Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Miscellanous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Disease Poster III: Autoimmune Conditions and Therapies
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) occurs in approximately 15% of patients with autoimmune diseases (AD) [1]. Its presence is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality [2]. In the present study, we aimed to determine the frequency of ILD associated with AD (AD-ILD) among patients sent for assessment to a clinic of lung transplantation from a referral center. The different types of AD-ILD were described.
Methods: Clinical records of patients seen at the ILD clinic of Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain between May 2016 and May 2019 were reviewed. A diagnosis of ILD was made by the pneumologists based on clinical and radiological findings and pulmonary function test abnormalities. A definitive histological confirmation by transbronchial biopsy, surgical lung biopsy or cryobiopsy was performed according to the pneumologist consideration. All patients with ILD seen at the clinic were also assessed by an experienced rheumatologist to exclude the presence of an underlying AD.
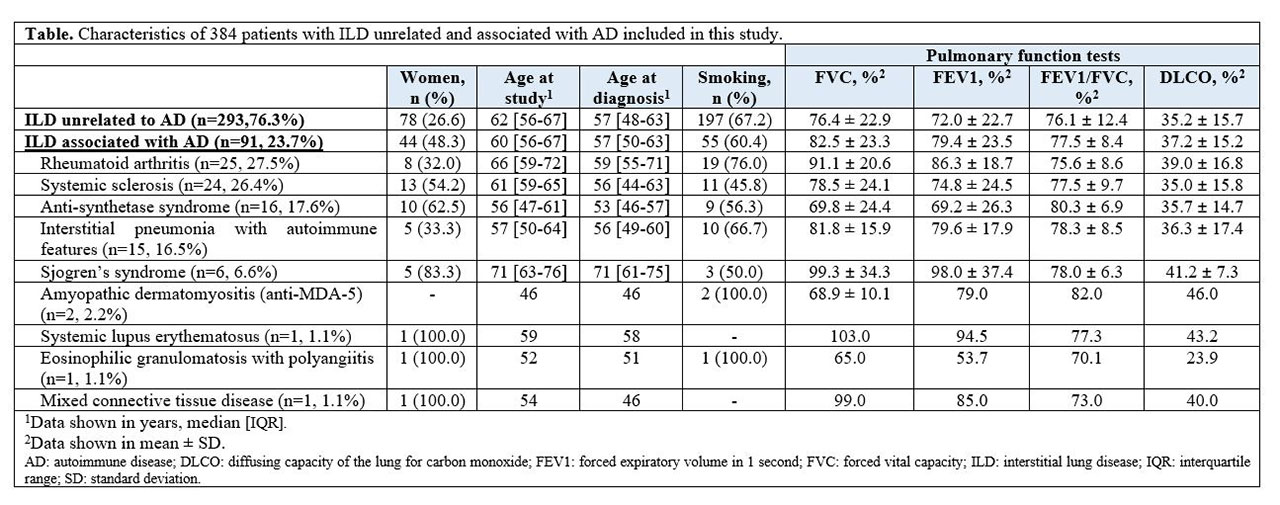
Results: During the period of assessment, 384 patients were diagnosed with ILD in this referral clinic (Table). The diagnosis of ILD was histologically confirmed in 208 (54.2%) patients. Among the 384 ILD patients, 129 were diagnosed as having idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (33.6%). Other frequent conditions unrelated to AD were chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (n= 40; 10.4%), non-classifiable interstitial pneumonia (n= 44; 11.5%) and non-specific interstitial pneumonia (n=20; 5.2%). Ninety-one (23.7%) of the ILD patients fulfilled definitions for AD. Most cases with AD-ILD were due to rheumatoid arthritis (n= 25/91; 27.5%); systemic sclerosis (n=24/91; 26.4%), anti-synthetase syndrome (n= 16/91; 17.6%) and Sjogren’s syndrome (n= 6/91; 6.6%). Interestingly, 15 of 91 patients with AD-ILD (16.5%) were diagnosed as having an interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Other AD associated with ILD are shown in Table. The predominant radiological pattern in patients with rheumatoid arthritis was usual interstitial pneumonia. In contrast, a predominant non-specific interstitial pneumonia pattern was found in the remaining patients with AD.
Conclusion: Almost a quarter of patients with ILD seen at a referral clinic center have an underlying AD. Close assessment of patients with ILD by rheumatologists is of main importance to identify AD in patients with ILD.
References:
[1] Cottin et al. Eur Respir Rev 2018;27:180076; [2] Antoniou et al. Eur Respir J 2009;33:882-896.
Acknowledgments:
SR-M is supported by funds of the RETICS Program RD16/0012/0009 (Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII), co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Remuzgo-Martínez S, Prieto-Peña D, Calderón-Goercke M, Mora Cuesta V, Iturbe Fernández D, Fernández Rozas S, Cifrian Martínez J, González-Gay M. The Spectrum of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Autoimmune Diseases: Data of a 3-Year-Prospective Study from a Referral Center of Lung Transplantation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-spectrum-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-autoimmune-diseases-data-of-a-3-year-prospective-study-from-a-referral-center-of-lung-transplantation/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-spectrum-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-autoimmune-diseases-data-of-a-3-year-prospective-study-from-a-referral-center-of-lung-transplantation/