Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis (LN) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at risk of serious infections (SIs) due to the impact of the disease itself and treatments that modulate immune function. Rates of SIs resulting in hospitalization among these patients have not been compared to the general population. The objective of this study was to compare the rates of SIs resulting in an inpatient claim in adult patients with SLE/LN, RA and the general population using population-based claims data.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the US-based Truven Healthcare MarketScan® Claims database for individuals aged 18-64 years enrolled between January 2007 and September 2015. Patients were required to have continuous enrollment for ≥ 90 days pre- and ≥ 365 days post-index date. Patients with SLE/LN (including non-renal SLE and LN) and RA were identified using modifications to algorithms developed for use in registry and/or claims data. The general population included individuals without SLE/LN or RA. Index date for the SLE/LN and RA cohorts was the date when patients fulfilled the diagnostic algorithms for SLE/LN, or RA. Index date for the general population occurred after 90 days of continuous enrollment. Patients were excluded from all cohorts if they had: an auto-immune (AI) condition other than SLE/LN or RA; cancer; received a solid-organ transplant; or HIV/AIDs. First incident SIs were identified as those that resulted in an inpatient claim for a pre-specified set of ICD-9 codes within 365 days of index date. Incidence rates (IRs) and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs) were calculated along with 95% confidence intervals (CI) adjusted for age, gender, index year, prevalent SI and glucocorticoid use.
Results: The SLE/LN, RA, and general population cohorts included 58,105, 183,229, and 50,530,269 patients, respectively. Table 1 provides a summary of cohort-specific patient characteristics. As anticipated, the SLE/LN and RA cohorts were predominantly female. The RA cohort was generally older than the other cohorts. Index date was fairly consistent across study year and cohort. In all cohorts, the unadjusted SI IRs increased with age, were higher among patients who had a prior SI (claim ≤ 90 days prior to the index date), and were slightly increased in patients who received systemic glucocorticoids ≤ 365 days after their index date. Adjusted SI IRs (95% CIs) were 21.2 (21.1, 21.2) in SLE/LN patients, followed by 15.8 (15.8, 15.8) in RA patients, and 3.8 (3.7, 3.8) in the general population (Table 2). Adjusted SIRs were 4.4 and 2.8 times higher among patients with SLE/LN and RA compared to the general population, respectively.
Conclusion: In this population-based analysis of claims data, adjusted SI IRs were highest in SLE/LN patients. Both AI cohorts experienced excess SI rates compared to the general population. These rates were based on inpatient claims from patients with varying disease severity and treatment patterns. Further characterization of the role of treatment and type of infection is warranted. Findings demonstrate the important contribution of SIs on the burden of disease among SLE/LN and RA patients.
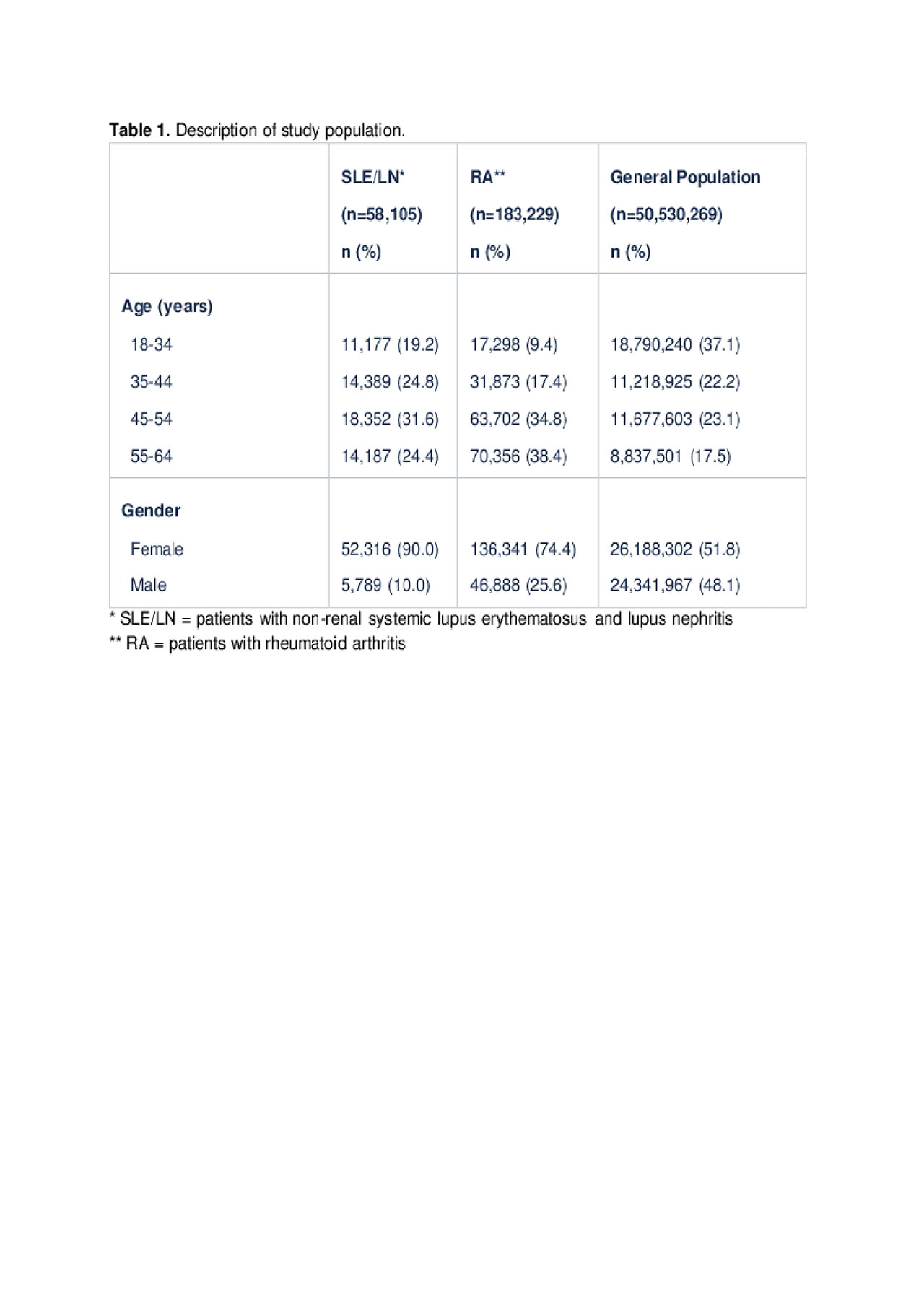
Serious Infection in Patients with SLE, LN, RA and Gen Pop Table 1
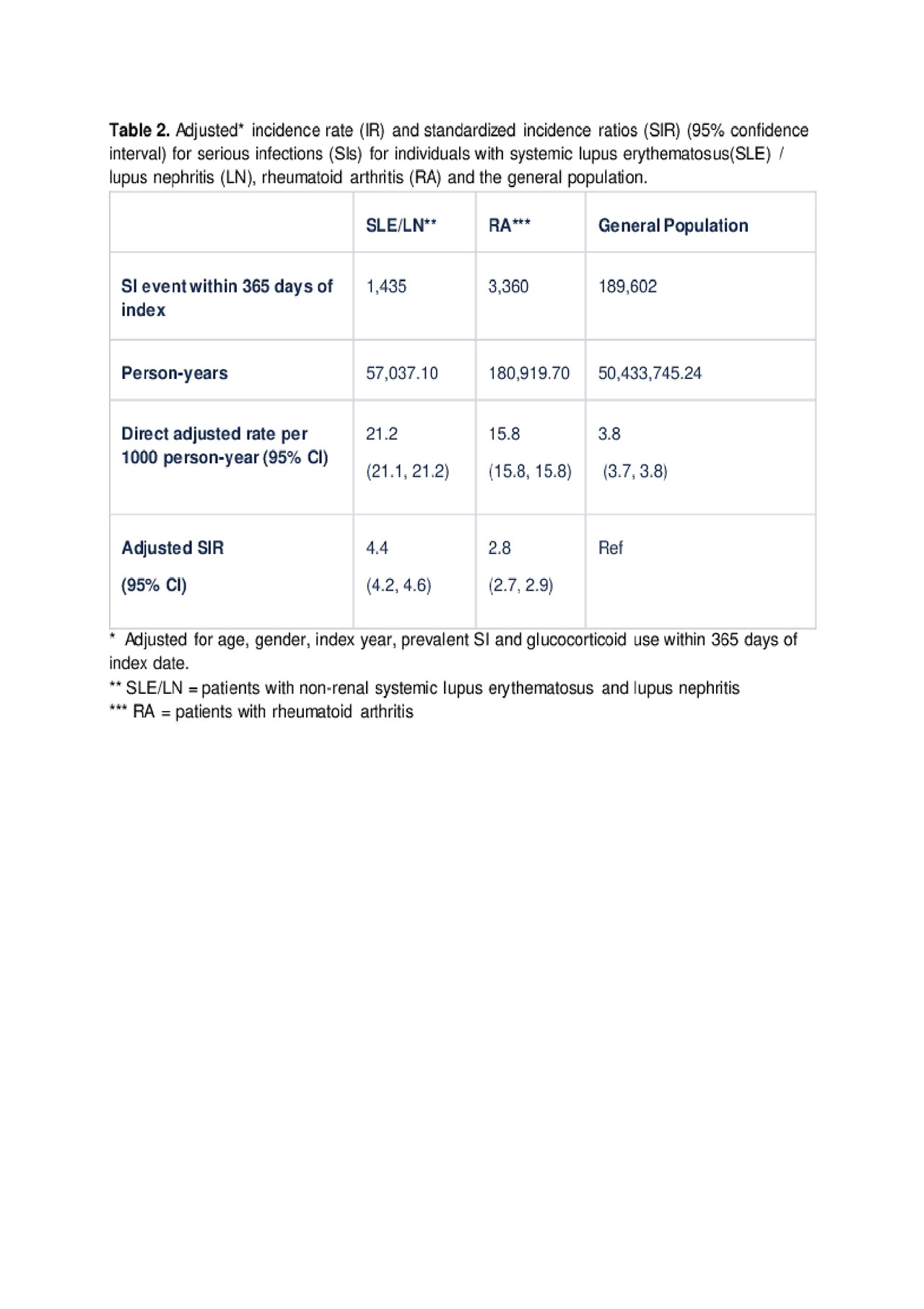
Serious Infection in Patients with SLE, LN, RA and Gen Pop Table 2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lindsay L, Chuo C, Jones N, Galanter J, McGregor A, Tuckwell K. Serious Infection in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Lupus Nephritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared to the General Population: Incidence Rates Using Real-World Claims Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serious-infection-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-lupus-nephritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-compared-to-the-general-population-incidence-rates-using-real-world-claims-data/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serious-infection-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-lupus-nephritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-compared-to-the-general-population-incidence-rates-using-real-world-claims-data/
