Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the AMPLE trial, patients (pts) with RA with higher baseline anti-CCP2 antibody concentrations showed a better response to treatment with abatacept (ABA) than those with lower concentrations.1 This association was not observed with adalimumab treatment.1 The present study assessed the association between baseline (BL) anti-CCP2 concentration and 6-month treatment responses to ABA or any TNF inhibitor (TNFi) in a real-world setting.
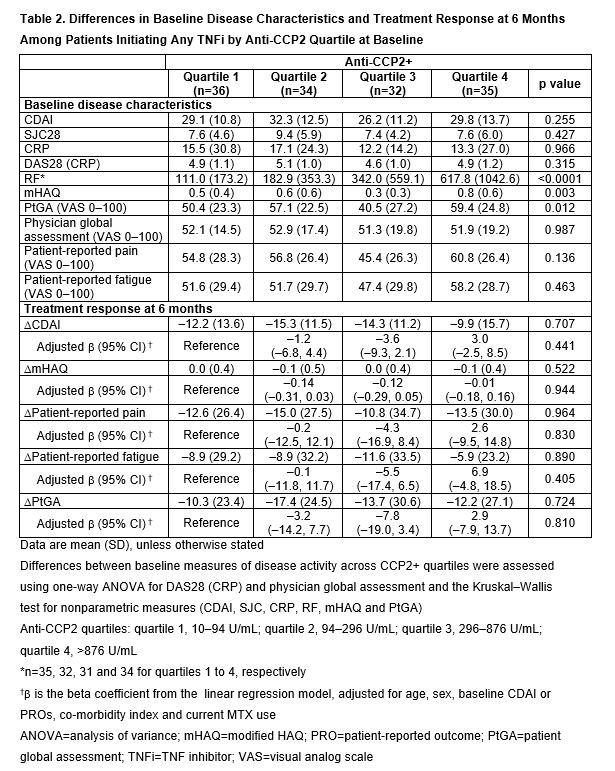
Methods: CERTAIN (Comparative Effectiveness Registry to study Therapies for Arthritis and Inflammatory CoNditions) is a prospective cohort study of adult pts with RA,2 recruited from the Corrona network, who had at least moderate disease activity (CDAI >10) and either started therapy with or switched to a TNFi or non-TNF biologic. Pts were followed for 12 months (mths) or until they switched/discontinued biologic therapy. This analysis included pts from CERTAIN who initiated ABA or any TNFi, were CCP3+ ( >20 U/mL), had CDAI >10 at BL and had serum samples at BL and at 6 mths. Eligible pts also had known BL anti-CCP2 concentration and serostatus (–, ≤10 U/mL; +, >10 U/mL) and prior biologic exposure. TNFi initiators were matched to ABA initiators based on CDAI by line of therapy. BL demographics, pt and disease characteristics were compared within treatment groups using descriptive statistics. Treatment response by BL anti-CCP2 quartile in anti-CCP2+ pts, assessed by change from BL at 6 mths in CDAI and patient-reported outcomes (PROs: modified [m]HAQ, pain, fatigue and patient global assessment [PtGA]), was evaluated separately in the ABA and TNFi groups using a linear regression model adjusted for age, sex, CDAI or PROs at initiation, co-morbidity index and current MTX use.
Results: In total, 151 matched biologic-experienced ABA and TNFi initiators were included (13 and 14 were anti-CCP2– and 138 and 137 were anti CCP2+, respectively). At BL, median age was 57–60 years (yrs), 74–75% were female, median duration of RA was 10–12 yrs and mean BMI was 29.2–29.8. There were significant differences between anti-CCP2 quartiles at BL in mean CDAI, SJC28, CRP, DAS28 (CRP), RF, mHAQ and physician global assessment, and in mean RF, mHAQ and PtGA among TNFi initiators. Among ABA initiators (Table 1), but not TNFi initiators (Table 2), a greater improvement at 6 mths in CDAI and all PROs was observed with increasing CCP2 quartile. In the adjusted analysis, among ABA initiators, there was a numerically greater improvement in CDAI (p=0.208) and statistically significantly greater improvements in all PROs (p< 0.05) with increasing anti-CCP2 quartile.
Conclusion: In a relatively small sample of abatacept-treated pts, higher anti-CCP2 concentrations at BL were associated with significantly greater improvement in PROs in the adjusted and unadjusted models, a numerically greater improvement in CDAI score in the adjusted model and a significantly greater improvement in CDAI score in the unadjusted model after 6 mths. This association was not observed in a small sample size of TNFi-treated pts.
References:
- Sokolove J, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:709–14.
- Pappas DA, et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2014;15:113.
Professional medical writing: Catriona McKay, Caudex; funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harrold L, Bryson J, Lehman T, Zhuo J, Gao S, Han X, Schrader A, Rebello S, Kremer J. Association Between Baseline Anti-CCP2 Antibody Concentration and Clinical Response After 6 Months of Treatment with Abatacept or a TNF Inhibitor in Biologic-Experienced Patients with RA: Results from a US National Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-baseline-anti-ccp2-antibody-concentration-and-clinical-response-after-6-months-of-treatment-with-abatacept-or-a-tnf-inhibitor-in-biologic-experienced-patients-with-ra-results-from/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-baseline-anti-ccp2-antibody-concentration-and-clinical-response-after-6-months-of-treatment-with-abatacept-or-a-tnf-inhibitor-in-biologic-experienced-patients-with-ra-results-from/