Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients are at elevated risk for cardiovascular (CV) events, but efficient risk stratification based on CV prediction models is not part of routine clinical practice. We constructed and validated a biomarker-based CV risk prediction model and compared it to alternative risk prediction approaches.
Methods: Using Medicare administrative data 2006-2016, we constructed a cohort of RA patients age ≥40 with ≥1 RA diagnosis from a rheumatologist, excluding patients with malignancy, past myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke. Patients were linked to multi-biomarker disease activity (MBDA) test results obtained as part of routine care. The composite CV outcome consisted of MI, stroke, and CV death occurring within 3 years, using validated algorithms. The cohort was split 2:1 to create a training dataset and an internal validation dataset. Clinical predictors were examined based on subject matter expertise, informed by existing risk prediction scores: age, sex, race, traditional CV risk factors (e.g. diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, high-risk CV conditions [e.g. ischemic heart disease]), RA-related factors (e.g. glucocorticoid use, methotrexate, number of prior biologics), MBDA score, and its 12 biomarkers, log-transformed. Backward elimination was used to remove predictors with p ≥0.05. The resulting MBDA-based CV risk score was applied to the validation dataset to compare it to four different prediction models (age+sex; age+sex+CRP; age+sex+diabetes+hypertension+smoking+high risk CV [±CRP]). We evaluated: 1) the incremental improvement in the likelihood ratio (LR) statistic, 2) discrimination (AUROC), and 3) calibration (predicted vs. observed, based on Kaplan-Meier estimates with 95% CI) in CV event-based deciles. Validation followed a pre-specified analysis plan.
Results: 30,751 RA patients were linked to MBDA test results and eligible for analysis. Patient characteristics were mean (SD) age of 68.7 (9.5) years, 23.4% age < 65, 82% women. Comorbidities included diabetes (39%), hypertension (78%), smoking (24%), and history of high-risk CV condition (37%). RA-related features included use of glucocorticoids (58%), methotrexate (60%), TNFi (33%) and other biologics (16%). Mean (SD) MBDA score was 41 (14). The final features included in the MBDA-based CV risk score were age, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, history of high-risk CV conditions, the MBDA score, leptin, TNFRI and MMP-3. Median (IQR) of predicted 3-year CV risk was 3.4% (2.1%, 5.6%). Based on extrapolation to 10-year risk, 19.6% of patients would be considered low/borderline, 52.2% intermediate, and 28.2% high risk per ACC/AHA 2018 guidelines.
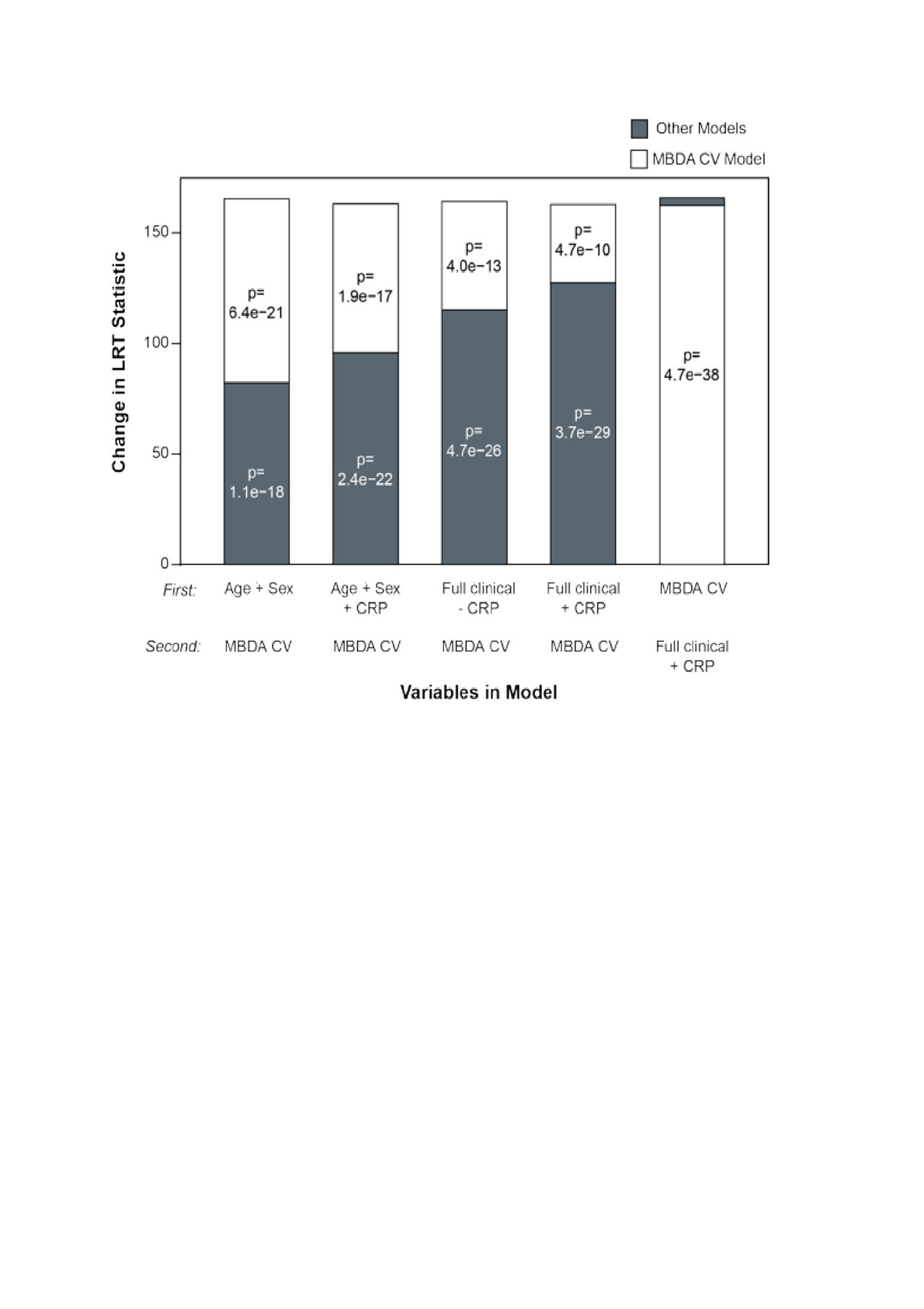
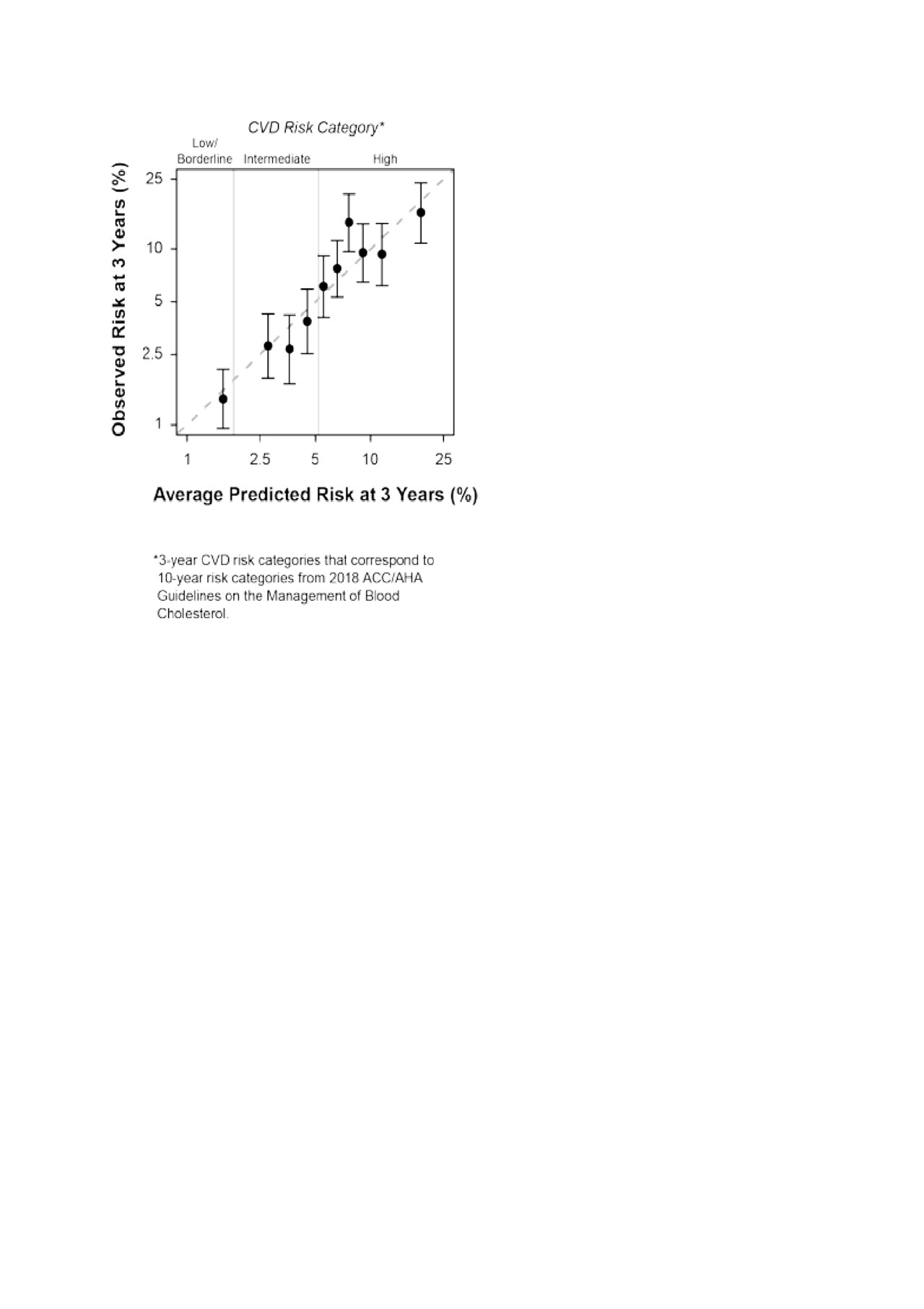
Compared to all four simpler CV prediction models, significant improvement in the LR statistic was observed with the addition of the MBDA-based CV risk score (Figure 1). Model accuracy (calibration) was good across deciles (Figure 2). The AUROC was 0.70.
Conclusion: A simple, biomarker-based prediction score incorporating a few clinical risk factors appears to have good accuracy to predict CV risk in RA. Additional validation in independent cohorts will be helpful to verify its performance characteristics.
MGI-FY19-119 ACR Curtis CVD_03 JUN2019 ES3 RB1 ES2 clean 3
MGI-FY19-119 ACR Curtis CVD_03 JUN2019 ES3 RB1 ES2 clean 4
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, Xie F, Crowson C, Mabey B, Flake D, Bamford R, Chin C, Sasso E, Hitraya E, Gutin A, Lanchbury J. Derivation and Validation of a Biomarker-Based Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/derivation-and-validation-of-a-biomarker-based-cardiovascular-risk-prediction-score-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/derivation-and-validation-of-a-biomarker-based-cardiovascular-risk-prediction-score-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
