Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: KZR-616, a first-in-class selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome, is being evaluated for the treatment of multiple autoimmune diseases, including LN and PM/DM. At 30 and 45 mg subcutaneously (SC) weekly (QW), KZR-616 is well tolerated and achieves target levels of immunoproteasome inhibition in healthy volunteers (HV) (Lickliter et al. ACR 2017). Initial doses of 60 mg or higher were associated with an adverse drug reaction including self-limited vomiting in both HV and SLE patients (pts) (Furie et al. EULAR 2019). Preliminary evidence from SLE pts suggests intrasubject dose escalation (‘step-up dosing’) may allow use of higher doses of KZR-616. Here we report the preliminary results of a single-center, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled study evaluating the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD) of a new lyophilized formulation of KZR-616 administered SC using step-up dosing (ACTRN12618002060224).
Methods: Female HV were enrolled because autoimmune diseases, eg, SLE, predominantly affect females who also have an apparent increased adverse drug reaction risk. There were 3 multiple ascending dose (MAD) SC cohorts (Table 1) and 3 single ascending dose intravenous (IV) cohorts at 15, 30, and 45 mg. Randomization of KZR-616:PBO was 6:2 per cohort; HV who discontinued early could be replaced. Safety was assessed via adverse event (AE) monitoring, physical examinations, vital signs, electrocardiograms, and laboratory tests, with analyses both by cohort and by dose. Placebo data were pooled. Pharmacokinetics were measured by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry, and PD (immunoproteasome inhibition) was measured using enzymatic activity and active site binding (ProCISE) assays in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Plasma cytokines/chemokines were measured by electrochemiluminescent detection (Meso Scale Diagnostics).
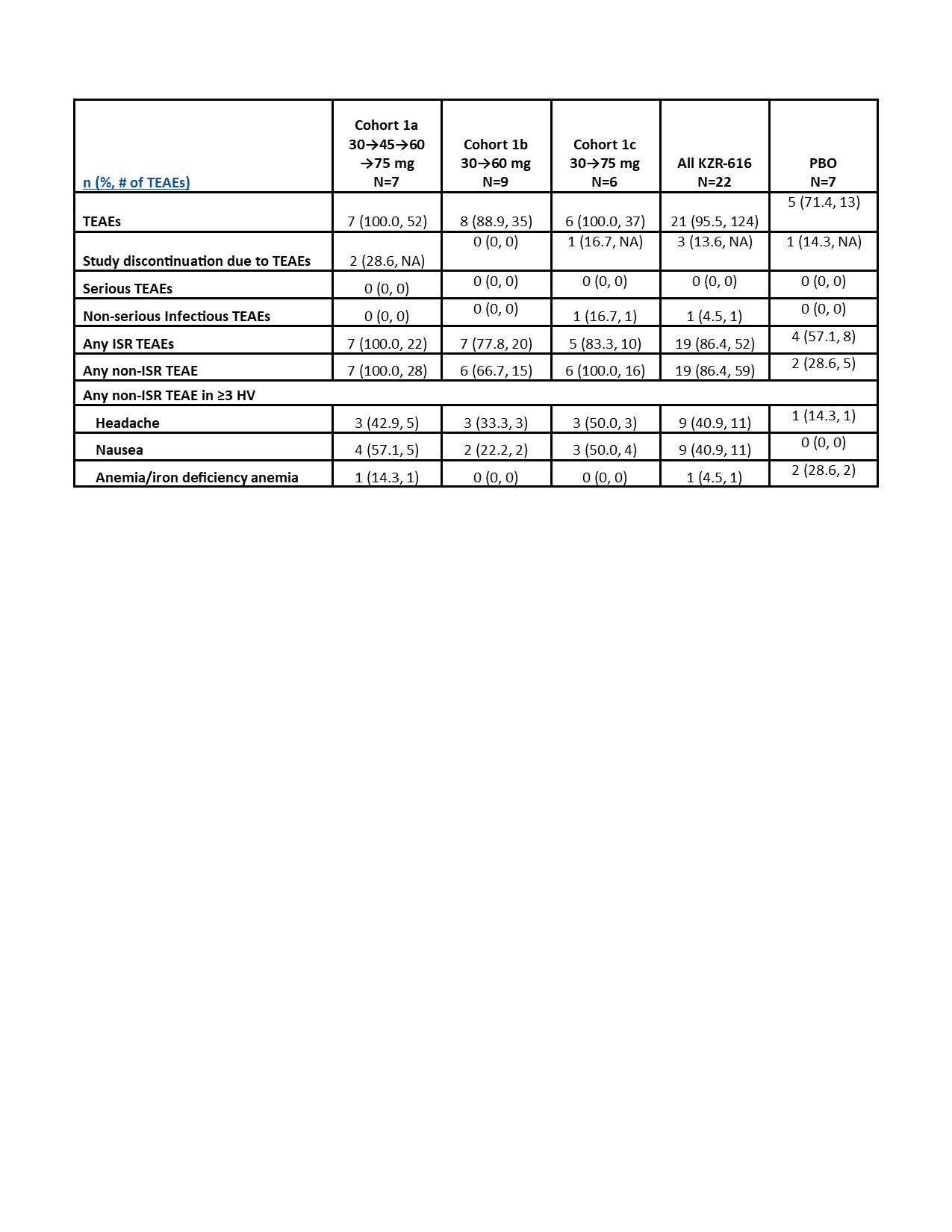
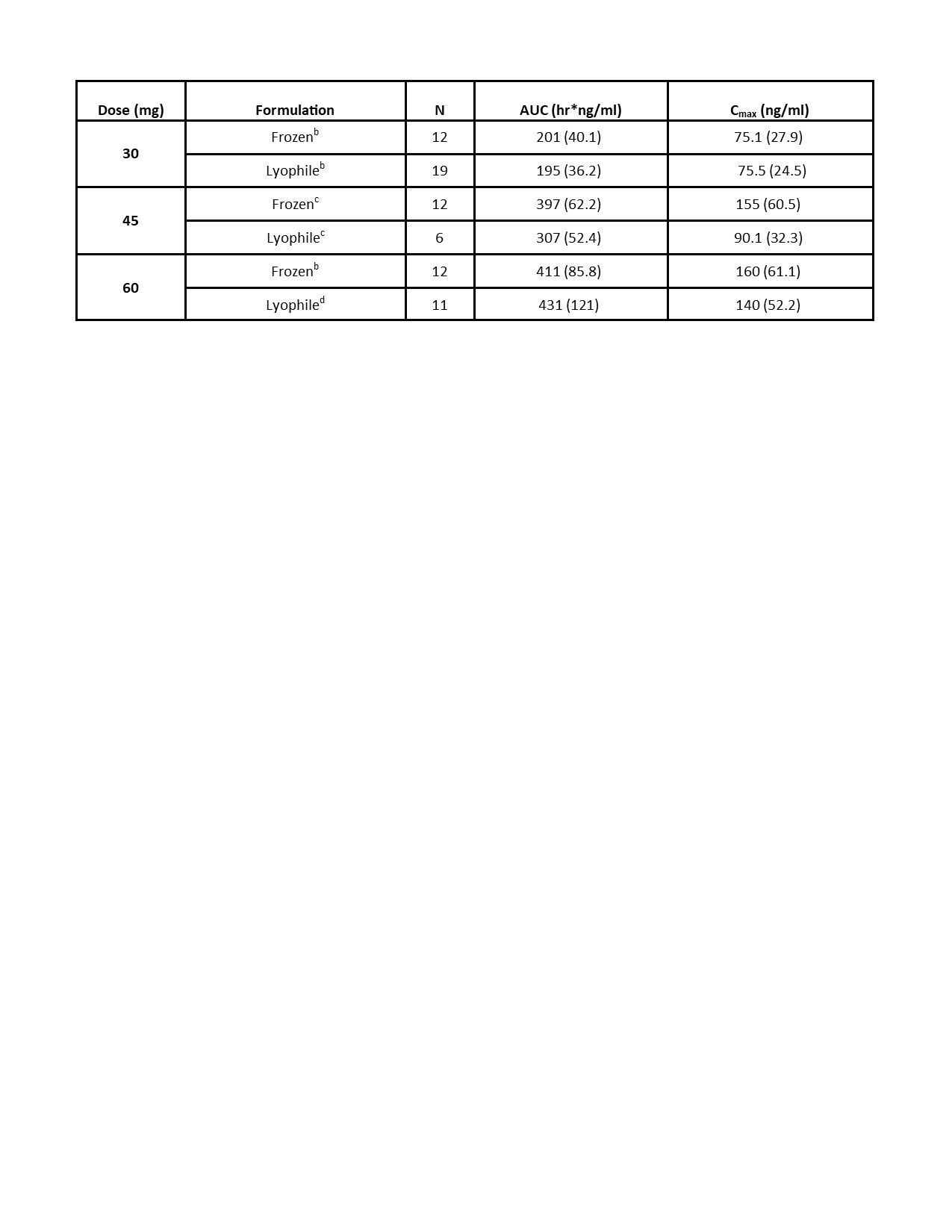
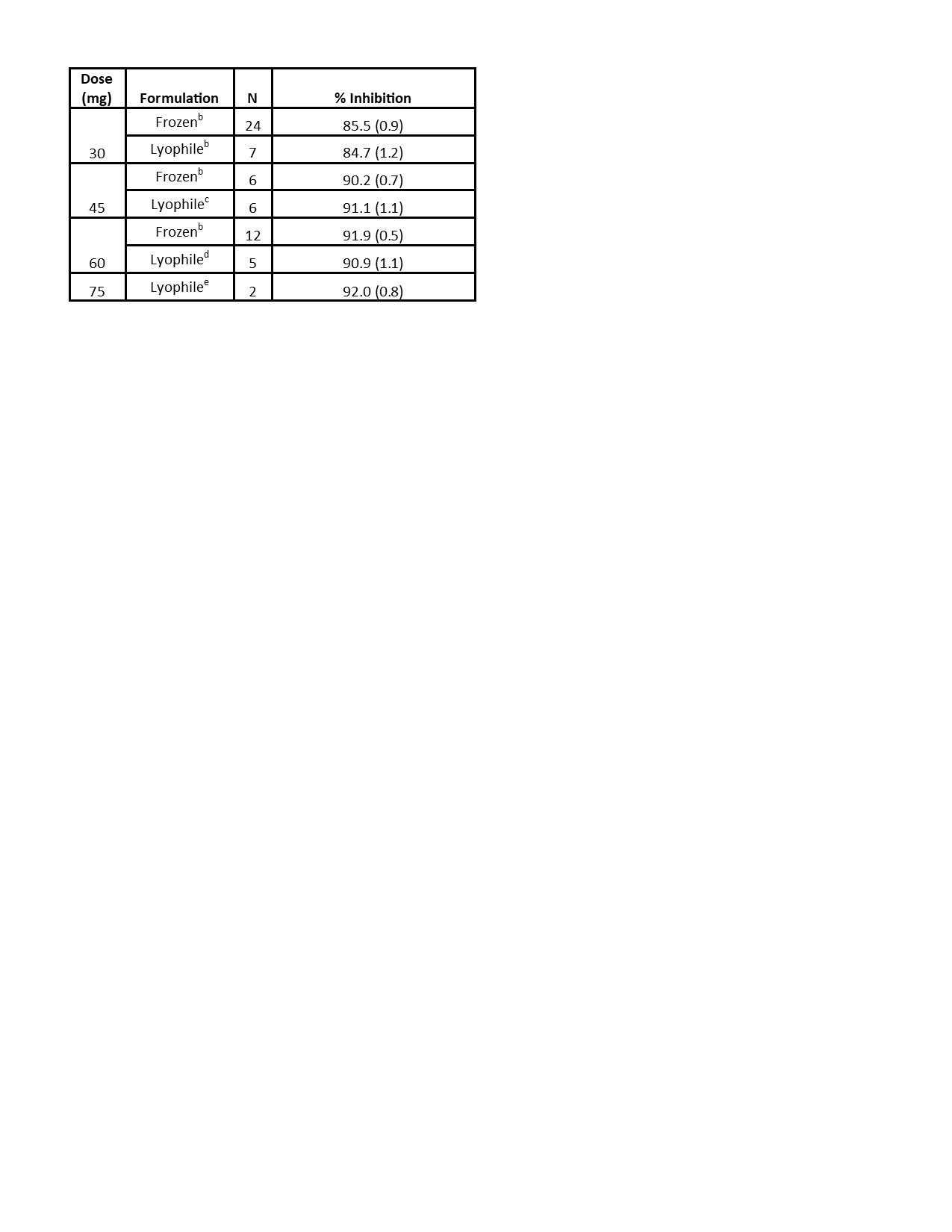
Results: Preliminary results from the SC cohorts are presented. There were 29 HV enrolled, 22 of whom received ≥1 dose of KZR‑616. Average age was 22.6 years (PBO) and 27.9 years (KZR-616). In the SC cohorts, 95.5% of KZR-616 treated and 57.7% of PBO-treated HV experienced AEs (Table 1). All AEs were mild to moderate. The most common AEs were injection site reactions (ISRs), headache, and nausea, which were generally transient. The AE frequency or severity did not seem to increase with dose increase. There was one isolated Grade 3 laboratory value on KZR-616-treated: neutropenia in Cohort 1b at Day 4. The PK at 30, 45, and 60 mg were similar to data reported in the previous HV study (Table 2). Based on comparisons to the IV cohorts’ PK, KZR-616 administered SC was 100% bioavailable. Inhibition of immunoproteasome enzymatic activity was also similar with SC administration of the new drug product as compared to previously reported data (Table 3).
Conclusion: No apparent dose limiting toxicities were observed in the MAD SC subjects at doses up to 75 mg when an initial dose of 30 mg was administered. The PK and PD in this study support the utilization of this lyophilized formulation of KZR-616 and administration of doses SC up to 75 mg in patients with rheumatic diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Snyder B, Bomba D, Harvey K, Anderl J, Kirk C, Wang J, Fan R, Goel N. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of a Lyophilized Drug Product of KZR-616, a Selective Inhibitor of the Immunoproteasome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-a-lyophilized-drug-product-of-kzr-616-a-selective-inhibitor-of-the-immunoproteasome/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-a-lyophilized-drug-product-of-kzr-616-a-selective-inhibitor-of-the-immunoproteasome/