Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ACR/EULAR guidelines recommend remission or low DAS28 as the treat to target goal for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Alternative patient reported outcomes include the rheumatoid arthritis impact of disease (RAID), a self-reported index which assesses seven domains by visual analogue scale: pain, disability, fatigue, sleep, coping, physical and emotional well-being. Responses are weighted differently, producing a final score from 0-10. A score less than 2 is considered a patient-acceptable status. We have assessed the relation of RAID to (i) DAS28 categories in routine care, (ii) it’s utility to identify patients in DAS28 remission (RDAS) or low disease activity (LDAS) and (iii) the burden of unmet patient needs in those achieving RDAS/LDAS.
Methods: RA patients attending for routine review in the outpatient clinic at St George’s Hospital were assessed. DAS28 CRP and ESR scores were recorded and RAID questionnaires completed by patients and calculated using the on-line EULAR tool. Summary statistics and Spearman correlation coefficient were analysed on Excel and Mann-Whitney U tests using socscistatistics.com.
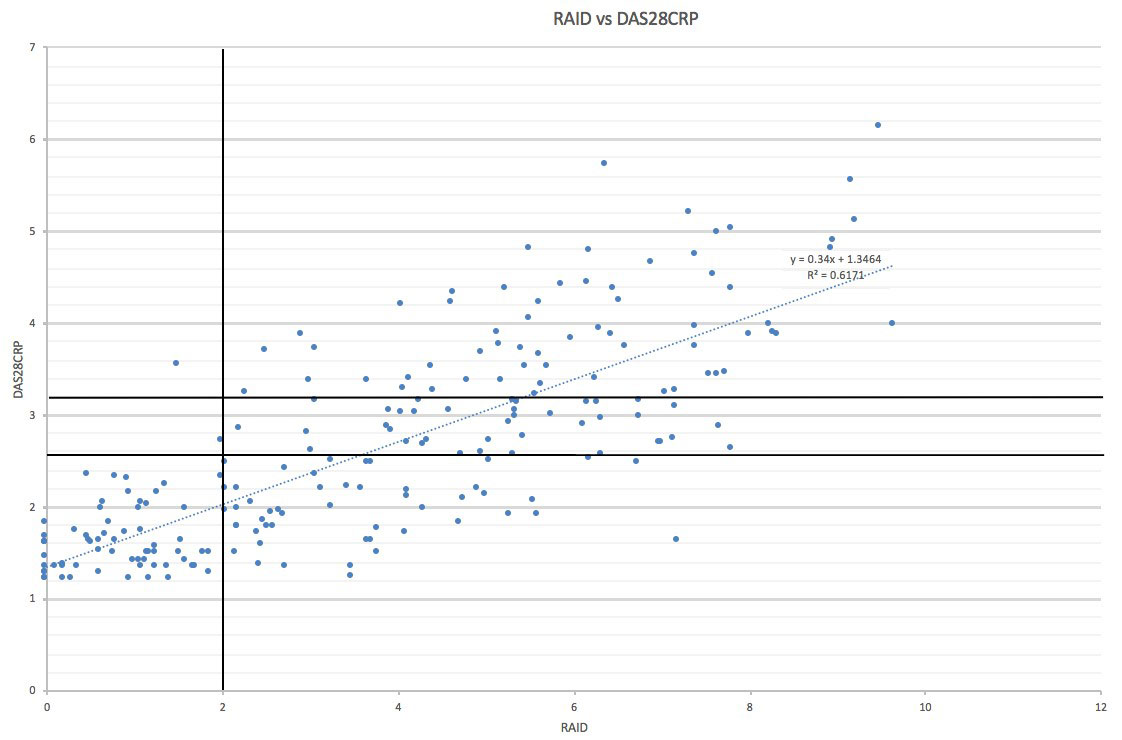
Results: 219 patients with established RA were assessed, 81.3% female, mean age 58.8 years, 72.1% RF positive and 79.5% ACPA positive. The number of patients per DAS28 CRP category was RDAS (< 2.6) n=119 (54.6%), LDAS (2.6-3.2) n=34 (15.6%), moderate (MDAS 3.21-5.1) n= 60 (27.5%), high (HDAS >5.1) n= 5 (2.3%). RAID scores correlated strongly with patient global (r=0.69), DAS28 CRP (r=0.62) and DAS28 ESR (r=0.55) but poorly with tender joint count (r=0.30), swollen joint count (r=0.14), ESR (r=0.15) and CRP (r=0.09). The mean RAID score per DAS28 CRP category was RDAS 2.14, LDAS 5.23, M+HDAS 6.09. RAID scores were significantly different (Mann-Witney U) between RDAS versus LDAS (p< 0.00001), RDAS versus M+HDAS (p< 0.00001), LDAS versus M+HDAS (p=0.02). Similar significant differences in RAID scores were found between DAS28 ESR categories. Of 66 patients with RAID < 2, DAS28 CRP was < 2.6 in 64 (97%) and < 3.2 in 65 (98.5%). Of 151 patients with DAS28 CRP < 3.2, RAID was >2 in 86 (57%) with fatigue followed by sleep being the worst scoring domains.
Conclusion: In patients with established RA in routine care, RAID strongly correlates with patient global and DAS28, and scores are significantly lower in patients achieving RDAS versus LDAS and either RDAS or LDAS versus M+HDAS. Virtually all patients with a RAID score < 2 are in DAS28 remission or low disease activity defined by DAS28, and this could be used to minimise unnecessary consultations. However, over half of all patients with DAS28 < 3.2 have unacceptable RAID, and fatigue dominates the unmet needs driving this unacceptable state.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mistry J, Sibley M, Smith C, Sumbwanyambe M, Kiely P. Utility of Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease (RAID) in Routine Care; Identification of Patients Achieving DAS28 Remission or Low Disease Activity, and Burden of Unmet Patient Reported Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-impact-of-disease-raid-in-routine-care-identification-of-patients-achieving-das28-remission-or-low-disease-activity-and-burden-of-unmet-patient-reported-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-impact-of-disease-raid-in-routine-care-identification-of-patients-achieving-das28-remission-or-low-disease-activity-and-burden-of-unmet-patient-reported-outcomes/