Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) is a progressive, systemic autoimmune disease causing inflammatory changes to the skin and skeletal muscles. TRIM family proteins are composed of approximately 80 E3 ubiquitin ligase proteins and some have a role in membrane resealing.
Methods: We employed the STARGEO platform to search the Gene Expression Omnibus and conduct meta-analysis on human skin (60 DM vs 34 healthy) and muscle biopsy (71 DM vs 22 healthy) samples. We analyzed the signature using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis, restricting genes with significance (p< 0.05) and an absolute experimental log ratio greater than 0.1, focusing on TRIM family genes. We conducted similar analysis on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) blood (114 RA vs 90 healthy) and synovial samples (130 RA vs 68 healthy), sarcoidosis (SD) bronchoalveolar lavage (21 SD vs 20 healthy) and blood (216 SD vs 271 healthy) samples, systemic scleroderma (SSc) skin (63 SSc vs 31 healthy) biopsies, and Kawasaki (KA) blood (121 KA vs 40 healthy) for comparative TRIM activity analysis. Lastly, we conducted immunoblotting analysis on muscle biopsy specimens from 4 DM, statin-induced necrotizing myopathy, and healthy subjects. Bands of interest were visualized by chemiluminescence and fold change in TRIM72 protein levels evaluated by densitometry using ImageJ and Dunett’s Test analysis.
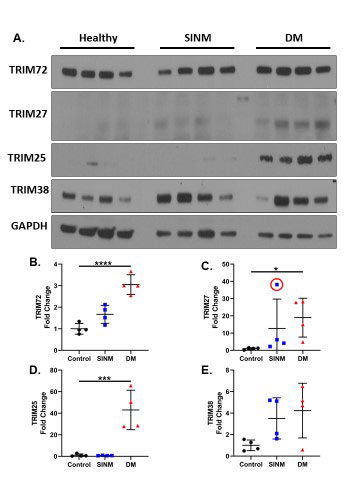
Results: From our skin biopsy analysis in DM we found upregulation of TRIM genes TRIM5 (p-value 5.72e-12, log ratio 0.225), TRIM14 (p-value 3.36e-8, log ratio 0.132), TRIM34 (p-value 1.48e-6, log ratio 0.105), TRIM6 (2.97e-4, log ratio 0.212), TRIM21 (p-value 0.0111, log ratio 0.193), and TRIM38 (p-value 0.0189, log ratio 0.106). TRIM73 was downregulated (p-value 6.58e-13, log ratio -0.102). From our muscle biopsy analysis, we found upregulation of TRIM genes TRIM14 (p-value 0.0405, log ratio 1.02), TRIM22 (p-value 0.0361), TRIM25 (p-value 0.0287, log ratio 0.421), TRIM27 (p-value 0.00276, log ratio 0.298), and TRIM38 (p-value 0.0409, log ratio 0.949). Protein expression of TRIM 72, 25 and 27 protein expression were significantly upregulated and TRIM 38 trending although did not reach statistical significance in our DM cohort compared to healthy controls. Additional comparisons were made between DM and necrotizing myopathy and was significant for TRIM 25 only. Immunoblotting of human muscle proteins shown in Figure A and densitometry analysis shown in B-E. B.) TRIM72: Healthy vs. DM p< 0.0001. C) TRIM27: Healthy vs. DM p=0.012. D.) TRIM25: Healthy vs. DM p=0.0006. E.) TRIM38: Healthy vs. DM p=0.064. From our comparative analysis, there was no overlap in TRIM gene expression patterns in rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis, systemic scleroderma, and Kawasaki with our skin and muscle biopsy DM analysis. The only overlapping expression was a similar upregulation of TRIM21 (p-value 3.97e-8, log ratio 0.158) in sarcoidosis blood samples.
Conclusion: TRIM protein family role in immune modulation is emerging. It has not been studied well in the context of DM. Our results suggest certain TRIM family members have a tissue and disease specific role in DM pathogenesis and may have diagnostic and therapeutic implications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aljabban J, Syed S, Syed S, Sahenk Z, Weisleder N, McElhanon K, Hoffman K, Adapa N, Allarakhia Z, Hasan L, Hadley D, Aljabban M, Jarjour W. Tripartite Motif (TRIM) Gene Family Expression in Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tripartite-motif-trim-gene-family-expression-in-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tripartite-motif-trim-gene-family-expression-in-dermatomyositis/