Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S108: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Cardiovascular Comorbidities (921–926)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: In the general population, statins reduces atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events in those with a computed tomography (CT)-assessed coronary artery calcium (CAC) score ≥100 units, regardless of background level of predicted ASCVD risk. Since general ASCVD risk models underperform in RA, we sought to identify RA-specific clinical indicators of an actionable level of CAC [i.e. CAC ≥100 (alCAC)] to distinguish those seemingly at lower ASCVD risk who would benefit from CAC screening and/or ASCVD prevention.
Methods: Data were pooled from 4 cohorts of RA patients and a cohort of non-RA controls who all underwent CT-assessed CAC calculated using the Agatston method. Those on statins or with prior known CVD were excluded. Predictors of alCAC were modeled using logistic regression for those with low (< 5%) and intermediate (5-15%) ASCVD risk based on the ACC/AHA 10-year risk equation. The number needed to screen (NNS) with CT to identify an individual with alCAC was assessed before and after classifying patients according to ASCVD strata-specific predicted probabilities.
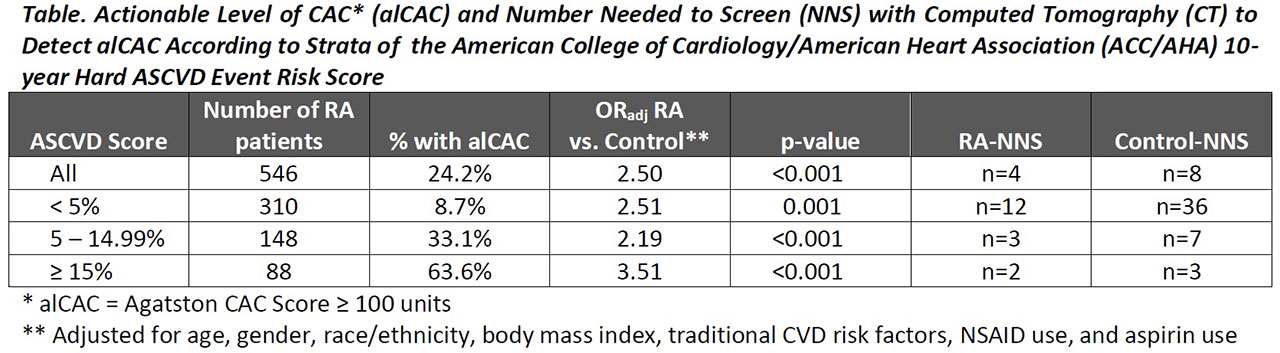
Results: A total of 546 RA patients and 5,279 non-RA controls were studied. The majority (57%) of the RA group had an ASCVD risk score< 5% and 27% had risk between 5-15%. alCAC was observed in n=132 (24%) of the RA group, and 58% of the total alCAC for the RA cohort was contained within the two lower ASCVD risk groups, including 20% in the group with an ASCVD score < 5%. The adjusted odds of alCAC was greater in the RA vs. control groups for all strata of ASCVD risk (Table), and the NNS was lower in RA for each stratum. In the low ASCVD risk RA group, alCAC was associated significantly and independently with higher age, ever smoking, lower BMI (particularly among ever smokers), antihypertensive use, very low and high LDL-C, aspirin use, RA duration (particularly among those not treated with biologics), and higher DAS28 score. The AUC-ROC for these indicators was 0.921 (95% CI 0.858, 0.984) and was significantly higher than modeling the ASCVD score alone (AUC=0.657; p-value for model comparison< 0.001). A different set of indicators of alCAC was present for those with ASCVD risk between 5-15% [male gender, waist circumference, current smoking (particularly among those with a normal BMI), antihypertensive use, and non-use of methotrexate]. The AUC-ROC for these indicators was 0.776 (95% CI 0.694, 0.857) and was significantly higher than modeling the ASCVD score alone (AUC=0.605; p-value for model comparison=0.004). Taking only those in the 4th quartile of predicted probability from each ASCVD risk stratum identified 67% of the seemingly low/intermediate ASCVD risk RA patients with alCAC (NNS=3), including all but n=4 in the low risk group. Taking the 3rd and 4th quartiles identified 80% with an alCAC (NNS=3), including all in the low risk group.
Conclusion: Using ASCVD strata-specific prediction models, clinical characteristics that included RA features were able to distinguish a large proportion of the seemingly lower ASCVD risk RA patients with alCAC who would benefit from additional screening and/or aggressive preventive treatment. External validation is warranted in order to apply this approach to clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Giles J, Chung C, Wasko M, Kao A, Oeser A, Stein C, Bathon J. Indicators of Actionable Levels of Atherosclerosis in RA Patients Who Appear to Have Low or Intermediate Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk Based on Standard Risk Algorithms [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/indicators-of-actionable-levels-of-atherosclerosis-in-ra-patients-who-appear-to-have-low-or-intermediate-atherosclerotic-cardiovascular-risk-based-on-standard-risk-algorithms/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/indicators-of-actionable-levels-of-atherosclerosis-in-ra-patients-who-appear-to-have-low-or-intermediate-atherosclerotic-cardiovascular-risk-based-on-standard-risk-algorithms/