Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S078: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Pulmonary & Other Comorbidities (839–844)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: The frequency of pulmonary involvement in rheumatoid arthritis varies between 7-35%. The most important cause of death in RA patients is lung disease in UIP pattern. The aim of this study was to determine the mortality and associated factors in RA- related lung disease (RA-LD) patients followed up in a single tertiary center.
Methods: During January 2010 and March 2019, 826 RA patients had lung computerized tomography in Hacettepe University. Three radiologists re-evaluated lung CTs and 156/826 (18.8%) patients with RA-LD were included in the final analysis. Overall, 104 patients (%66.7) had at least one control lung CT. Lung CT findings were classified as UIP, NSIP and isolated airway disease (AD). Demographic, clinical, laboratory and therapeutic data was collected. Information on death of patients was obtained either by chart review of through the national death registration database. Factors related to mortality were analyzed with univariate and multivariate analysis; Kaplan-Meier plots were used for survival analysis.
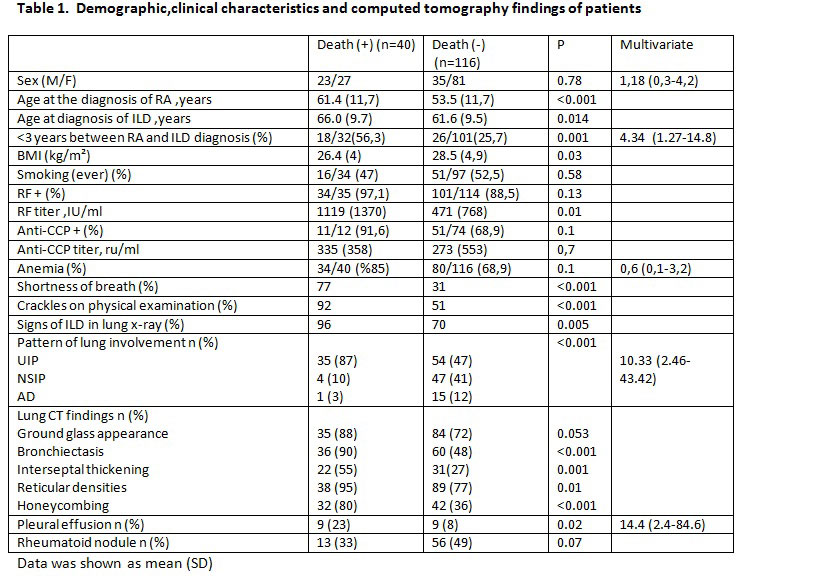
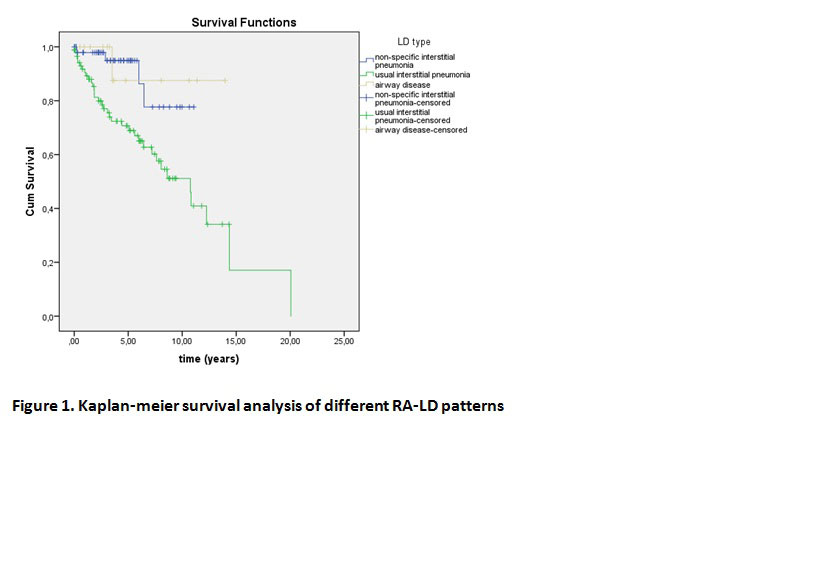
Results: Totally, 156 patients (30.8% male) were included in the study. The mean (SD) follow-up duration was 129 (90) months for RA, and 53.8 (45) months for RA-ILD. Eighty-nine patients had UIP (57.0%), 51 (32.7%) had NSIP and 16 (10.2%) had AD pattern. 40/157 (25.6%) patients died during the follow-up period. The mean age of death was 70.7 years (10). The mean follow-up duration was 4.4 (4,4) years for the patient who had died, and 4.7 (3,5) years for the living patients. Presence of crackles was higher in the patients who died (34/37 [%92] vs 50/98 [51%], p < 0.001). Initial lung functions were similar (FVC: 85% (24.5) vs 82% (19), FEV1: 91% (22.4) vs 84% (20.5) however, patients who had died had lower lung volumes at last control visit (FVC: 57.1% (16.7) vs 91.0% (22.3), p < 0.001, FEV1: 61.0% (17.4) vs 87.0% (23.4), p = 0.001). Mortality was higher in patients with UIP (log-rank: 0.004) (figure 1). Among the treatments used, only the history of methotrexate and cyclophosphamide use were related with mortality (methotrexate 24 (60%) vs. 95 (81.9%) p = 0.005, steroid 39 (97.5%) vs 112 (96.6%) p = 0.7, leflunomide 29 (%) 72.5) vs 90 (77.6%) p = 0.5, sulfasalazine 18 (45%) vs 70 (60.3%) p = 0.09, hydroxychloroquine 30 (75%) vs 101 (87%, 1) p = 0.07, azathioprine 7 (17.5%) vs 10 (8.6%) p = 0.14, cyclophosphamide 10 (25%) vs 7 (6%) p = 0.002, pulse steroid 8 ( 20%) vs 3 (2.6%) p = 0.001, taking any biological treatment 16 (40%) vs 53 (45.7%) p = 0.53, Anti TNF 6 (15%) vs 32 (% 27.6) p = 0.11, abatacept 1 (2.5%) vs 11 (9.5%) p=0.29, rituximab 14 (35%) vs 24 (20.7%) p=0.06). Relationship between mortality and other parameters is shown in the table 1. UIP pattern, pleural effusion and the shorter time interval (< 3 years) between the diagnosis of RA and RA-LD were independent predictors of mortality in multivariate analysis (Table 1).
Conclusion: In our study, for RA-LD mortality, UIP pattern is usual suspected risk factor and pleural effusion, shorter time-interval between diagnosis RA and RA-LD are newly defined strong predictors. These risk factors may be used in the early risk stratification in the management of RA-LD routine practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ekici M, Sarı A, Baytar Y, Bolek E, Armagan B, Bilgin E, Farisoğulları B, Karadag O, Ertenli A, Kiraz S, Apras Bilgen �, Kilic L, Akdoğan A, durhan G, arıyürek M, Kalyoncu U. Mortality Ratio and Risk Factors in CT Confirmed Rheumatoid Arthritis Related Lung Disease: UIP, Pleural Effusion and the Time of Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis – Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-ratio-and-risk-factors-in-ct-confirmed-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-lung-disease-uip-pleural-effusion-and-the-time-of-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-ratio-and-risk-factors-in-ct-confirmed-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-lung-disease-uip-pleural-effusion-and-the-time-of-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-lung-disease/