Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: SLE is a systemic inflammatory and autoimmune disease. IL-34 plays pivotal roles in the proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocyte cells, osteoclastogenesis and inflammation. IFN-α play an important role in SLE pathogenesis and proportion of patients displays increased serum IFN-α and IFN-λ1. Interestingly, the gene signatures of IFN-λ1 and IFN-α overlap. Our objective was to assess IL34, IFN-λ1 and IFN-α in SLE with relationship to clinical, laboratory parameters, treatment response and disease progression. We hypothesized a subgroup of patient with a concordance of high level of these cytokines that could have a different disease behavior.
Methods: 82 newly diagnosed SLE Egyptian patients. History, examination and laboratory investigation with assessment of disease activity. Pretreatment assessment of IL34, IFN-α and IFN-λ1 level by ILIZA. Patients started treatment (antimalarial ±Steroid ±immunosuppressive drugs) with response evaluation after six months.
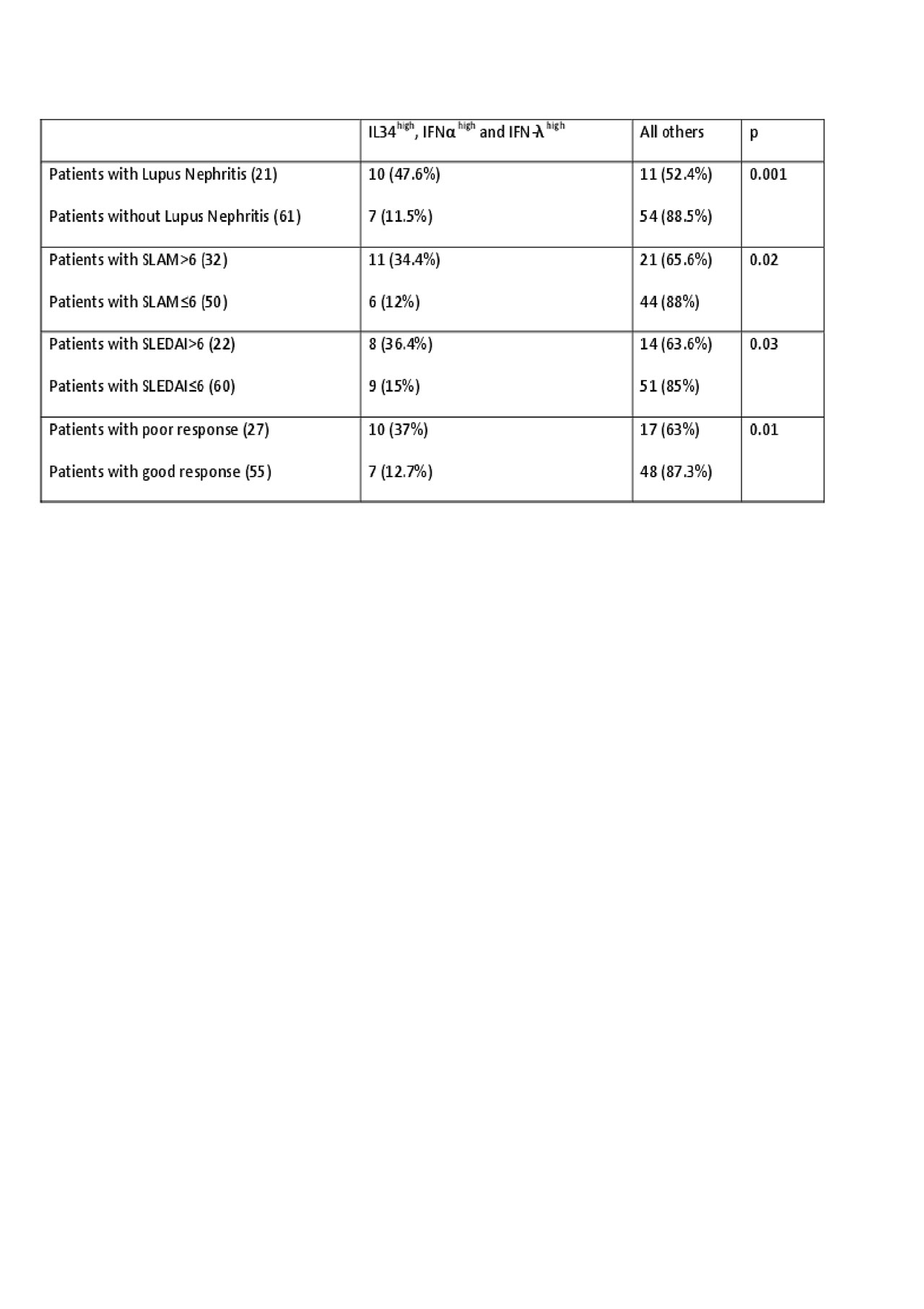
Results: 14 male (17.1%) and 68 female (82.9%), age mean±SD (48.6±8.2). Mean±SD of IL34, INFα and INF-λ1were 175.9±125.9 pg/mL, 109.3±32.5 pg/mL and 227.9±144.8 pg/mL respectively. 21 patients (25.6%) had lupus nephritis, 32 patients (39%) with SLAM >6 and 22 patients (26.8%) with SLEDAI >6. IL34 was positively correlated with anti-dsDNA (P= 0.002) but inversely correlated with C3 level (P = 0.009). IL34 was highly presented with lupus nephritis (P 0.005), SLAM >6 (P 0.03), SLEDAI >6 (P 0.007) and poor responder to treatment (P 0.02). IFNα was inversely correlated with C3 (P 0.001). IFNα was highly presented with lupus nephritis (P 0.02) and poor responders (P 0.01) however no relation with SLAM >6 nor SLEDAI >6. INF-λ1 was positively correlated with anti-dsDNA (P= 0.02) but inversely correlated with C3 (P = 0.01). INF-λ1 was highly presented with lupus nephritis (P 0.001), with SLAM >6 (P 0.04), with SLEDAI >6 (P 0.02). Accumulation of ≥3 clinical features during follow up was associated with high IL34 (P 0.001), high IFNα (P 0.001) and high INF-λ1 (P 0.001). We assigned high levels (i.e., ≥ 75% or third quartile) of each cytokine. Triple high (IL34high, IFNα high and IFN-λ1 high) found in 17 patients (20.7%) and were positively correlated with anti-dsDNA (P= 0.001) but inversely correlated with C3 (P = 0.001). Triple cytokines level was highly presented with lupus nephritis (P 0.001), SLAM >6 (P 0.02), SLEDAI >6 (P 0.03) and poor response to treatment (P 0.01) indicating these patients have aggressive disease. 28 patients developed (3 – 8) accumulated clinical features during the disease course, out of them 15 patients (53.5%) have high level of the triple cytokines indicating a poor prognosis of these subgroup.
Conclusion: High pretreatment serum IL-34 or IFN-λ1 has a prognostic significance in SLE patients. Patients with high IL-34 or IFNα or IFN-λ1 had more kidney affection and poor response to treatment. Triple cytokines elevation significantly associated with lupus disease activity, more kidney affection and poor response to treatment so, this aggressive phenotype of patients may be in need for combination of targets or a multicytokines targeted therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hussein Y, Sadeq Y. Impact of IL34, IFN-α and IFN-λ1 on Disease Activity of SLE Patients in Egypt [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-il34-ifn-%ce%b1-and-ifn-%ce%bb1-on-disease-activity-of-sle-patients-in-egypt/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-il34-ifn-%ce%b1-and-ifn-%ce%bb1-on-disease-activity-of-sle-patients-in-egypt/