Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The alternative complement pathway has been implicated in the pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV). Change in markers of complement activation within patients have not been reported. This study measured levels of urinary complement fragment Ba (uBa) longitudinally in patients with AAV.
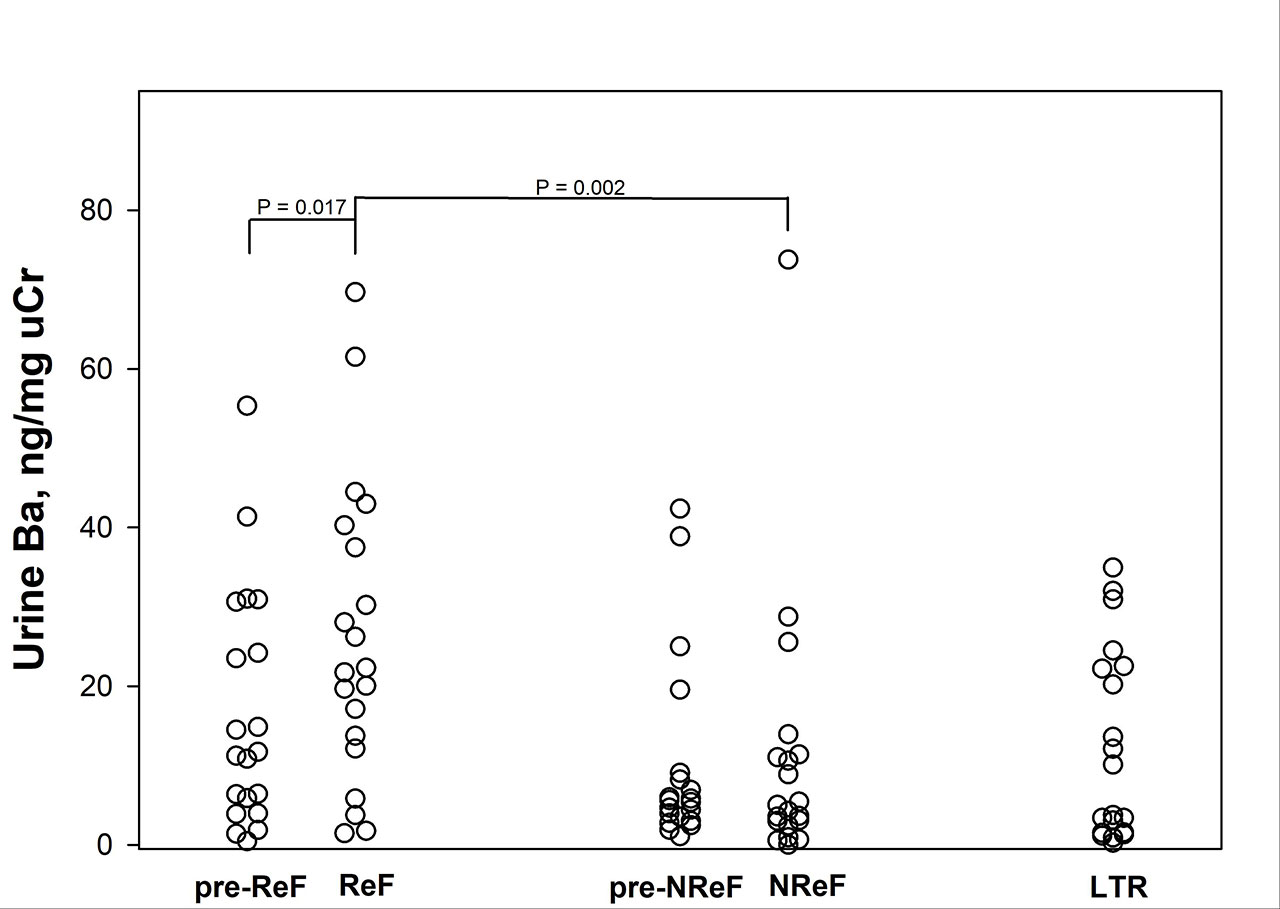
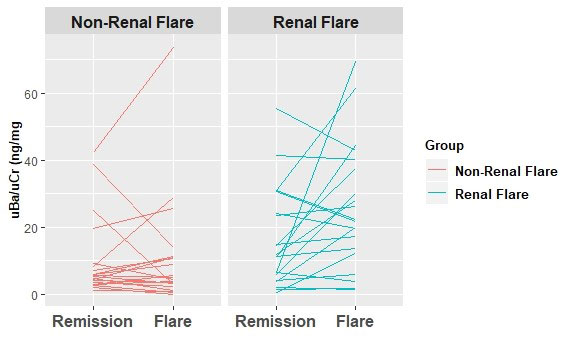
Methods: Urine levels of uBa were measured by ELISA (corrected to urine creatinine) in 3-4 serial samples in 60 patients with AAV: 20 who developed a flare with renal disease (ReF), 20 who developed a non-ReF (NReF), and 20 in long term remission (LTR). Because timing of pre-flare to flare visits differed from patient to patient, these values were averaged for each patient (pre-ReF or pre-NReF), normalized by natural log-transformation, and compared to flare by paired t test. Differences between ReF and NReF levels were assessed by unpaired t test. Differences between pre-ReF, pre-NReF, and average LTR levels were assessed by ANOVA.
Results: The median age of participants was 59 years, 53% were male, 93% were White, and 93% were ANCA positive. There were no differences in uBa levels between pre-ReF, pre-NReF, and LTR (P=0.360) (Figure). Despite overlap, overall uBa levels were higher in ReF compared to pre-ReF (P=0.017), and to NReF (P = 0.002). Levels of uBa levels did not change from pre-NReF to NReF (P=0.232).
Conclusion: Increased uBa levels suggests that alternative complement pathway activation contributes to the pathogenesis of ReF in AAV. However, many patients experiencing ReF do not show high uBa levels. Thus, uBa may identify a subset of patients with ReF who might benefit from complement-targeted therapies. Other factors defining this subset remain to be determined.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Almaani S, Toy C, Levesque A, Fussner L, Meara A, Yu L, Cuthbertson D, Carette S, Khalidi N, Koening C, Langford C, McAlear C, Moreland L, Pagnoux C, Seo P, Sreih A, Ytterberg S, Monach P, Merkel P, Rovin B, Birmingham D. Urine Complement Ba Levels During Flares of Renal Disease in Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-complement-ba-levels-during-flares-of-renal-disease-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/urine-complement-ba-levels-during-flares-of-renal-disease-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis/