Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent concerns over osteoarthritis (OA) pharmacotherapy safety have led to revision of treatment guidelines and highlight the need for therapies with good safety profiles. Lorecivivint (LOR; SM04690) is a small-molecule, intra-articular (IA) CLK/DYRK1A inhibitor which modulates the Wnt pathway and is in development as a potential disease-modifying treatment for knee OA. A pooled analysis of safety data from three completed placebo-controlled studies of this new agent is reported here.
Methods: Safety data were pooled from three randomized controlled trials evaluating four concentrations (0.03 mg, 0.07 mg, 0.15 mg, and 0.23 mg) of a single IA LOR injection in subjects with moderate-to-severe symptomatic knee OA. Two trials (NCT02095548; NCT03122860) evaluated subjects for 24 weeks and one trial (NCT02536833) for 52 weeks. Two subject groups were compared: a LOR-exposed group (subjects who received any dose of LOR) and a control group (non-LOR treated subjects). Adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs (SAEs) were collected and categorized using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MeDRA) classification. Bone health AEs were also categorized upon medical review. Proportions of subjects with treatment-emergent AEs and SAEs were calculated for control and LOR-exposed groups. Incidence rates of bone health AEs were estimated per 100 person-years [PY] exposure for LOR and control groups.
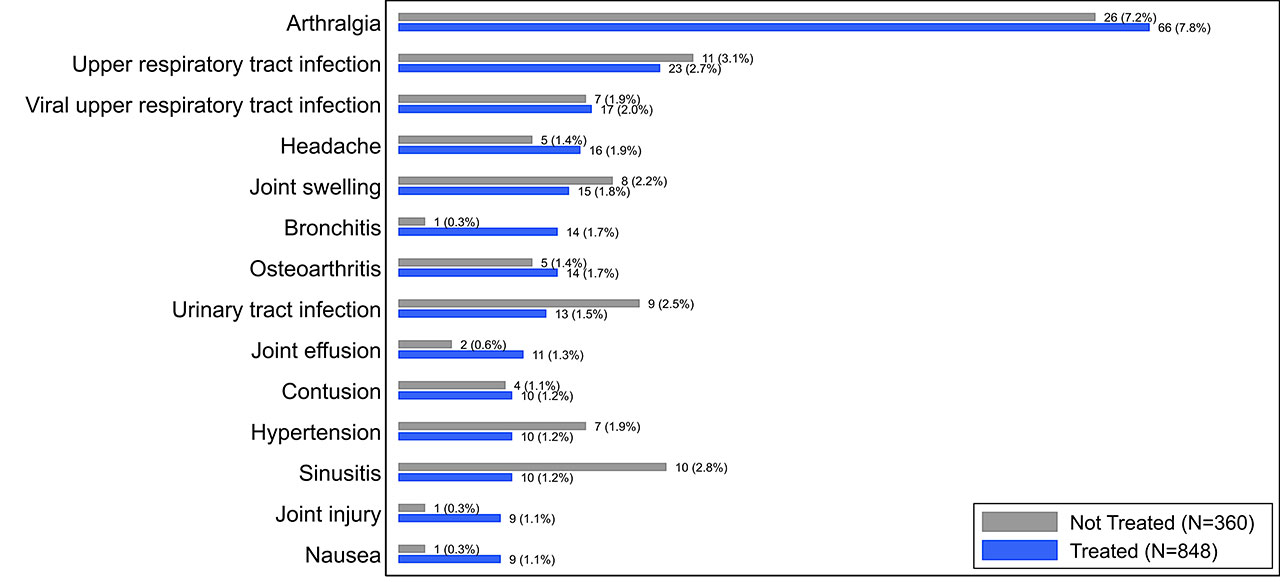
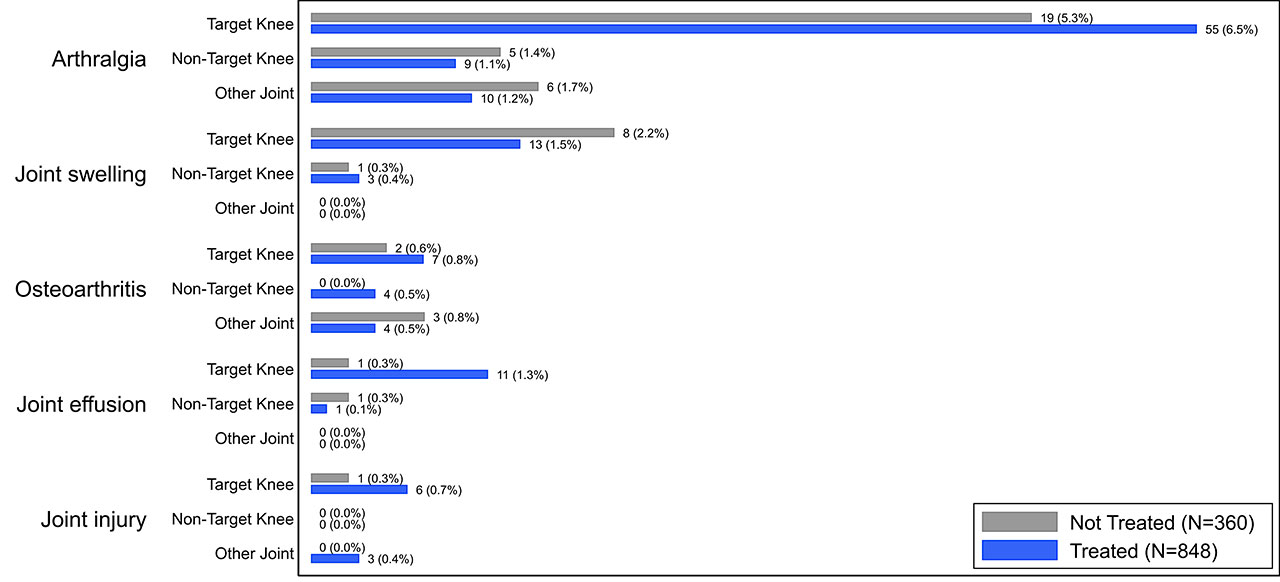
Results: The overall incidence of AEs and SAEs were infrequent in both treated (total 350/848 [41.3%], SAE 20/848 [2.4%], 559 PY exposure) and control subjects (total 138/360 [38.3%], SAE 4/360 [1.1%], 219 PY exposure). The most common AE reported in the treated subjects was arthralgia (treated 7.6%, control 7.2%) and it was the only AE reported at >5% in either subject group (Fig. 1). Of joint-specific AEs categorized by the affected joint (Fig. 2), target-knee arthralgia was most common (treated 6.5%, control 5.3%). No AEs in other joints exceeded an incidence of 2% in either group. In all categories, individual AEs were reported at comparable rates between groups and no SAEs were deemed related to LOR by investigators.
There were 16 bone-health-related AEs in 12/1208 (1.0%) subjects; the rate of bone health AEs per 100 PY exposure was 1.61 for LOR and 1.37 for control. Of the bone health AEs, 2 were osteopenia/osteoporosis in 2 LOR-treated postmenopausal women and 14 were fractures in 10 subjects (7 LOR 1.25/100 PY, 3 control 1.37/100 PY). All fractures were adjudicated and determined to be caused by trauma and all healed uneventfully within the expected timeframe. Bone health AE incidence rates between LOR and control were similar.
Conclusion: In total exposure to date (559 PY), IA LOR for the treatment of knee OA appeared to be safe and well tolerated. These data support the continued evaluation of LOR as a treatment for OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Simsek I, Swearingen C, Kennedy S, Tambiah J, Yazici Y, Lane N, Hochberg M. Safety Profile to Date of the Novel, Intra-articular Agent Lorecivivint (LOR; SM04690), a CLK/DYRK1A Inhibitor That Modulates the Wnt Pathway, in Subjects with Knee Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-profile-to-date-of-the-novel-intra-articular-agent-lorecivivint-lor-sm04690-a-clk-dyrk1a-inhibitor-that-modulates-the-wnt-pathway-in-subjects-with-knee-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-profile-to-date-of-the-novel-intra-articular-agent-lorecivivint-lor-sm04690-a-clk-dyrk1a-inhibitor-that-modulates-the-wnt-pathway-in-subjects-with-knee-osteoarthritis/