Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Regular aerobic exercise has been shown to improve inflammatory arthritis (IA) symptoms and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular events observed in these patients. Practice guidelines recommend regular exercise in the management of patients with IA. Despite this, exercise is infrequently assessed and recommended in routine rheumatology care, and few patients with IA achieve the level of exercise recommended in the Canadian physical activity guidelines. The aim was to increase documentation of physician exercise counselling in patients with IA by 50% by April 30, 2019.
Methods: Baseline data on documented exercise recommendation to patients with IA (defined as a physician diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis) were collected at a single academic rheumatology clinic in Toronto, Canada, over four weeks in September 2018. Rheumatologists and patients were interviewed to determine barriers to exercise counselling and uptake. Four Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles were completed between January and April, 2019. Interventions included assessing level of exercise participation on patient intake forms, rheumatologist education, providing a standardized exercise prescription pad in all clinic rooms, creation of a smartphrase to assist electronic record documentation, and poster reminders about exercise counselling in the clinical setting. The primary outcome was the percentage of patients who had documentation of exercise recommendation by their rheumatologist from clinic charts. The weekly percentage of patients with IA, for whom a physician recommendation to exercise was documented, was calculated from a sample (approximately 50%) of weekly follow-up patients.
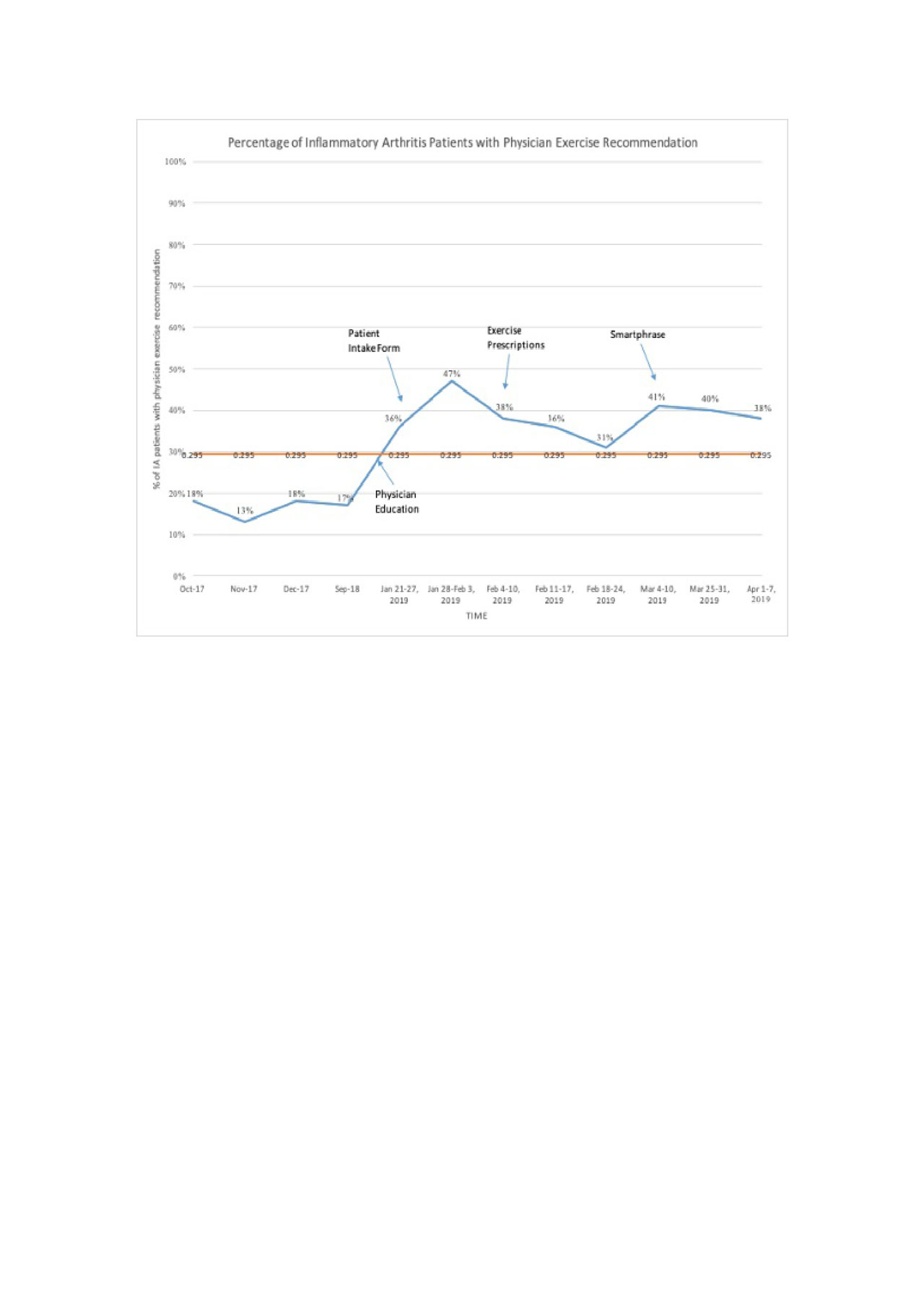
Results: Baseline physician exercise recommendation was 15%. Over eight weeks of study, this increased to a mean of 38% (range 31-47%) and showed special cause variation based on eight consecutive points above the mean (Figure). There were no reports of patient adverse events or negative impact on clinical efficiency.
Conclusion: In this quality improvement study, physician education regarding exercise counselling, provision of written exercise prescriptions, education and reminders increased the documentation of physician recommended exercise in patients with IA. Future research is required to determine if increasing exercise counselling translates into increased levels of exercise among IA patients and if this is effective and feasible at other centres.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Albasri A, Al-Araimi T, Gottheil S, King L, Koppikar S, Shamis J, Lake S, Natasha G. Improving Exercise Counselling of Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis: A Quality Improvement Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-exercise-counselling-of-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis-a-quality-improvement-project/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-exercise-counselling-of-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis-a-quality-improvement-project/