Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Daily health care deals with a wide spectrum of RA patients from statuses of remission (R) to disease activities at low (L), moderate (M) and high (S) based on DAS28. Each patient has 4 potential outcomes of either R, or L, or M, or S at certain time layer. But predicting efficacy and selecting regimens are in trial-and-error style. The objective of this study is to develop an algorithm for efficacy prediction and regimen selection in RA via SSDM.
Methods: SSDM includes 2 APPs for both physicians and patients. The patients input medication and laboratory test results, and perform self-evaluation (DAS28) after training. The data synchronizes to the physician’s APP and the advices could be delivered.
In order to develop a prediction model, top 2 regimens, Leflunomide (LEF, 5-10 mg/d) and LEF+MTX (7.5-10mg/w) were selected as samples from SSDM database. Repeat evaluation of DAS28 scores were extracted at 3 months interval.
The study was divided into 2 phases: phase 1. To develop Markov model and generate the probability (P) of prior believe, P(B|A), based on Bayes Theorem, and phase 2. Calculate P of posterior believe, P(A|B), and validate the reliability comparing with true evidence of outcome via Intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC).
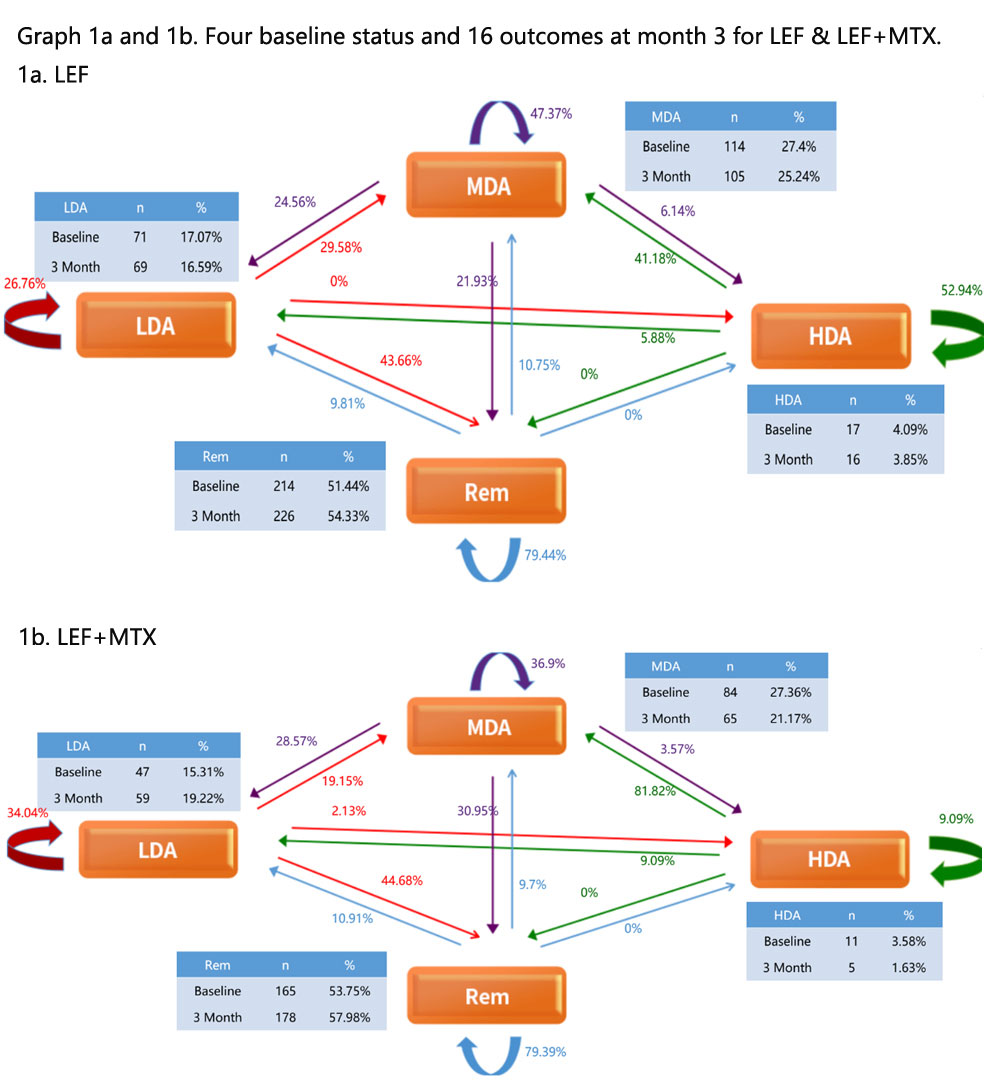
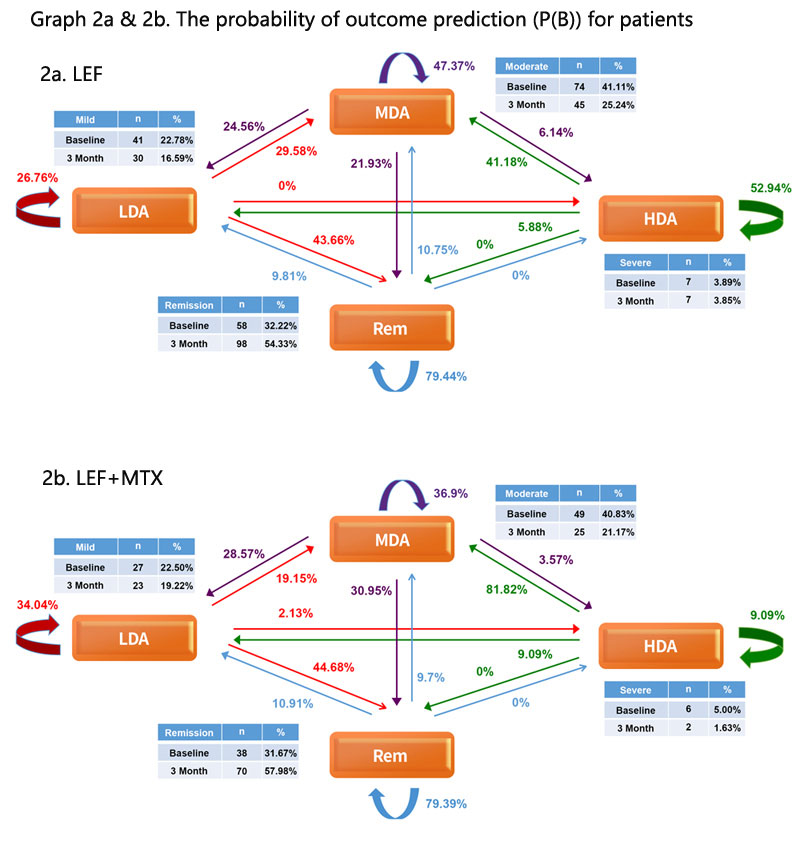
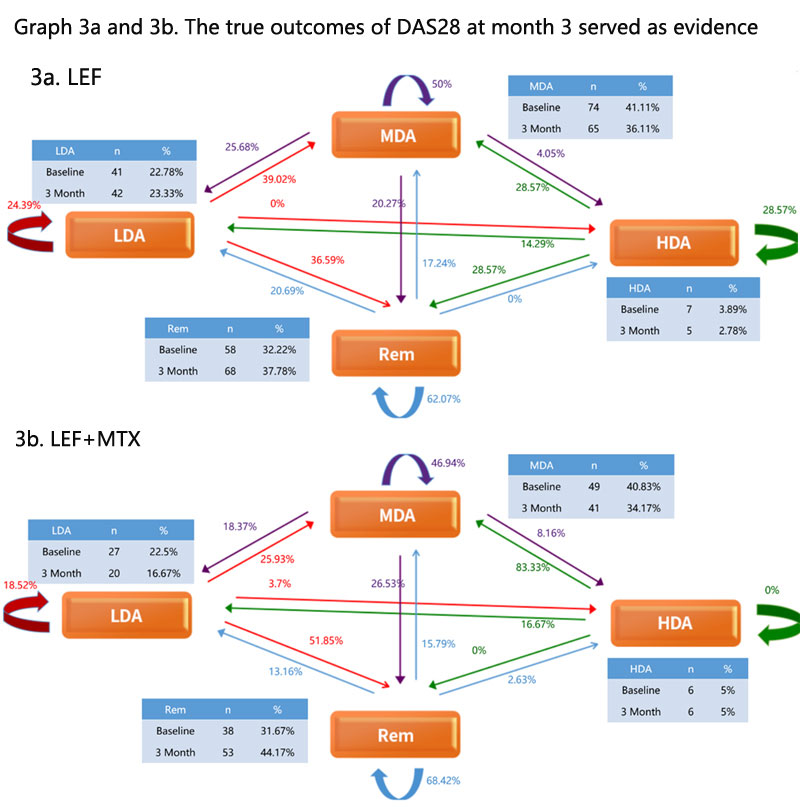
Results: From June 2014 to May 2019, 54,149 RA patients from 587 centers registered in SSDM. Among those with 3 months data available, 416 patients with LEF and 307 with LEF+MTX who registered before June 1 of 2018 were enrolled in phase 1, and 180 patients with LEF and 120 with LEF+MTX after June 1 of 2018 were included as phase II. There were no significant difference considering gender, age, race, disease history and DAS28 distribution between 2 phases. Phase I: Four baseline status (P(A)) and 16 outcomes at month 3 (P(B)) for LEF or LEF+MTX are presented in graph 1a and 1b, respectively, based on Markov Chain. The algorithm of probabilistic inference for next month 3 outcome was created as Σ p{Xt+1|Xt (Rt, Lt, Mt, Ht)}=1 0< t< ∞. The beta distribution and P(B|A) were generated. Phase II: The probability of outcome prediction (P(B)) for patients was calculated using the DAS 28 at baseline via the Bayes algorithm: P(A|B)=P(B|A)*P(A)/P(B) and were shown in graph 2a & 2b. The true outcomes of DAS 28 were obtained through repeat self-valuation at month 3 served as evidence (graph 3a & 3b). Comparing the distribution of evidence with those in P(A|B), ICC for LEF was 0.90, and ICC for LEF+MTX was 0.96, which indicated high inter-observer reliability. Based on the algorithm, the inferences of efficacy for both LEF and LEF+MTX were obtained. The advices were that LEF at low dose was good for RA with R and L, but for RA with H, adding MTX was preferred. Both were good for M.
Conclusion: Through patterns extraction, data mining and modeling, a master algorithm of efficacy prediction and decision making for RA were developed. Following data inputting and machine leaning, an artificial intelligent system in assisting clinical practice may be achieved with SSDM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mu R, Li C, Yang J, Wang X, Wu B, Zhang F, Wang Y, Qin L, Mi C, Guo H, Wei W, Liu W, Huang Q, Lu J, Liu Y, Li H, Wu B, Xiao H, Jia Y, Xiao F. Create an Algorithm of Outcome Forecasting and Decision Making for RA Treatment: Data Mining and Machine Learning via the Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/create-an-algorithm-of-outcome-forecasting-and-decision-making-for-ra-treatment-data-mining-and-machine-learning-via-the-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/create-an-algorithm-of-outcome-forecasting-and-decision-making-for-ra-treatment-data-mining-and-machine-learning-via-the-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/