Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Among DMARDs (disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs), methotrexate (MTX), bDMARDs (biologic DMARDs) and JAK (Janus kinase) inhibitors are the major. Many adverse events of these are reported to Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) from all over Japan and listed in the Japanese Adverse Event Report database (JADER). There have been few studies adopting on that database concerning DMARDs.
Methods: The total numbers and numbers of each adverse event related to MTX, bDMARDs, and TOFA were searched in JADER of PMDA homepage, year by year. Biologic DMARDs included those covered by Japanese Health Insurance System for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Infliximab (IFX), Etanercept (ETN), Tocilizumab (TCZ), Adalimumab (ADA), Abatacept (ABT), Golimumab (GOL), Certolizumab pegol (CZP). Conventional synthetic DMARDs other than MTX were out of search this time.
Categories of adverse events were only partially reclassified to suit the clinical entities. Adverse events searched included infectious diseases, cytopenia, pulmonary diseases, lymphoproliferative diseases, and other tumors. The data of the first year of introduction of the drugs were not included because of that total prescription number might have differed from that in the years afterward. Linear regression analysis was adopted, and the statistical significance was by p < 0.05.
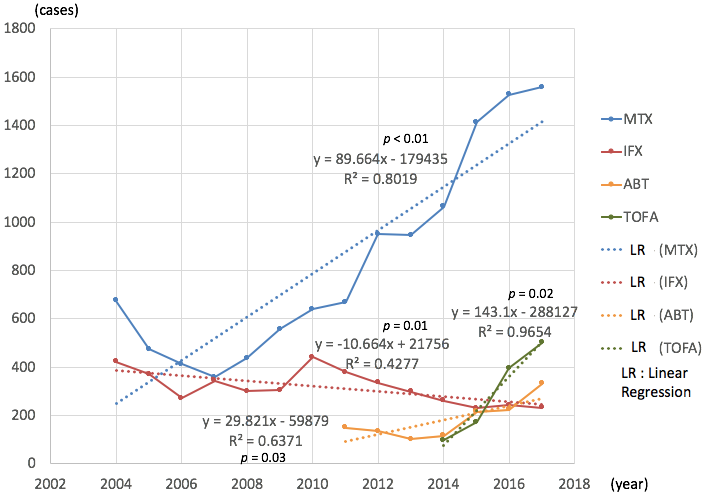
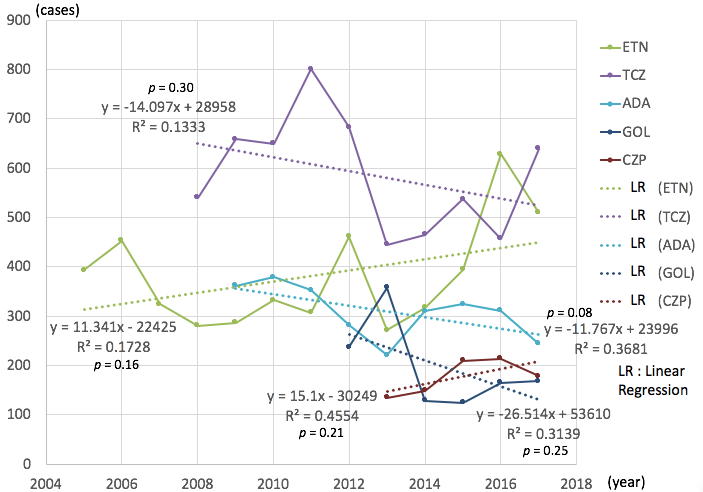
Results: The total number of adverse events related to MTX has increased significantly year by year (average 90 cases per year, correlation coefficient (CC) = 0.80, p < 0.01) (Figure 1). As for either ABT (average 30 / year, CC = 0.64, p = 0.03) or TOFA (average 143 / year, CC = 0.97, p = 0.02), the numbers were also increased. But the numbers decreased as for IFX (average -11 / year, CC = 0.43, p = 0.01) by each year, whereas other DMARDs showed no significant increase or decrease (Figure 2).
For MTX, LPD (lymphoproliferative disorders) contributed most to the increase among the detailed adverse events (average 41/ year, CC = 0.85). Secondary, infections other than those specified (average 8.0 / year, CC = 0.66) and solid tumor (average 6.6 / year, CC = 0.88) contributed (Table 1).
As for ABT, solid tumor (average 4.7 / year, CC = 0.59), pneumonia (average 4.0 / year, CC = 0.59) and other infections (average 3.6 / year, CC = 0.50) were top 3. As for TOFA, other infections (average 19 / year, CC = 0.99), pneumonia (average 16 / year, CC = 0.91) and herpes zoster (average 16 / year, CC = 0.91) contributed.
IFX related adverse events were decreased, including other infections (average -4.0 / year, CC = 0.62), pneumonia (average -3.8 / year, CC = 0.81) and gastrointestinal disorder (average -2.0 / year, CC = 0.46).
Conclusion: The adverse events related to MTX, ABT, TOFA have been increasingly reported to PMDA. Among them, LPD under MTX has more and more.
– with significant change –
– with no significant change –
– linear regression analysis –
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsuda N, Inokuma S, Hiraga K, Masui Y, Kano T. Analysis of Adverse Events of Methotrexate (MTX), bDMARDs and Tofacitinib (TOFA) Reported to Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-adverse-events-of-methotrexate-mtx-bdmards-and-tofacitinib-tofa-reported-to-pharmaceuticals-and-medical-devices-agency-pmda-japan/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-adverse-events-of-methotrexate-mtx-bdmards-and-tofacitinib-tofa-reported-to-pharmaceuticals-and-medical-devices-agency-pmda-japan/