Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are inflammatory arthritides associated with significant potential functional disability if not well controlled. We reviewed the baseline demographic and disease characteristics over nineteen years in the RAPPORT registry to understand changes in prescribing patterns of biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) over time.
Methods:
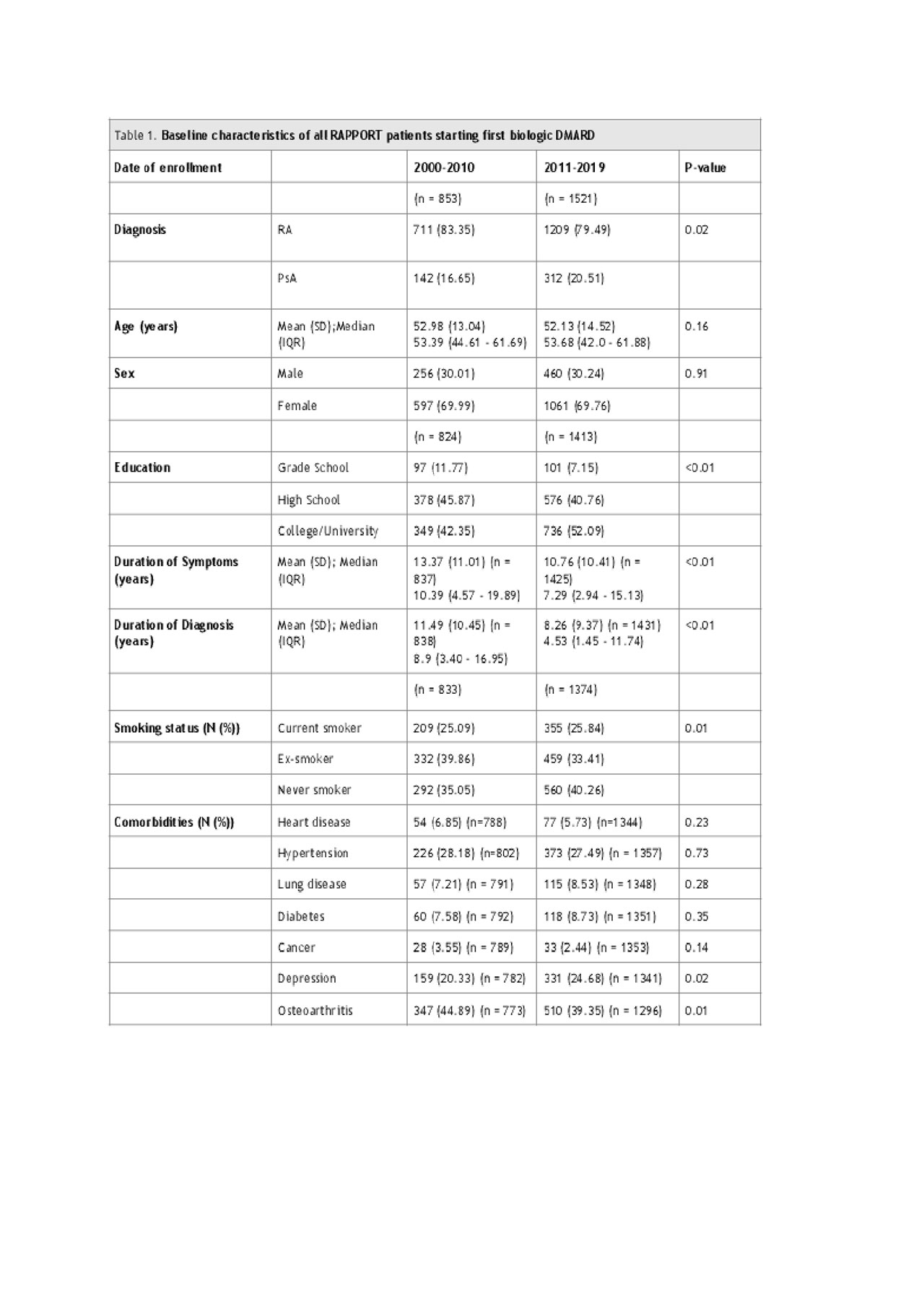
The Rheumatoid Arthritis Pharmacovigilance Program and Outcomes Research in Therapeutics (RAPPORT) registry is a large prospective inception cohort for Northern Albertan inflammatory arthritis (IA) patients about to start advanced therapy with at least 4 months of exposure to conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARD) including parenteral weekly methotrexate, methotrexate plus a DMARD in combination, and leflunomide. We compared baseline demographic and disease characteristics in two cohorts according to registration year: 2000-2010 (n=1071) and 2011-2019 (n=1632). Specifically, we compared patient demographics including age, sex, education, comorbidities and smoking status; disease characteristics including tender and swollen joint count, HAQ, patient global, CRP, and DAS28, symptom duration; and first bDMARD therapy. Descriptive statistics were use to asses baseline demographics along with univariate analysis for comparison of variables between cohorts.
Results: Of the 2703 RAPPORT patients, IA patients in the later cohort (2011 onwards) were started on biologic therapy an average of 2.61 years earlier from symptom duration (p< 0.001) (Table 1). There were differences in the pattern of bDMARD prescriptions within and between classes between the two cohorts; however, there were no significant differences in age, sex or number of comorbidities (Table 1). The prevalence of self-reported depression and osteoarthritis were higher in the later cohort but there was no difference in heart disease or associated cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes). Statistically significant but clinically unimportant differences in markers of disease activity including HAQ, swollen joint count, and CRP were found between cohorts (Table 2). Biologic DMARD prescriptions in the latter cohort showed increased TNF inhibitor use and increased use of other classes (Table 3).
Conclusion:
Prescribing patterns of bMDARDs changed between the first and second decade of RAPPORT with earlier introduction of bDMARDS in IA patients from time of diagnosis. Possible reasons include the rapid increase in availability of bDMARDs between and across classes and increased uptake and confidence in bDMARD use by prescribing rheumatologists over time. Further work to evaluate the impact of bDMARD prescription patterns on patients and society is planned.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jones B, Pan B, Homik J, Russell A, Maksymowych W, Hall J, Keeling S. Earlier Biologic Initiation over Two Decades of Real World Observational Data from the RAPPORT Biologics Registry of Northern Alberta, Canada [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/earlier-biologic-initiation-over-two-decades-of-real-world-observational-data-from-the-rapport-biologics-registry-of-northern-alberta-canada/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/earlier-biologic-initiation-over-two-decades-of-real-world-observational-data-from-the-rapport-biologics-registry-of-northern-alberta-canada/