Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment recommendations directed to rheumatoid arthritis patients (RA) may be more easily adopted if they are patient-centered. The adoption of health behaviors is associated with the recognition of risks. Risk perception (RP) is a multidimensional phenomenon that describes the individual’s judgment of the likelihood of experiencing something unpleasant (1). Assessing perceived risk helps to explain how RA patients integrate their ideas concerning the disease and its treatments, and how this understanding impacts their self-care management. There is no validated instrument to assess RP in RA patients. The objective of the study was to develop and validate the RP Questionnaire (RPQ) for Spanish speaking patients with RA.
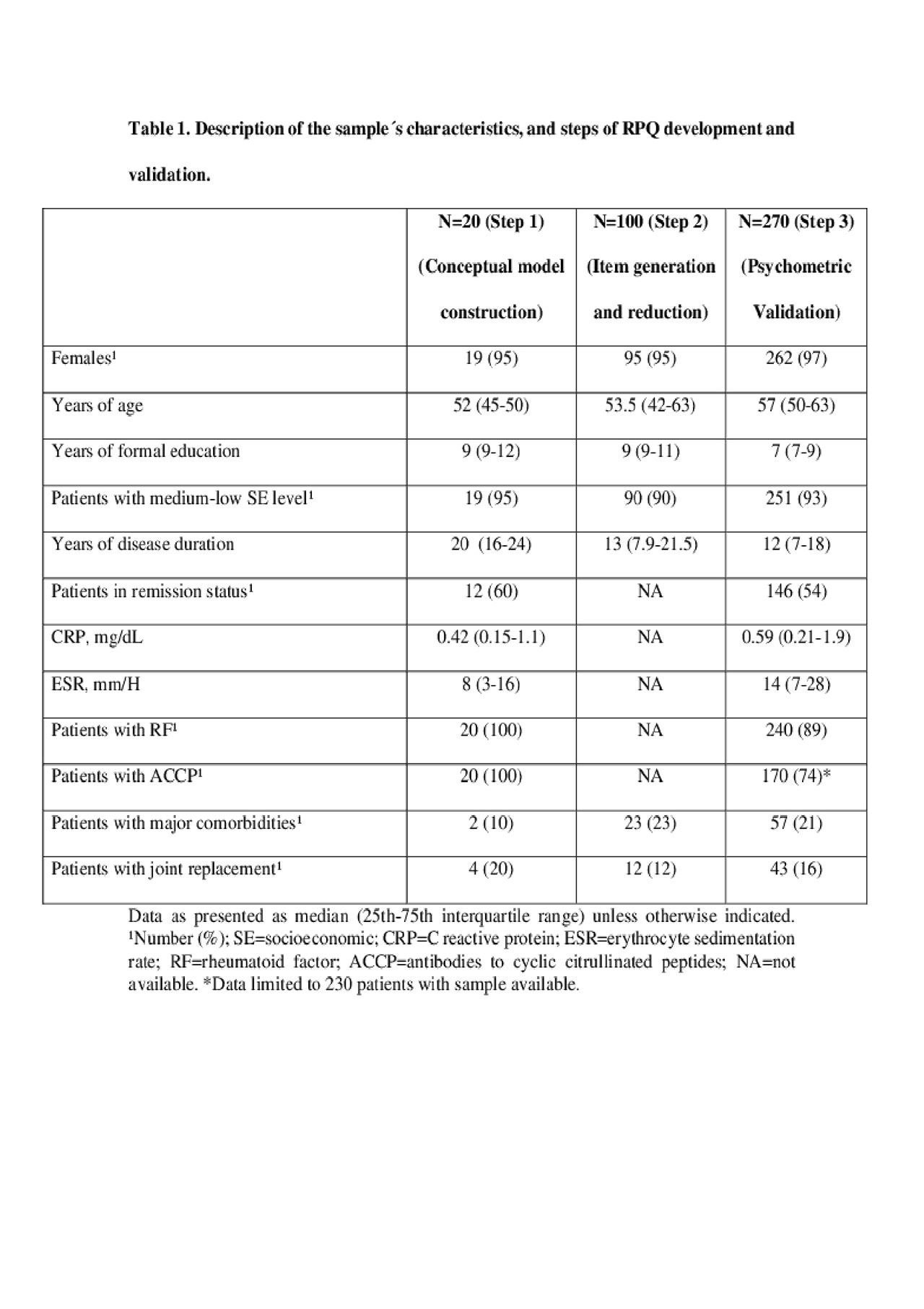
Methods: RPQ development and validation was performed in 3 steps, using convenience samples (Table 1). Step-1 included the conceptual model construction (literature review), 20 patient’s interviews to identify components from the conceptual model-dimensions and 11 healthcare provider´s consultations who identified RA-related manifestations/complications (network and frequencies analysis). Step-2 consisted of item generation and reduction and questionnaire feasibility (n=100); for scaling response we selected a direct estimation method of responses, on a visual analogue scale and for item scoring we proposed the method of standard scores to be able to compare our results with those eventually described in other populations. Step-3 consisted of RPQ psychometric validation (n=270), which included content, face, construct (exploratory factor analysis) and criterion validity (logistic regression analysis) and consistency and stability (Cronbach’s α and test-retest). The study received IRB approval and patients included signed informed consent form.
Results: Patients included in the 3 samples were representative of typical RA outpatients attending a tertiary care level center (Table 1).
Step 1. The initial conceptual model included 7 dimensions, 3 for probability and 1 each, for responsibility, prevention, control and for severity.
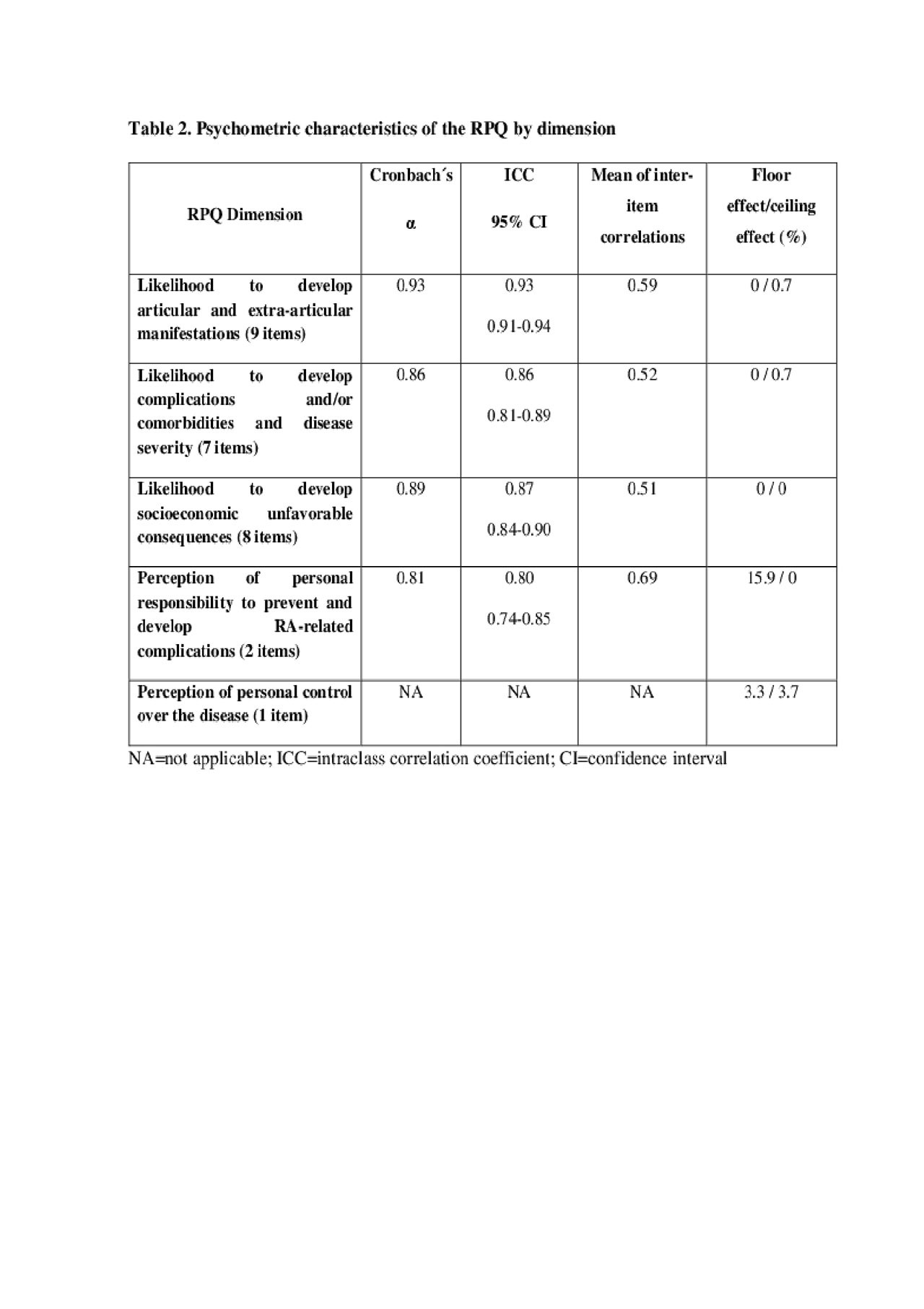
Step 2. The final version of the RPQ included 27 items distributed in 5 dimensions (table 2), and was feasible: mean of time required to fill it was of 13 minutes and all patients agreed the time was convenient; 89% of the patients agreed about instructions and item´s semantic clarity and 97% of them agreed about adequacy of the RPQ format. (Mean±SD) RPQ score for the sample was 50±6.69.
Step 3. A five-factor model was most appropriated and resulted in 68.8% of the variance explained; Cronbach’s α=0.90, intraclass-correlation-coefficient=0.93 (95% CI=0.90-0.95). Psychometric properties by dimension are summarized in table 2. A positive relation between number of external criteria recorded from the charts and RP was found as summarized in table 3.
Conclusion: The RPQ was valid and reliable to evaluate RP in RA outpatients; it can be incorporated to routine care and clinical research, and guide interventions to improve patient’s health behaviors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Contreras-Yáñez I, Lavielle P, Clark P, Pascual-Ramos V. Validation of a Risk Perception Questionnaire Developed for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-a-risk-perception-questionnaire-developed-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-a-risk-perception-questionnaire-developed-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/