Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, inflammatory and heterogeneous autoimmune disorder of unknown etiology characterized by progressive joint damage. Although TNF inhibitors (TNFi) have contributed to change the natural history of RA, approximately 30-50% of patients do not respond to this therapy and only a maximum of 47% achieved clinical remission. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the blood immunological profile at baseline of patients with RA could contribute to predict clinical remission to TNFi.
Methods: This is a prospective bi-center pilot study including 98 patients with RA that initiated a TNFi therapy. Clinical activity was assessed at baseline and after 6 months of treatment by disease activity score 28 (DAS28), considering optimal response if patients reached remission (DAS28≤2,6). We obtained PBMC before treatment and different leukocyte subsets were evaluated by flow cytometry in a FACSCantoII instrument. Baseline characteristics of the patients included in the study were collected. All the analyses were adjusted by sex, anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA), rheumatoid factor (RF), baseline-c reactive protein (CRP) and baseline-DAS28 through univariable and multivariate logistic regression models (odds ratio; 95% CI; p value).
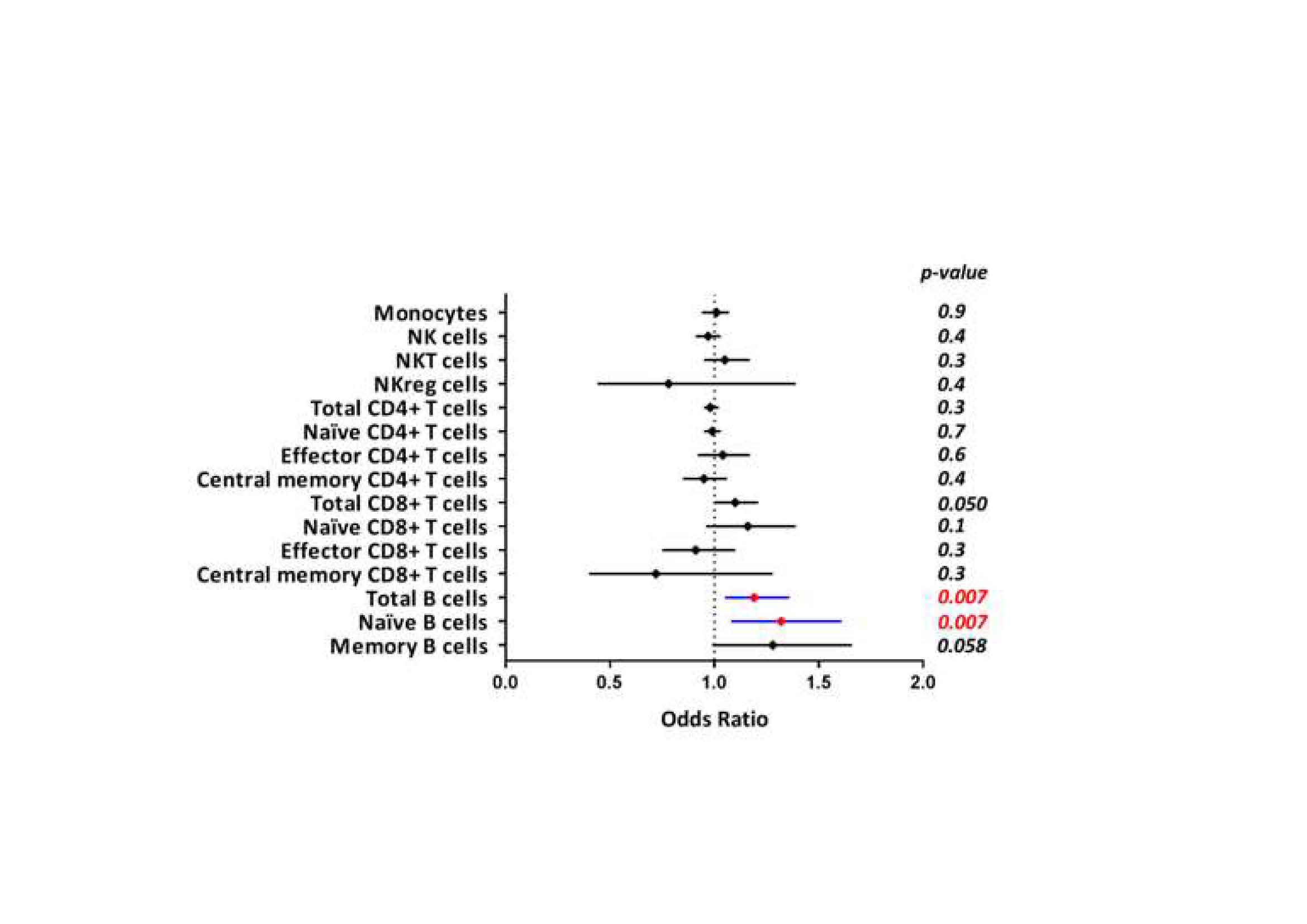
Results: At 6 months of follow-up, 39% of patients reached remission by DAS28 (REM patients). Univariable analyses were performed to investigate the association between clinical remission and baseline variables: a significant association was found for positivity of RF, presence of ACPA, lower CRP and lower baseline DAS28. In the multivariate analysis, only lower baseline DAS28 (OR: 0.32; 95% CI: 0.18-0.56; p< 0.0001) remained independently associated with REM after 6m of treatment. Basal leukocyte profile clearly differentiated between REM versus no-REM patients. REM patients showed higher percentage of B cells (OR=1.19; 95%; CI:1.05-1.35; p=0.007) and naive B cells (Bn; OR=1,32; 95%; CI:1.08-1.61; p=0.007) than no-REM patients at baseline (Figure 1). The other PBMC subsets (monocytes, NK cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells subtypes) did not show statistical differences.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that B cell profile would be the group of determinant cells to organize the response to TNFi in patients with RA. Further studies are necessary for a better understanding of the biological meaning of the increase in the naive B cells in REM patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sobrino C, Hernández-Breijo B, García-Hoz C, Nieto-Gañán I, Navarro-Compán V, Martínez-Feito A, Bachiller j, Bonilla G, Pijoán-Moratalla C, Lapuente-Suanzes P, Pascual-Salcedo D, Balsa A, Roy G, Vázquez Díaz M, Villar L, Plasencia C, Rodríguez-Martín E. B Cell Profile for Early Identification of Optimal Responders to TNF-inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/b-cell-profile-for-early-identification-of-optimal-responders-to-tnf-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/b-cell-profile-for-early-identification-of-optimal-responders-to-tnf-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/