Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatic diseases, also known as musculoskeletal pathologies, are steadily rising their prevalence. This worldwide phenomenon is depriving our society of their life quality and has become a grave economic burden. Among musculoskeletal pathologies, osteoarthritis (OA) stands as the major rheumatic disease, in fact, the World Health Organization (WHO) included OA within the TOP10 most disabling diseases.
The activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) by damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPS) promotes critical innate immune responses (IIR). Although TLR4 and OA IIR are linked, no drugs are available to block TLR4 in rheumatology. Interestingly, TLR4 share downstream signaling with interleukin 1 receptor (IL1R). The development of new drugs is necessary but requires decades of work and billions in investment. An alternative exists, the search for anti-TLR4 properties in currently available drugs.
Amitriptyline (AT) is a tricyclic antidepressant currently in-use for neuropathies. Naloxone (NLX) swiftly reverse opioid overdose thanks to its antagonist design. Thalidomide (TALI) initially used as a sedative was found to be teratogenic. In the present, it is used as an anti-neoplastic and to combat leprosy.
Recent studies indicate that AT, NLX and TALI might have anti-TLR4 activity, and could be repurposed to the rheumatology field.
Methods: AT [1µM], NLX [100µM] and TALI [500µM] effect on IIR was initially studied in mouse chondrocytes (ATDC5) and human synoviocytes (SW982) to evaluate the drug effects in the whole joint. Next, it was validated in human OA chondrocytes (hOAC) isolated from knee-joint replacements. Gene expression was evaluated by RT-PCR. Protein levels were determined by ELISA and MALDI/TOFF. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay.
Results: At the studied concentrations, AT reduced cell culture nitrite accumulation (Griess assay) and did not affect cell viability (MTT assay). NLX and TALI also reduced cell culture nitrite accumulation (Griess assay).
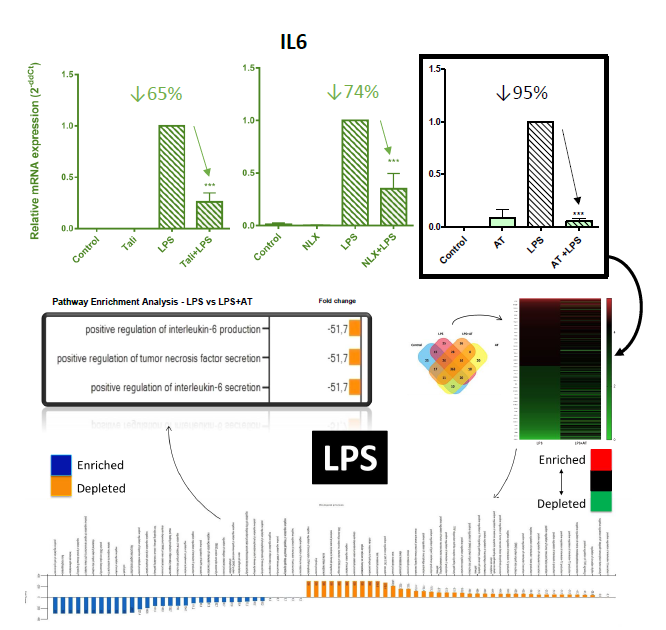
Stimulation with TLR4 agonist LPS [100ng/ml] or IL1R agonist IL1B [0,5ng/ml] increased IIR gene expression (LCN2, IL6, MCP1, COX2, NOS2, MMP9, MMP13, and ADAMTS4) in chondrocytes (hOAC & ATDC5) and synoviocytes (SW982). Inhibition of TLR4 by CLI95 [3µM] reduced IIR gene expression in LPS and IL1B-treated chondrocytes.
Upon treatment with AT, NLX or TALI, the observed IIR processes (mRNA) were significantly inhibited in synoviocytes and chondrocytes (Figure 1). AT showed the highest anti-TLR4 effect (↓95%) and was selected to perform a proteomic profile (MALDI-TOF) in hOAC. AT treatment depleted IIR-related pathways, including IL6 (Figure 1). To further validate the proteomic results, IL6 protein secretion was evaluated (ELISA) and showed reduced levels after AT treatment.
Conclusion: We show in chondrocytes and synoviocytes:
- TLR4 receptor is involved in IL1β-mediated innate immune responses (IIR).
- Amitriptyline, thalidomide, and naloxone blocked TLR4 and IL1R –mediated IIR gene expression.
- Amitriptyline inhibited the expression of multiple TLR4 and IL1R –mediated IIR proteins.
The rheumatologists have a new therapeutic tool to manage innate immune responses in osteoarthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Franco-Trepat E, Alonso-Pérez A, Guillán-Fresco M, Jorge-Mora A, Lois Iglesias A, Gualillo O, Gómez R. A Drug Repurposing Story: New Therapeutic Tools Ready to Block Innate Immune Responses in Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-drug-repurposing-story-new-therapeutic-tools-ready-to-block-innate-immune-responses-in-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-drug-repurposing-story-new-therapeutic-tools-ready-to-block-innate-immune-responses-in-osteoarthritis/