Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the SELECT-MONOTHERAPY trial, upadacitinib (UPA), an oral JAK1-selective inhibitor, showed efficacy when used as monotherapy over 14 weeks (wks) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients (pts) with an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX).1
Safety and efficacy of UPA monotherapy were assessed through 48 wks in an ongoing long-term extension period of SELECT-MONOTHERAPY.
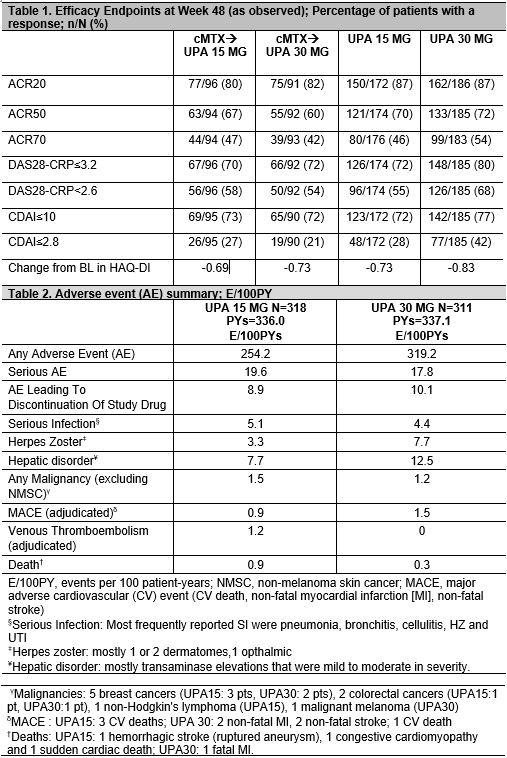
Methods: At baseline (BL), pts on stable MTX were randomized to either continue MTX (cMTX, given as a blinded study drug) or switch to once-daily (QD) UPA at 15 (UPA15) or 30 mg (UPA30) monotherapy for 14 wks. From Wk14, the start of a long-term blinded extension, pts randomized to cMTX were switched to UPA15 or 30mg per pre-specified assignment at BL, pts randomized to UPA15 or 30 continued their initial treatment. No dose adjustments for UPA were allowed. Starting at Wk26, for pts who did not achieve CDAI ≤10, background csDMARDS could be initiated. Efficacy data up to the Wk48 visit are reported “As Observed”. Adverse events (AE) per 100 pt yrs (PYs) are summarized up to May 25 2018.
Results: Of 648 pts randomized at BL, 598 (92%) completed 14 wks and continued on to the extension period. By May 25 2018, 16% discontinued study drug; 5% due to AE, 0.5% due to lack of efficacy, 4% withdrew consent, 1% were lost to follow-up, and 6% discontinued due to other reasons. Cumulative exposures to UPA15 and UPA30 were 336.0 PYs and 337.1 PYs, respectively. Starting from Wk26, background csDMARDs were initiated for approximately18% of pts. Based on As Observed data, for pts on UPA from BL through Wk48 on UPA15 [250/300 (83%)] and UPA30 [251/298 (84%)], clinical and functional outcomes continued to improve, or were maintained (Table 1). For pts continuing UPA15 and 30, DAS28-CRP< 2.6 was 55% and 68%, and CDAI≤2.8 was 28% and 42%, respectively. Pts who were switched from cMTX to UPA15 or 30 at Wk14 had similar responses at Wk 48. The most frequently reported treatment-emergent AEs were urinary tract infection, blood creatine phosphokinase increase, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, worsening of RA, herpes zoster (HZ), alanine aminotransferase increase, and bronchitis. The most frequently reported serious AE was pneumonia (8 events). Events/100PYs were numerically higher in the UPA30 vs UPA15 arm for HZ, and hepatic disorders, and were comparable for serious infections and malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (Table 2). Adjudicated venous thromboembolic events (VTE) were observed only on UPA15 (2 pts with deep vein thrombosis and 2 pts with pulmonary embolism; all patients had at least one risk factor for VTE).
Conclusion: UPA 15 or 30 monotherapy resulted in similar improvements in signs and symptoms and physical function through 48 wks. The overall benefit-risk profile of both doses of UPA was favorable based on the safety and efficacy data through Wk48 but will be confirmed through an integrated safety analysis across all the phase 3 trials.
1. Smolen et al. Arthritis and Rheumatol 2018 Nov 70;sup 10
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen J, Emery P, Rigby W, Tanaka Y, Vargas J, Damjanov N, Jain M, Sui Y, Enejosa J, Pangan A, Camp H, Cohen S. Upadacitinib as Monotherapy in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results at 48 Weeks [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upadacitinib-as-monotherapy-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-at-48-weeks/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upadacitinib-as-monotherapy-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-at-48-weeks/