Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) in hands is common in middle-aged and elderly population. The mainstay treatment of hand OA is to control the symptoms with a combination of non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions. Prior randomized clinical placebo-controlled trials (RCT) involving patients with hand OA showed that placebo itself significantly improved pain in those patients. The objective of this post hoc analysis was to identify the factors associated with good placebo response in patients with hand OA.
Methods: This post hoc analysis of two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trials investigating efficacy of GCSB-5 or diacerein in hand OA analyzed the efficacy of the placebo in patients with hand OA. The efficacy endpoints included the changes at baseline and 4 weeks for the following variables: AUSCAN (Australian/Canadian
Osteoarthritis Hand Index) pain score (0–100), AUSCAN stiffness score (0–100), AUSCAN function score (0–100), patient global assessment (0–100), physician global assessment (0–100). A clinically meaningful improvement in pain was defined as an improvement in AUCAN pain of 10 (0-100) or more.
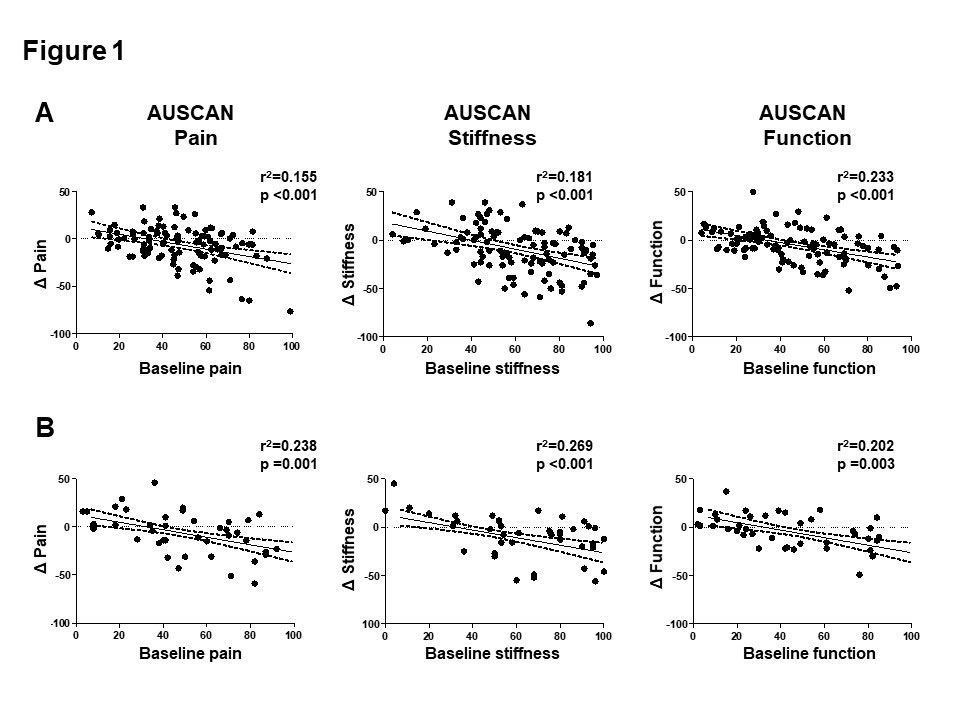
Results: In RCT 1, the mean improvement in AUSCAN pain was -6.0 ± 19.7. However, the placebo-response varied markedly between the OA patients (range -76.4 to 33.2) from baseline. Clinically meaningful improvement in pain was observed in 37 (36.3%) patients. Patients with worse AUSCAN pain (44.9 ± 19.8 vs. 53.1 ± 19.0, p=0.044) and physician global assessment (38.9 ± 11.4 vs. 44.6 ± 14.8, p=0.031) at baseline was associated with clinical meaningful improvement. Structural joint changes such as tender, swollen, enlarged or deformed joint counts did not differ between placebo responders and non-responders. Pain improvement correlated with the respective pain level at baseline (r=0.155, p< 0.001). In a validation study with RCT 2, patients showed a similar placebo response. Improvement in pain, stiffness and function correlated with their respective baseline value in RCT 2 as well.
Conclusion: This post hoc analysis of two prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies showed that clinically meaningful response to placebo was observed in up to one third of patients with hand OA. This positive placebo response was associated with high pain level at baseline. Further researches are needed to optimize and utilize the benefit of placebo response in OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahn S, Park J, Shin K, Lee Y, Song Y, Choi Y, Lee E. Predictor of Placebo Response in Hand Osteoarthritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of Two Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictor-of-placebo-response-in-hand-osteoarthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictor-of-placebo-response-in-hand-osteoarthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-randomized-controlled-trials/