Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Predicting remission in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an important goal for tailoring therapy. Tocilizumab (TCZ) has been found in randomized controlled trials (RCT) to have similar efficacy when used as monotherapy or in combination with csDMARDS. We recently derived a remission prediction score for TCZ monotherapy (TCZm) using data from four RCTs to predict remission (CDAI < 2.8) at 24 weeks follow-up (Collins, ARD, 2019). Herein, we describe external validation for the prediction score using “real world data” (RWD) from Corrona.
Methods: We identified patients in the RWD who used TCZm for a minimum of 3 months with at least 1 follow-up visit no later than 9 months after TCZm initiation. Patients starting TCZ in combination with other DMARDs were included if TCZm initiation was within 3 months of first TCZ. We followed patients to determine whether they were in remission (CDAI < 2.8) at the next visit closest to 24 weeks (follow-up) after TCZm initiation. The cohort and remission criteria were chosen to mimic the characteristics of the population in the TCZm RCTs. We compared the performance of prediction models derived in our prior work to an additional baseline model, both in the RCTs and RWD. Each of the 3 models is a logistic regression based on a different selection of variables measured before TCZ initiation (baseline): Model A (variables selected based on odds ratio), Model B (selection based on AIC/BIC) and Model C (baseline CDAI only). We studied both a) application of model parameters learned in the RCTs to RWD, and b) cross-validation of models fit to the RWD. We examined the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) as a measure of discrimination and the calibration slope, comparing predicted remission probability with observed remission.
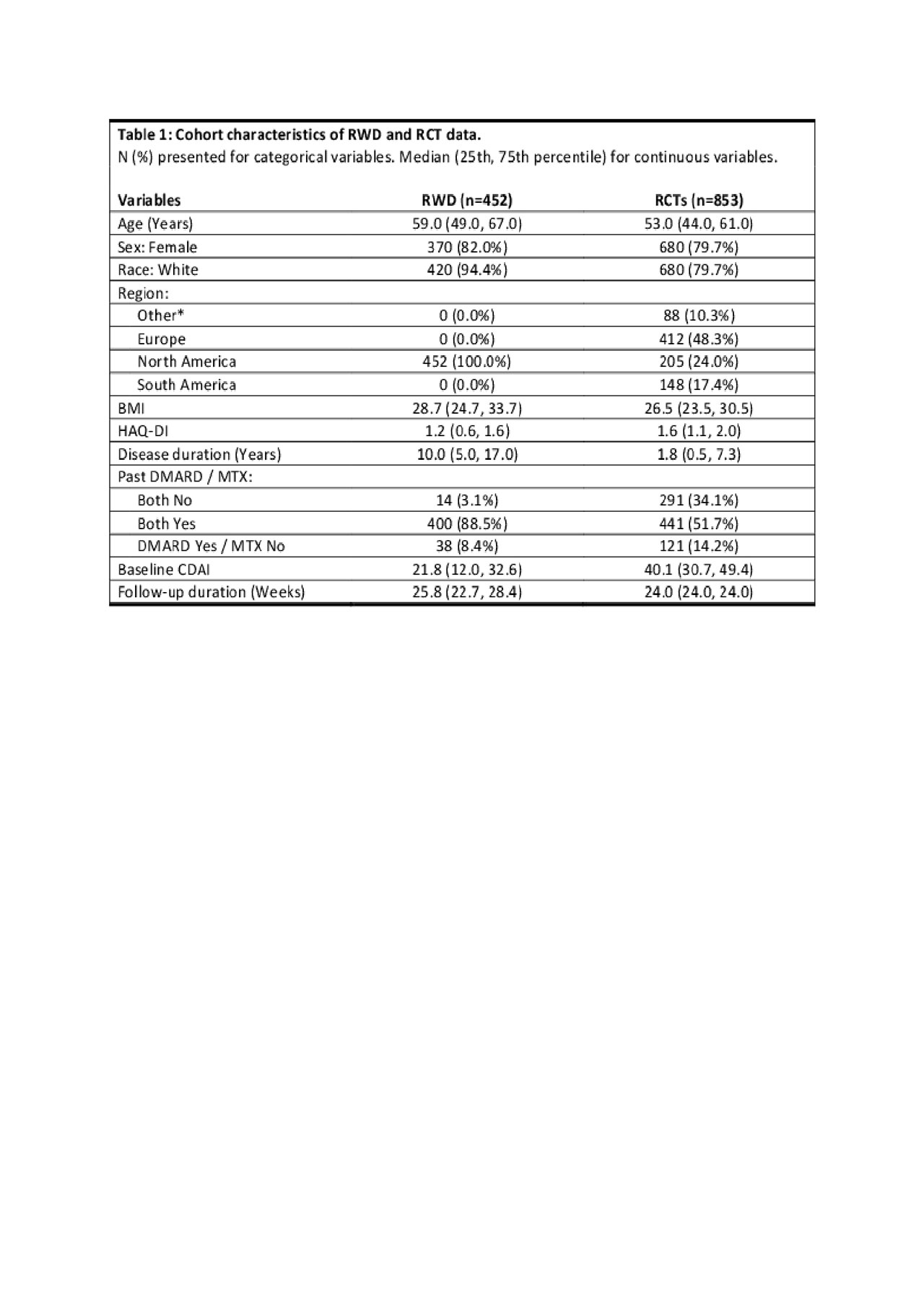
Results: We identified 453 patients from the RWD (out of 54646) who met the inclusion criteria. The 4 RCTs comprise a total of 853 patients with demographics generally similar to the RWD cohort (see Table 1). The number of patients reaching remission on TCZm by their follow-up visit was 12% (n=53) in RWD vs 15% (n=127) in RCTs. The baseline disease activity and history differed considerably: median CDAI 22 in RWD vs 40 in RCTs, and median RA duration 10 years in RWD vs. 2 years in RCTs. We found that discrimination was as good in RWD given baseline covariates as in the RCTs (see Table 2). The AUROC for Model A trained in RCTs and evaluated in RWD was 0.70 vs. 0.71 in the RCTs, and for Model B 0.69 and 0.65, respectively. The CDAI-only (Model C) achieved AUROC of 0.75 in RWD and 0.59 in RCTs.
Conclusion: We found that the remission prediction scores derived in RCTs, based on demographics, baseline disease activity and treatment history, discriminated patients in RWD about as well as in RCTs, despite notable cohort differences in treatment history and disease duration. We found that baseline CDAI alone was highly discriminative in the RWD cohort, but not in the RCTs. We believe that this is because the rapid changes in disease activity in early, untreated RA, characteristic of the RCT cohort, is more unpredictable from previous CDAI only than the slow progression of established RA, as in the RWD cohort. Therefore, we consider models A and B more robust to future changes in treatment practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Johansson F, Collins J, Gale S, Guan H, Kim S, Losina E, Sontag D, Stratton J, Trinh H, Greenberg J, Solomon D. Predicting Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis: External Validation for Tocilizumab Monotherapy Using Corrona Real World Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-remission-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-external-validation-for-tocilizumab-monotherapy-using-corrona-real-world-data/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-remission-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-external-validation-for-tocilizumab-monotherapy-using-corrona-real-world-data/