Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anifrolumab, a fully human anti–IFN Type I receptor mAb, is under investigation for the treatment of SLE at a dose of 300 mg intravenously (IV) once every 4 weeks (Q4W), as added to Standard of Care (SOC) therapy. As subcutaneous (SC) administration may offer a greater treatment convenience and accessibility for patients, we evaluated the PK, PD, safety, tolerability, and efficacy of SC anifrolumab, when added to SOC in adults with Type I IFN test-high SLE and active skin disease.
Methods: Patients (all fulfilling 1997 ACR SLE criteria) were randomized to the following, added to SOC, for up to 52 weeks (followed by an 8-week follow-up period): anifrolumab 150 mg, anifrolumab 300 mg or corresponding placebo, all SC Q2W (NCT02962960). Primary endpoints: PK (concentration of anifrolumab) and PD (Type I IFN gene suppression) at Week 12. Secondary endpoints: safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of anifrolumab over 52 weeks. Exploratory endpoint: efficacy of SC anifrolumab on active SLE skin disease using change from baseline in Cutaneous Lupus erythematosus disease Area and Severity Index (CLASI) activity score.
Results: Patients (anifrolumab 150 mg [n=14], 300 mg [n=13], placebo [n=9]), were Caucasian (77.8%) or Asian (22.2%); mean age 44.9 years; 89% female; 94% ANA positive; and 64% anti-dsDNA positive. Low C3 or C4 was observed in 53% and 36% of patients, respectively. Baseline mean CLASI and mean total SLEDAI-2K scores were 15.5 and 9.6, respectively. The baseline mean OCS dose differed between treatment groups: 8.2 mg/day prednisone or equivalent for combined anifrolumab groups and 10.3 mg/day for placebo group. The majority (75%) were on stable anti-malarial therapy.
Anifrolumab exhibited nonlinear PK where trough concentration increases were more than dose-proportional (Figure 1A). At Week 12, the median percentage neutralization of the Type I IFN PD signature was 88.0%, 90.7% and 18.5% in the anifrolumab 150 mg, 300 mg, and placebo groups, respectively; suppression was sustained over the 52-week treatment period (Figure 1B). At Week 12, a ≥75% neutralization of the Type I IFN PD signature was observed in 66.7%, 76.9%, and 11.1% of patients in the anifrolumab 150 mg, 300 mg and placebo groups, respectively. Over 52 weeks, 85.2% (combined anifrolumab) and 77.8% (placebo) of patients experienced ≥1 AE (Table 1). Ten SAEs were reported in 6 patients, all in anifrolumab groups (Table 1). The most commonly reported AEs across all treatment groups were upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, bronchitis and headache. Anifrolumab exhibited low immunogenicity, with ADA detected post-baseline in only 2 patients and in low titers. No injection site reactions were reported. Greater reductions in CLASI activity score were observed at Week 52 in the anifrolumab 150 mg and 300 mg groups, vs. placebo (–10.2 and –13.2, vs. –6.3, respectively) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The observed PK/PD profile of SC anifrolumab was consistent with previous studies using IV administration. In addition, SC anifrolumab showed low immunogenicity and an acceptable safety and tolerability profile, similar to previous, larger IV studies in SLE. These findings support further development of SC anifrolumab as a treatment for SLE.
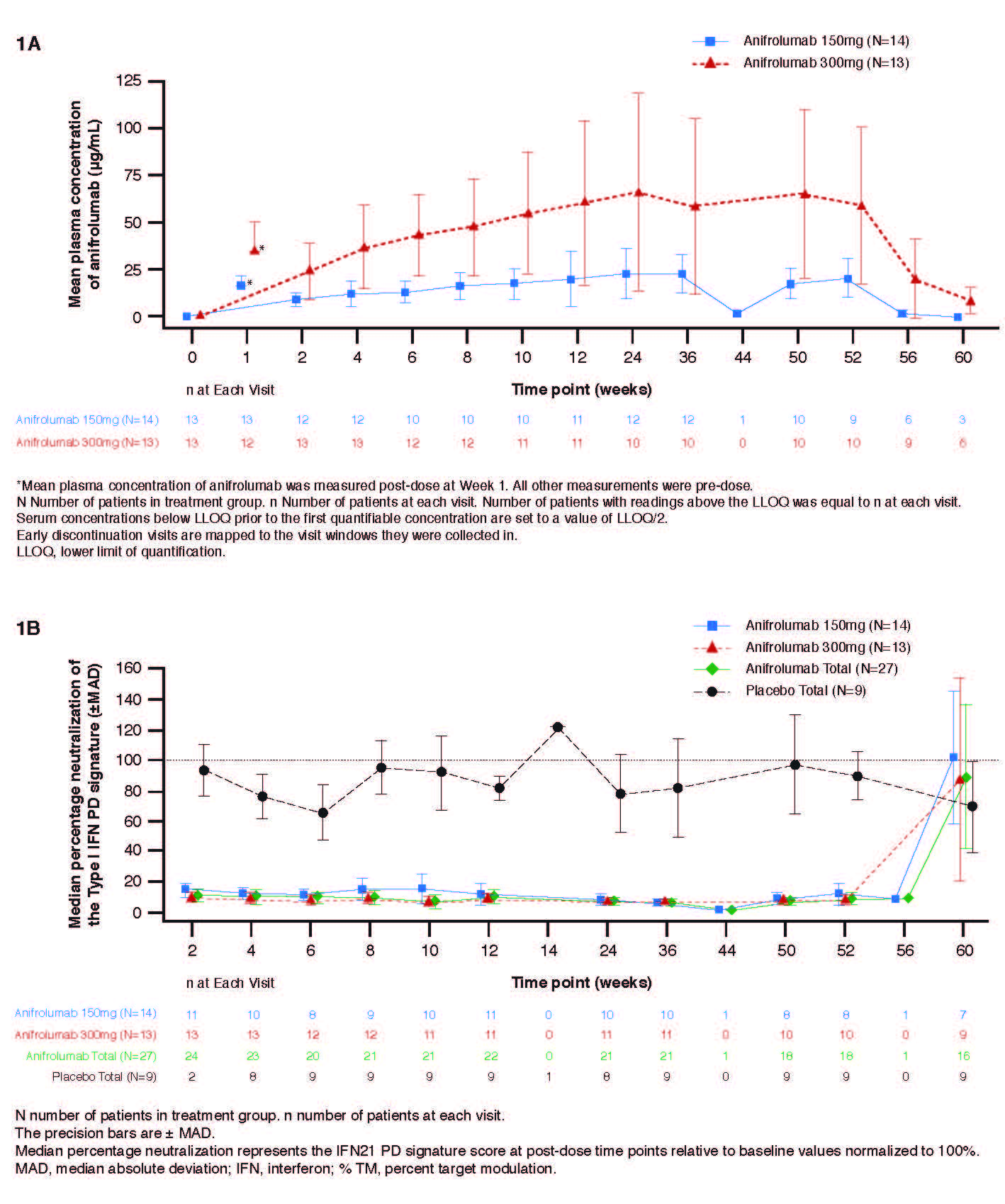
1120575 ACR abstract Figure 1A and 1B_Final
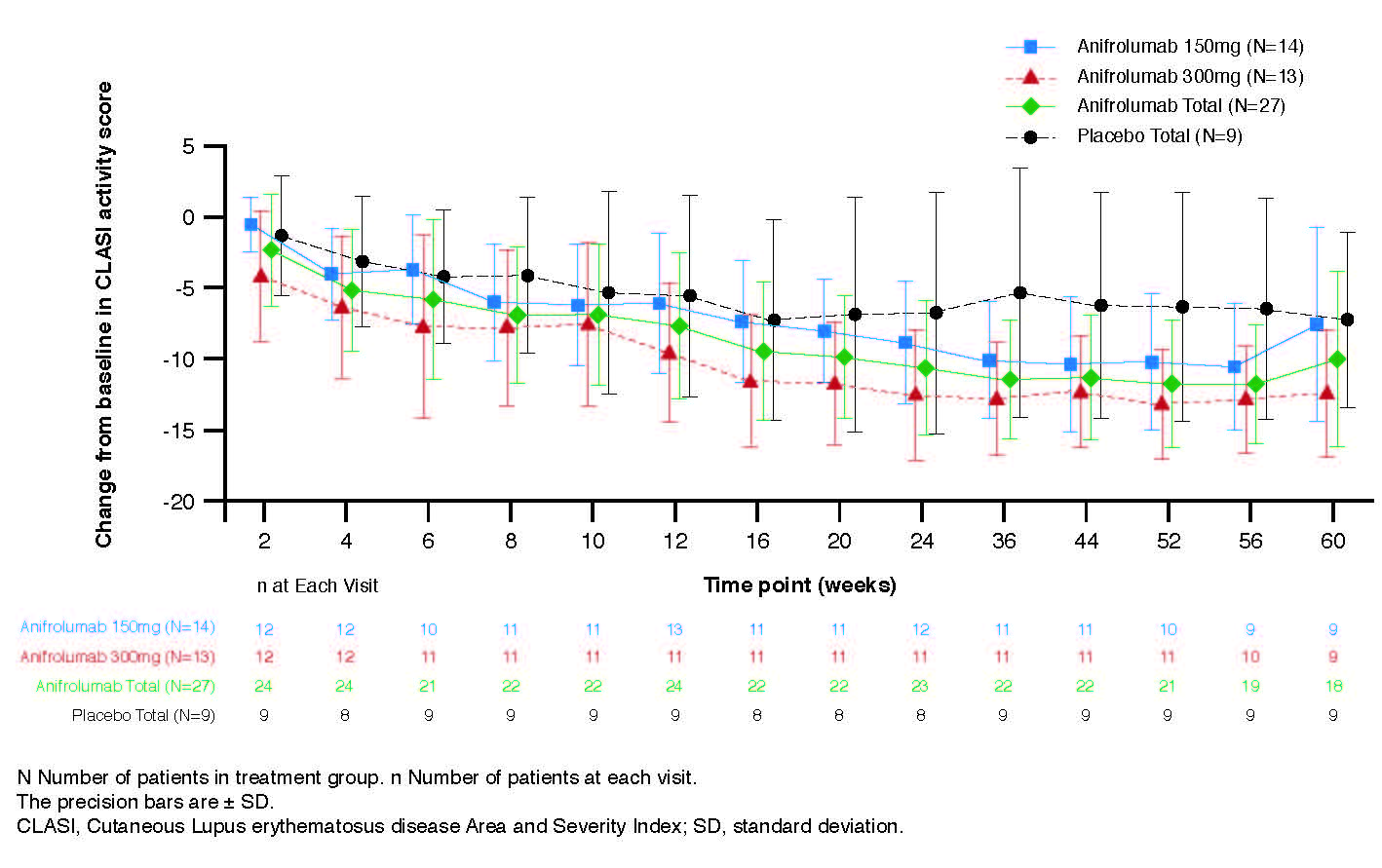
1120575 ACR abstract Figure 2_Final

1120575 ACR abstract Table 1 final
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bruce I, Nami A, Schwetje E, Pierson M, Chia Y, Kuruvilla D, Abreu G, Tummala R, Lindholm C. PK/PD, Safety and Exploratory Efficacy of Subcutaneous Anifrolumab in SLE: A Phase-II Study in Interferon Type I High Patients with Active Skin Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pk-pd-safety-and-exploratory-efficacy-of-subcutaneous-anifrolumab-in-sle-a-phase-ii-study-in-interferon-type-i-high-patients-with-active-skin-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pk-pd-safety-and-exploratory-efficacy-of-subcutaneous-anifrolumab-in-sle-a-phase-ii-study-in-interferon-type-i-high-patients-with-active-skin-disease/
