 1A). After 2 days of CD3/CD28 stimulation, Tph cells and Tfh cells expressed >2-fold higher levels of MAF protein than did naive or PD-1neg memory CD4+ T cells. High expression of MAF in both Tph cells and Tfh cells, two subsets that produce IL-21, suggested a possible connection between MAF and IL-21. To test this, we deleted MAF in primary human CD4+ T cells by nucleofection of a MAF-targeting CRISPR/Cas9 RNP. This method abrogated MAF protein expression in >80% of T cells. Compared to a control CRISPR targeting CD8, MAF deletion reduced mRNA expression of IL21 and IL10 in 4 independent donors and inhibited secretion of IL-21 protein (Fig. 1B). Using Tph cells sorted from blood of SLE patients, we confirmed that Tph cells stimulate differentiation of memory B cells into plasmablasts in an IL-21-dependent manner, as neutralization of IL-21, but not IL-10, inhibited plasmablast formation by ~50%. To evaluate the effect of MAF on B cell-helper function, we deleted MAF by CRISPR in sorted human Tph cells from SLE patients or controls and then co-cultured these cells with memory B cells. Deletion of MAF reduced the ability of Tph cells to induce B cell differentiation into plasmablasts by over 50% compared Tph cells treated with a control RNP (Fig. 1C).
Conclusion: High expression of MAF is a common feature of both Tph cells and Tfh cells, two T cell populations that produce high levels of IL-21. Loss of MAF inhibits IL-21 expression in primary human CD4+ T cells and abrogates the ability of Tph cells to help B cells. MAF may regulate key components of T cell help to B cells in autoimmune conditions.
A- MAF and Bcl6 expression in RNA-seq data of T cell subsets sorted from blood of RA -n=5- and SLE -n=6- patients. B- Reduced IL-21 mRNA expression -left- and protein secretion -right- by primary human CD4+ T cells after CRISPR-deletion of MAF -n=4 donors-. C- Plasmablast generation in co-cultures of Tph cells treated with MAF- or CD8-targeting complexes co-cultured with allogeneic memory B cells. *p<0.05 by paired t-test.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bocharnikov A, Wacleche V, Cao Y, Rao D. The Transcription Factor MAF Controls the Ability of T Peripheral Helper (Tph) Cells to Help B Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-transcription-factor-maf-controls-the-ability-of-t-peripheral-helper-tph-cells-to-help-b-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-transcription-factor-maf-controls-the-ability-of-t-peripheral-helper-tph-cells-to-help-b-cells/