Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Early identification, diagnosis, and treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is important in preventing long-term joint damage and disability, and the associated socioeconomic consequences.1 Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA. Here, we assessed the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in patients (pts) with PsA, stratified by time since first PsA diagnosis.
Methods: In this 12-month, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled, Phase 3 study (OPAL Broaden [NCT01877668]),2 pts received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily or PBO. Pts had active PsA and an inadequate response to ≥ 1 conventional synthetic DMARD. Pts were stratified by time since first PsA diagnosis: < 2 yrs and ≥ 2 yrs. Efficacy outcomes included response rates at Month (M)3 for ACR20/50/70, HAQ-DI, and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI)75. Safety outcomes up to M3 were also assessed.
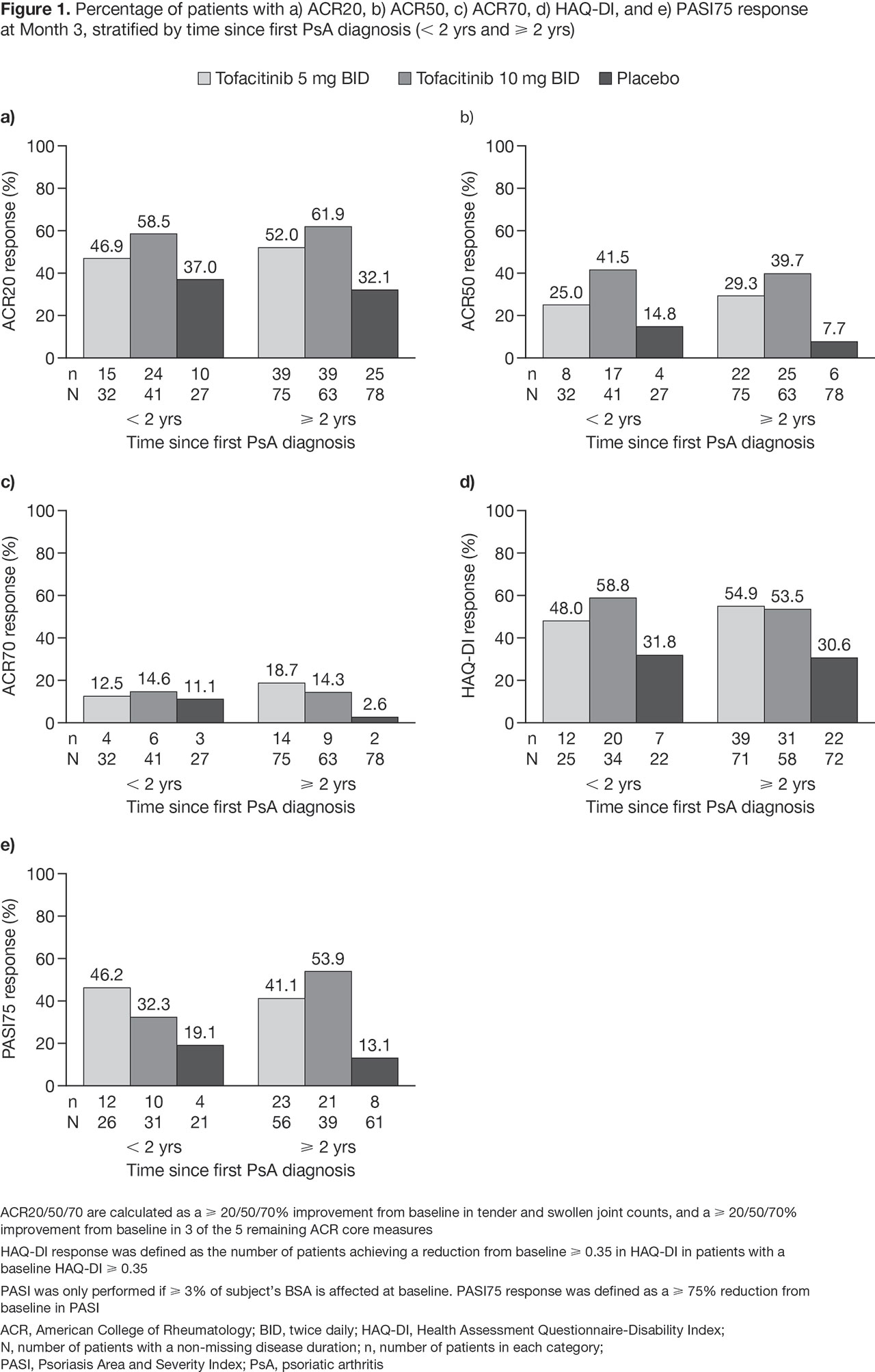
Results: This analysis included 316 pts; 100 pts in the < 2 yrs group, and 216 in the ≥ 2 yrs group. Baseline demographics and characteristics were generally similar between treatment groups and across stratification groups; however, pts in the ≥ 2 yrs group were older (mean age: 49.6 yrs vs 44.6 yrs in the < 2 yrs group). Mean disease duration was 1.0 yrs (min–max: 0.3–1.8 yrs) for the < 2 yrs group, and 8.8 yrs (min–max: 2.0–39.0 yrs) for the ≥ 2 yrs group. At M3, the response rates for ACR20/50/70, HAQ-DI, and PASI75 were greater in tofacitinib-treated pts, compared with PBO-treated pts for both the < 2 yrs and the ≥ 2 yrs group (Figure 1). Across the efficacy outcomes, the response rates for tofacitinib-treated pts in the < 2 yrs group were similar to the ≥ 2 yrs group; however, for pts treated with tofacitinib 10 mg, PASI75 response was lower in the < 2 yrs group. Response rates were higher with PBO in the < 2 yrs group vs the ≥ 2 yrs group. The difference in ACR20 response rates for tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg vs PBO was 9.8% and 21.5%, respectively, in the < 2 yrs group; and 20.0% and 29.9%, respectively, in the ≥ 2 yrs group. Adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, discontinuations due to AEs, deaths, and most common AEs are reported in Table 1. There was one case of herpes zoster (tofacitinib 5 mg, < 2 yrs group).
Conclusion: For pts with active PsA, the efficacy of tofacitinib was greater than PBO, irrespective of disease duration; however, PBO response was generally greater in the < 2 yrs group vs ≥ 2 yrs group. Due to the low numbers in the < 2 yrs group and the post hoc nature of this analysis, these results should be interpreted with caution. Safety outcomes were consistent with those previously reported for tofacitinib in pts with PsA.3
- Van den Bosch F et al. Lancet 2018;391:2285-94.
- Mease P et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1537-50.
- Gladman D et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1525-36.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support provided by Siobhán Hoy of CMC Connect and was funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nash P, Greenwald M, Lin L, Yu W, Santos Estrella P, Mundayat R, Graham D, Veale D. The Impact of Time Since First Diagnosis on the Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-time-since-first-diagnosis-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-time-since-first-diagnosis-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/