Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
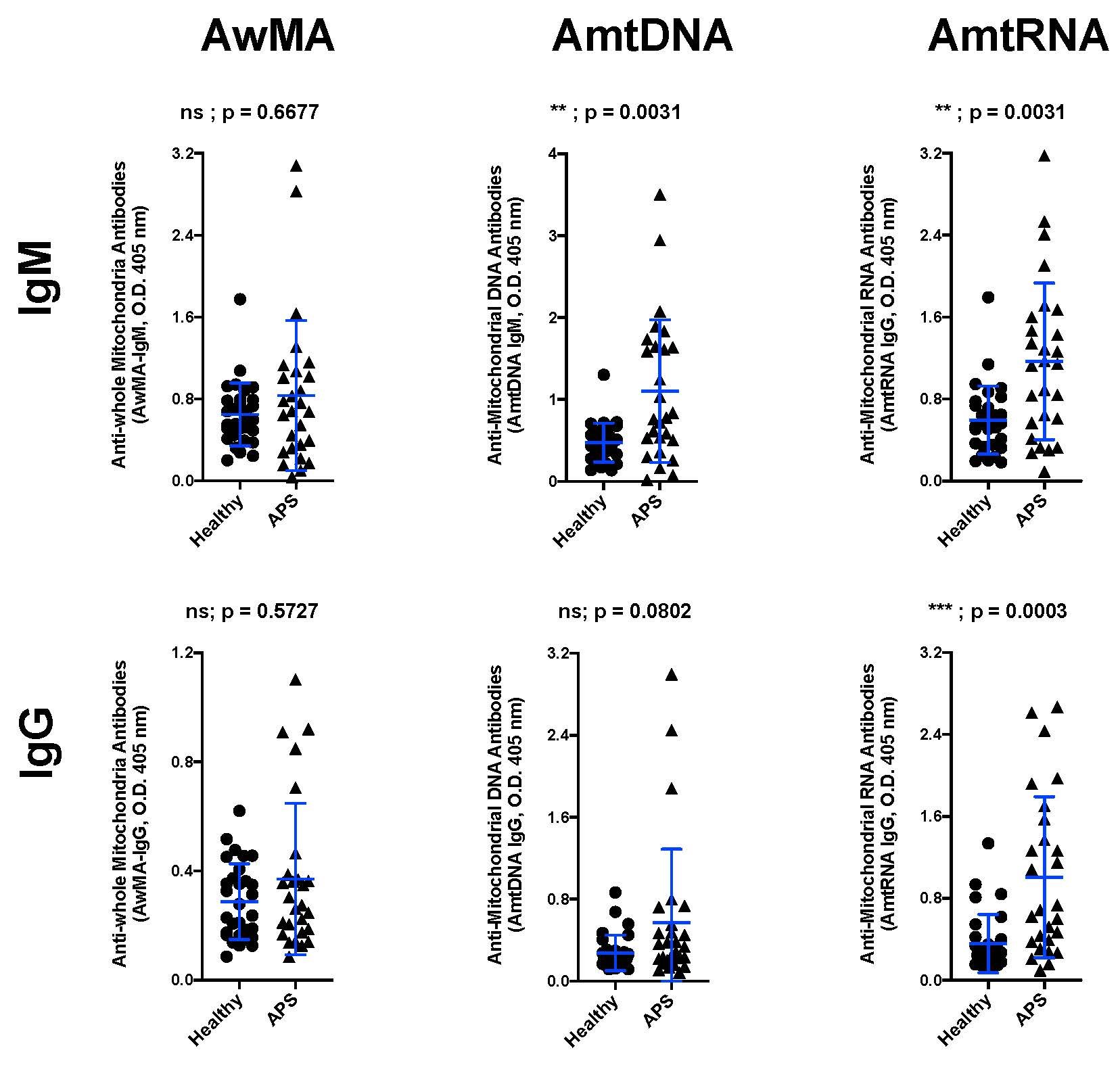
Background/Purpose: Mitochondria are intracellular organelles involved in many biological pathways such as energy supply by oxidative phosphorylation and apoptosis. Mitochondria are considered as derived from the endosymbiosis between an α-proteobacterion and a primitive eukaryotic cell. Mitochondria display molecular features derived from their bacterial origin such as N-formylated peptides or a circular double-stranded DNA with hypomethylated CpG motives. When released onto the extracellular milieu upon tissue damage or cell activation, mitochondria may elicit proinflammatory responses through their recognition by the innate immune system. Little is known about interplays between mitochondria and the adaptive immune system, despite descriptions of humoral responses to mitochondria in some diseases. Our laboratory already reported that anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA) targeting whole organelles (AwMA), mitochondrial DNA (AmtDNA) or RNA (AmtRNA) are expressed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease often associated with APS. In this study, we detected AMA in patients with APS and associated their titers with clinical features of APS.
Methods: AwMA, AmtDNA and AmtRNA – IgG and IgM were detected in healthy controls (n=30) and APS patients (n=27) by direct ELISA. All participants agreed to participate to our Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Biobank and Data Base. Demographic and disease characteristic variables were collected according to the standard APS ACTION protocol. Vascular events were defined as arterial, venous or microangiopathic and «any vascular event» was defined as the combination of all types of vascular events Morbidities during pregnancy were defined as spontaneous abortions before the 10th week of pregnancy, miscarriages after the 10th week or premature birth due to eclampsia or preeclampsia before the 34th week and «any pregnancy morbidity» was defined as any combination of one or more items. Kruskall-Wallis and Wilcoxon tests were used to compare groups. Vascular events and morbidities during pregnancy were predicted with logistic regressions.
Results: AmtDNA-IgM and both AmtRNA IgG and IgM were significantly elevated in APS patients compared to controls. AMA failed to discriminate primary APS (n=7) from secondary APS (n=20). AwMA-IgG were associated with positivity to lupus anticoagulant (p=0.01). While the AMA were not associated with morbidities during pregnancy, AwMA-IgM, AmtDNA-IgG and IgM and AmtRNA-IgM were all associated with reduced history of any thrombotic events (respectively p=0.0447, p=0.0414, p=0.0363 and p=0.0481). AmtDNA-IgM was also associated with reduced arterial vascular events (p=0.0463).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that AMA are represented within the autoantibody repertoire in APS and that various mitochondrial antigens display different clinical associations in the disease.
« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antibodies-targeting-mitochondrial-antigens-are-associated-with-reduced-thrombotic-events-in-aps/