Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) complicated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is detected in 27 to 67% of patients on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), and airway disease (AD) are detected in 39 to 60%. These contribute to an increase in the mortality rate in comparison with RA without respiratory complications. However, the most appropriate treatment for RA-ILD or AD has not been established. In this study, we examined the effectiveness of treatments for these disorders.
Methods: The subjects were consecutive RA patients with ILD and/or AD who were registered in the RA registry in our department between January 2015 and September 2017, and could be followed-up for ≥1 year after the start of intensified treatment. We investigated the clinical data, contents of treatment, imaging findings, and prognosis after 1 year. HRCT assessment was blindly performed by two pulmonologists specializing in interstitial pneumonia.
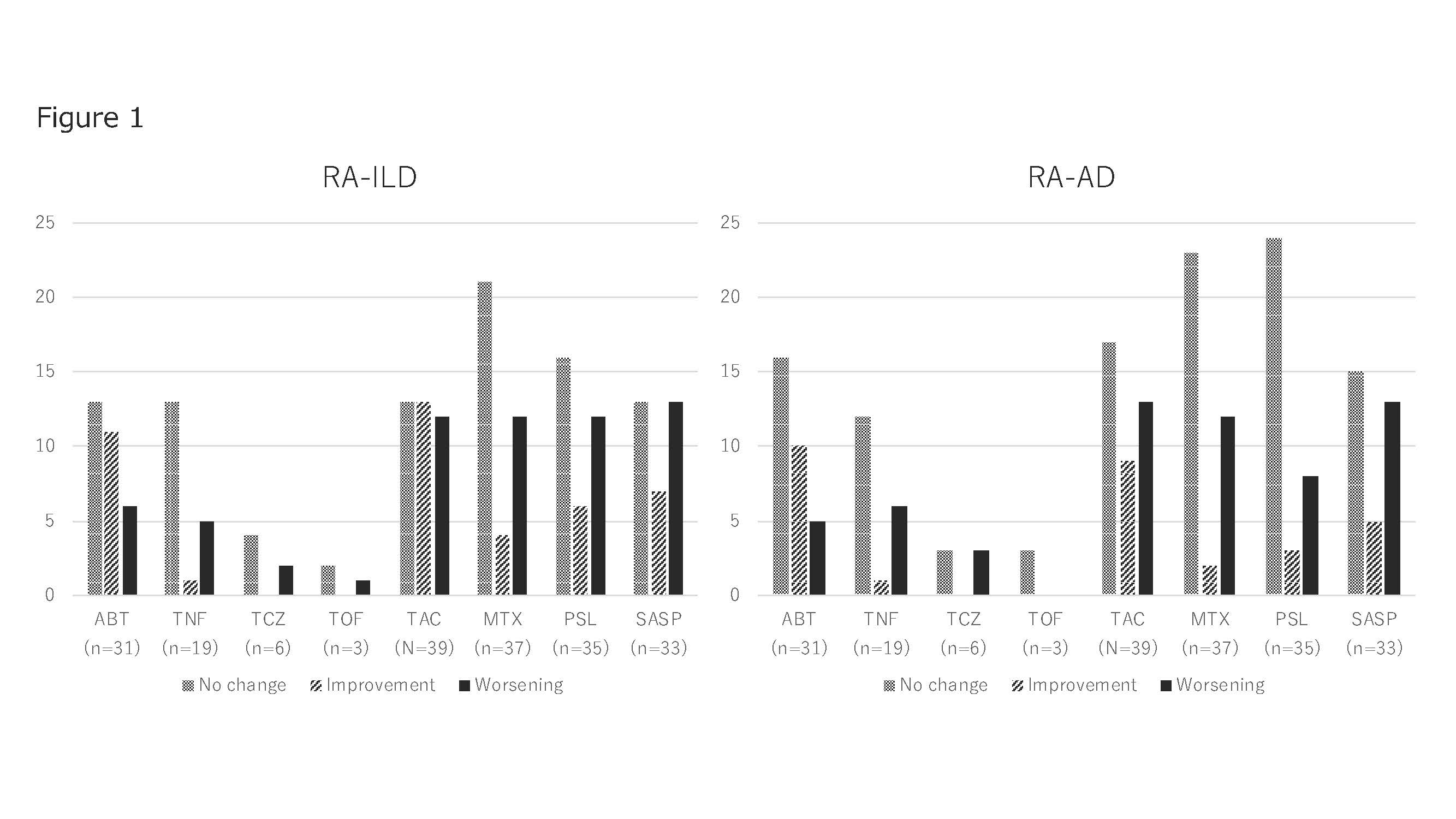
Results: The subjects were 95 patients with RA-ILD and/or AD complicated with RA (36 males, 59 females, mean age: 70.0 ± 9.9 years). 87 patients had RA-ILD, 65 had AD, and 57 (60%) had both. 80 patients (84.2%) were positive for RF, and 77 (81%) were positive for ACPA. The mean KL-6 level was 332 U/mL[223-602]. The HRCT pattern was evaluated as UIP in 49 patients (51.6%), NSIP in 27 (28.4%), and others in 11 (11.6%). Concerning treatment, MTX was selected in 37 patients (38%), with a mean dose of 6.9 ± 2.4 mg. PSL was selected in 35 (36%), with a mean dose of 5.6 ± 3.1 mg. TAC was selected in 36 (37%), with a mean dose of 2.1 ± 0.8 mg. IGU, SASP, and BUC were selected in 2 (0.02%), 33 (34%), and 6 (0.06%) patients, respectively. bDMARDs and TOF were used in 61 patients (64%): INF, 3 patients (3%); ETN, 6 (6%); ADA, 5 (5%); GLM, 5 (5%); CTZ, 0 (0%); ABT, 29 (30%); TCZ, 5 (5%); and TOF, 3 (3%). Many patients received ABT. With respect to the prognosis after 1 year, ILD exacerbation on HRCT was correlated with the KL-6 level (p=0.054), but there was no correlation between the exacerbation of AD and KL-6 level (p=0.408). As shown in Figure 1, the improvement ratings of ABT and TAC were higher than that of PSL when investigating the treatment response on HRCT. However, those of TNF and MTX were extremely low.
Conclusion: To treat RA-ILD, biologics were used in 64% of the subjects, suggesting their safety. ABT and TAC may be useful for the treatment of RA-ILD or AD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shoda T, Takeuchi T, Kotani T, Nagai K, Hata K, Makino S, Arawaka S. Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease and Airway Disease Complicated with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-interstitial-lung-disease-and-airway-disease-complicated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-interstitial-lung-disease-and-airway-disease-complicated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/