Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Both traditional cardiovascular (CV) risk factors and disease-related factors contribute to the increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Mechanisms of atherosclerosis include (1) Endothelial dysfunction/activation mediated by intercellular adhesion molecules (e.g., ICAM-1, VCAM-1, E-selectin), nitrite (NO), and oxidative stress (e.g., via MPO activity); (2) Inflammation mediated by cytokines (e.g., IL-6); (3) Plaque stability mediated by CD40-CD40L interactions; and (4) Proteolysis/Plaque rupture mediated by proteolytic enzymes (e.g. MMP-9). Inflammatory and immune biomarkers important in RA pathogenesis include erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and IL-17. This study seeks to develop easy to visualize decision rules for the differential effects of these serum biomarkers and CV risk factors on carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) in RA vs. control subjects.
Methods: Carotid ultrasounds measured maximum cIMT and plaque presence, and serum biomarkers (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, E-selectin, NO, MPO, IL-6, CD40L, MMP-9, ESR, hsCRP, IL-17) were measured on 87 RA cases and 101 controls. All RA subjects met 2010 ACR classification criteria. CV risk factors (age, gender, race, obesity, hypertension (HTN), diabetes (DM), hyperlipidemia (HL), smoking (ever), personal and family history of CVD) were collected on all subjects. Regression tree models were applied with cIMT as the outcome measure, and all the serum biomarkers and significant (based on an unadjusted linear model) CV risk factors (age, gender, DM, smoking, personal history of CVD) as potential splits in the tree model. Tree models are built by identifying the best split across all values of all variables and partitioning the data into the two resulting subgroups (or nodes); within each subgroup the process is repeated until the nodes are too small (n< 10) to split further. The trees were also pruned by eliminating nodes (beginning with the lowest branches of the tree) that did not contribute significantly to model fit.
Results: Demographics were similar between RA and controls except for age (mean 59.6+/-12.0 in RA vs. 54.0+/-14.7 years in controls; p=0.005), as were CVD risk factors except for hypertension (46.4% in RA vs. 23.3% in controls). The tree models (Figures 1-2) display the mean cIMT (with the percent in that group) for each terminal node (e.g. final subgroups). For RA cases, Figure 1 shows that RA patients age 51 or older with CD40 < 8235 had the highest mean cIMT, especially for MPO ≥ 343 or for age 67 or older with MPO < 343 (0.98-1.19). In controls, males with ESR ≥ 11 and female smokers age 34 or older with eSelectin ≥ 38.1 had the highest mean cIMT (0.86-1.09).
Conclusion: This study reveals that RA and control subjects have differential contributing effects of various serum inflammatory and vascular biomarkers and traditional CV risk factors on subclinical atherosclerosis risk, as measured by cIMT. Results may inform future studies to develop additional CVD risk stratification algorithms in RA patients.
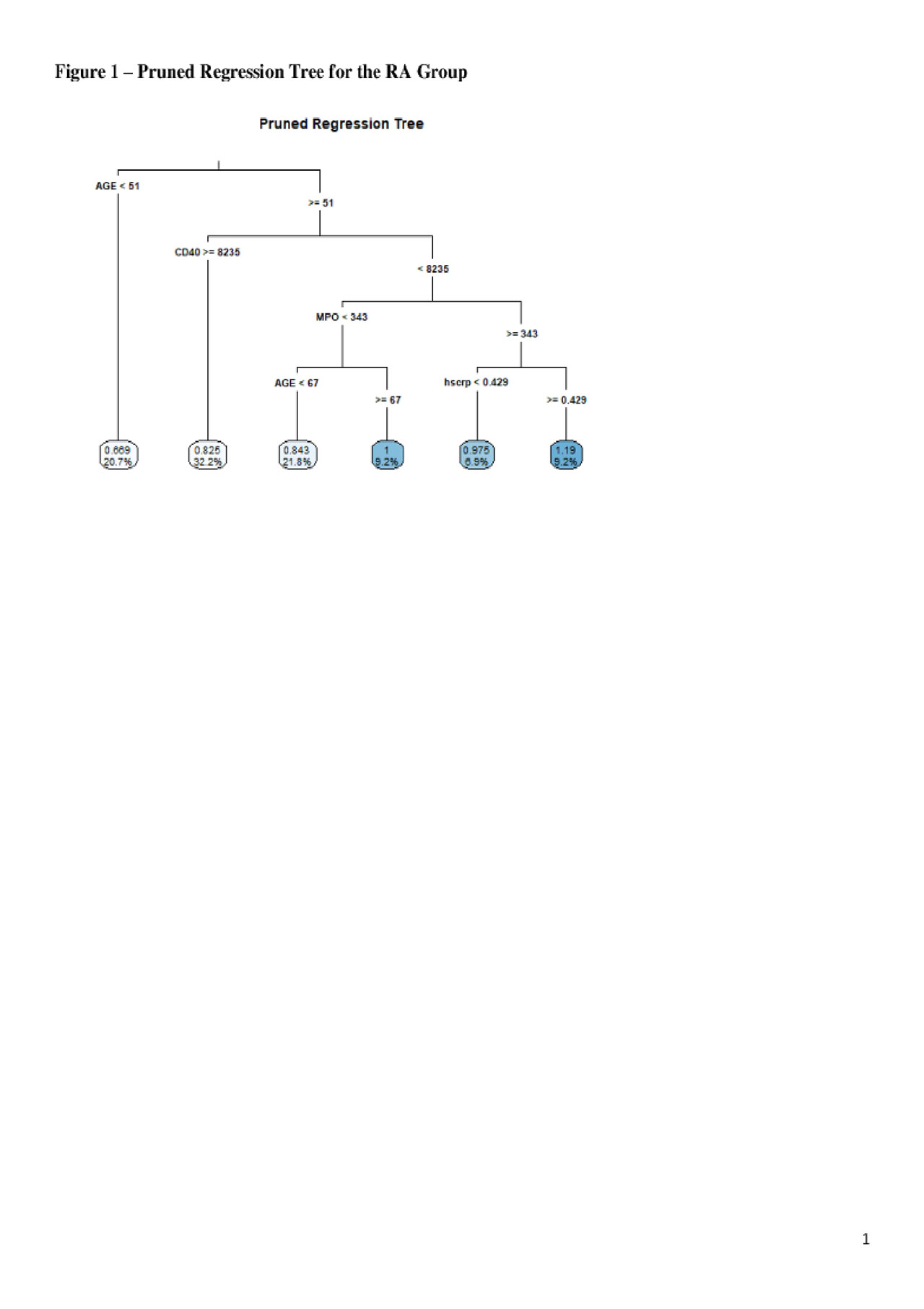
ACR 2019 abstract_tree models Figure 1
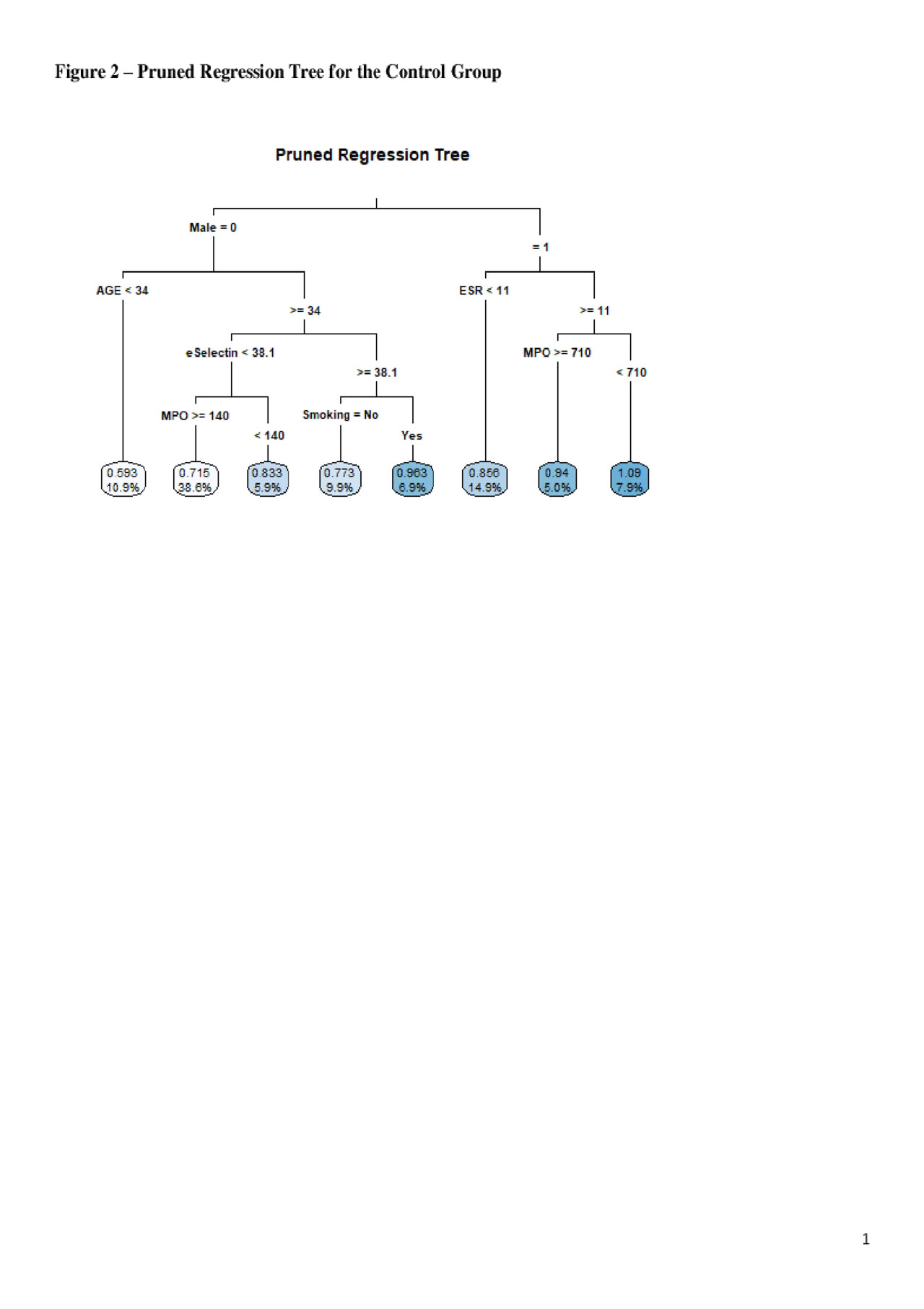
ACR 2019 abstract_tree models Figure 2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liang K, Li Y, Mulukutla S, Reis S, Levesque M, Jones D, Gartland R, Avolio J, Hakim Shoushtari A, Villanueva F, Moreland L, Landsittel D. Toward Cardiovascular Risk Stratification in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Use of Regression Tree Analyses to Evaluate Impact of Serum Biomarkers and Cardiovascular Risk Factors on Carotid Intima Media Thickness [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/toward-cardiovascular-risk-stratification-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-use-of-regression-tree-analyses-to-evaluate-impact-of-serum-biomarkers-and-cardiovascular-risk-factors-on-carotid-intima-media-thickn/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/toward-cardiovascular-risk-stratification-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-use-of-regression-tree-analyses-to-evaluate-impact-of-serum-biomarkers-and-cardiovascular-risk-factors-on-carotid-intima-media-thickn/
