Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Dendritic cells (DC) are specialized antigen-presenting cells (APC) that have a central role in the initiation of immune responses. However, prior studies showed numeric decreases of myeloid (mDC) and plasmacytoid (pDC) DC in RA. This apparent contradiction led us to hypothesize that depletion of these ‘canonical’ DC is only one manifestation of a more fundamental alteration in this important immunoregulatory compartment in RA and that the overall non-lymphoid APC population (CD3–CD19–HLA-DR+) does not decrease due to the appearance of anomalous APC phenotypes. We further hypothesized that alterations in DC subsets are associated with clinical aspects of RA including those driving RA-associated cardiovascular disease.
Methods: RA patients enrolled in a cohort study and healthy donors underwent immunophenotyping to define known DC subsets, including CD1c+ mDC, CD141+ mDC and CD303+ pDC in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs). We correlated DC subset features with disease characteristics and cardiac function. To screen for non-lymphoid cells with putative APC potential not conforming to conventional DC paradigms we defined ‘candidate nonlymphoid APC’ (DR+CD3–CD19–CD56–) as a DC superset. We used t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) to categorize the entirety of non-lymphoid APC candidate cells and identify possible novel RA APC subsets.
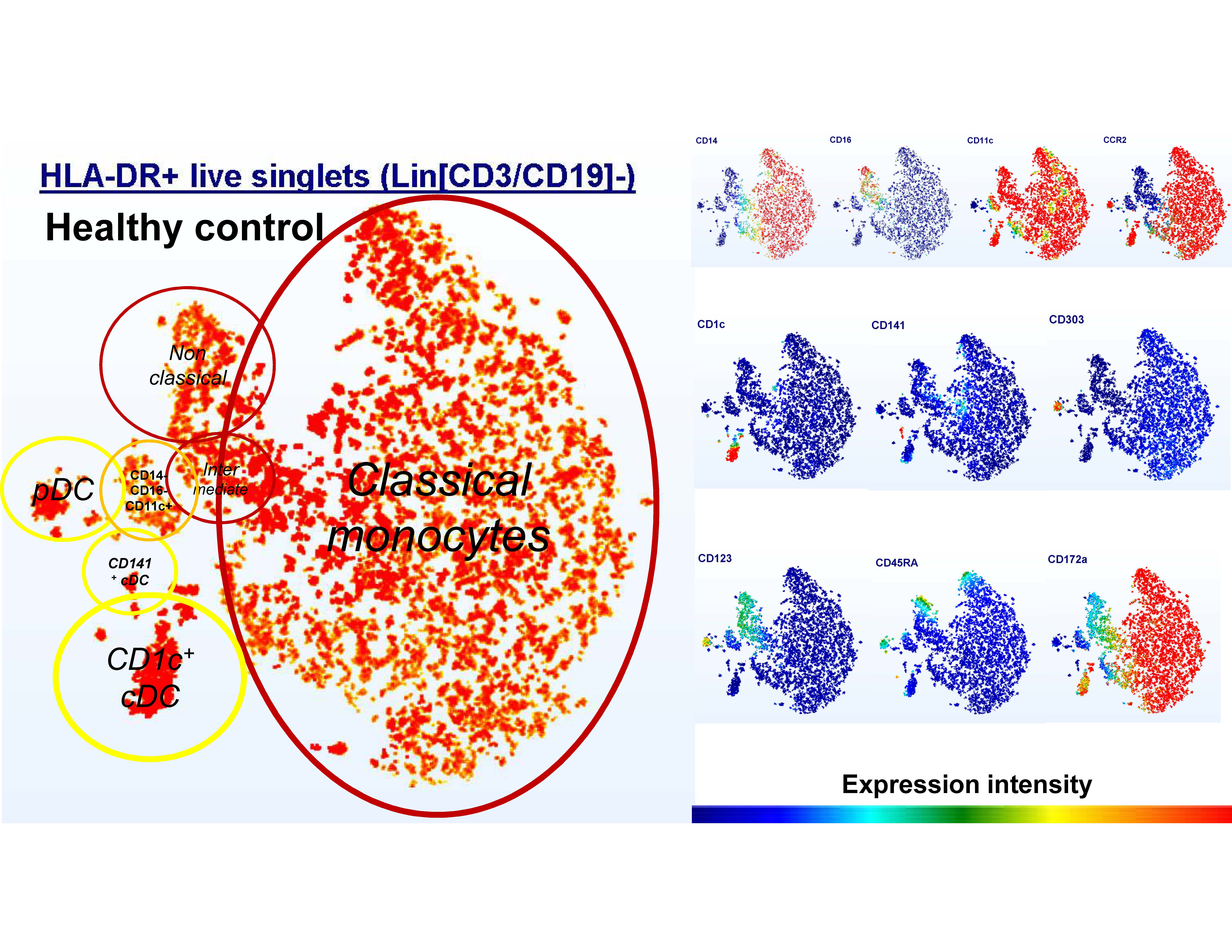
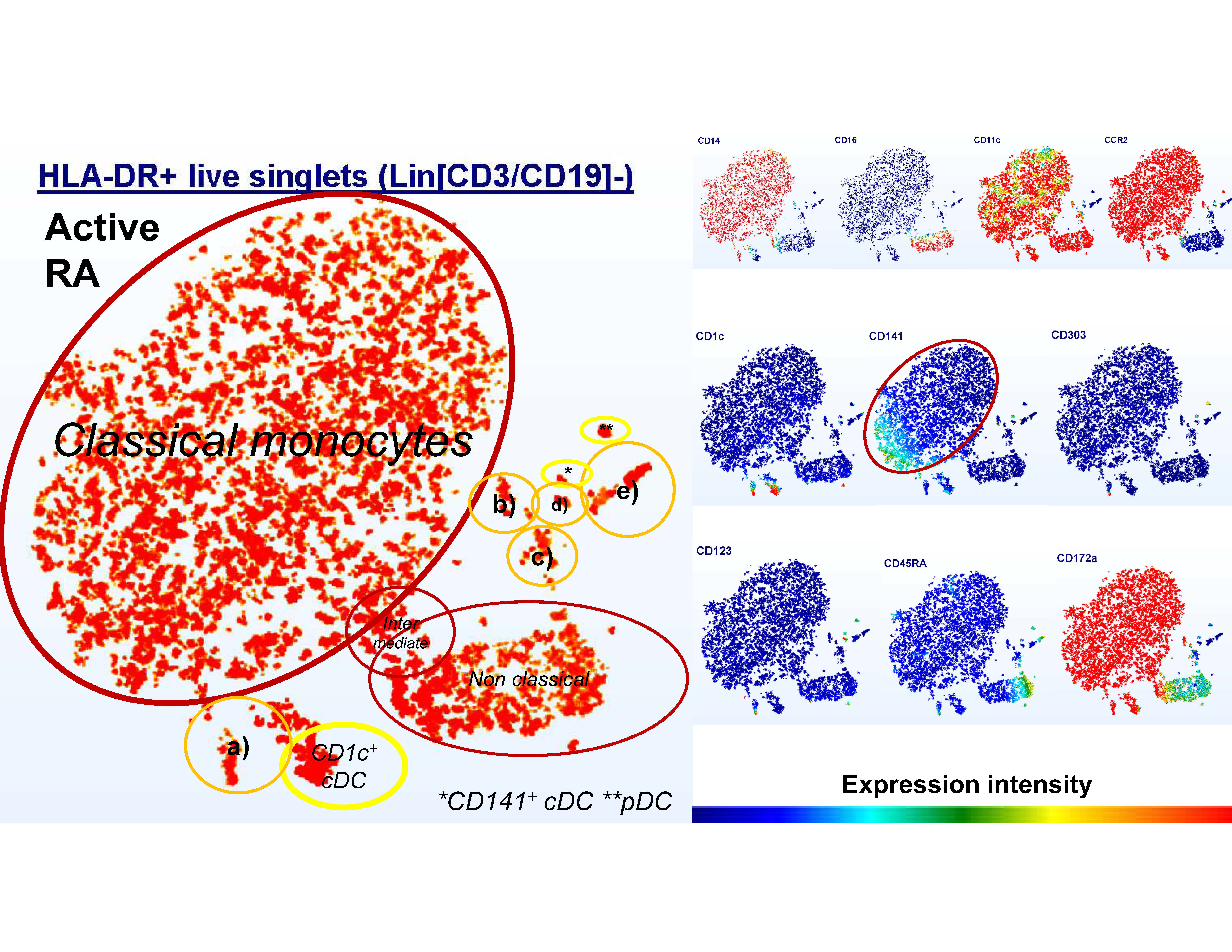
Results: Circulating CD1c+ frequencies were, as expected, remarkably decreased in RA (mean 1.0% of PBMCs vs controls 2.6%; p=0.009). Mean CD141+ frequencies were 0.1% (RA) vs 0.2%; p=0.019. CD303+ pDC frequencies did not differ (p=0.285). HLA-DR intensity in both myeloid subsets was significantly lower in RA whereas CCR2 intensity was higher in CD1c+ DC. In RA, a lower CD1c+ frequency was associated with lower cardiac index (corr.=-0.54, p=0.008) and CCR2 expression of CD1c+ DC was associated with lower Ejection Fraction (EF) (corr.=-0.70, p=0.001). Interestingly, despite the decrease in canonical DC; the overall frequencies of ‘candidate non-lymphoid APC’ did not differ (Table 1) suggesting that the declines of canonical DC were compensated for by increases in other populations of this DR+ DC superset. t-SNE analysis of healthy controls allowed clear categorization with distinct clusters of APC subsets as well as a homogenous cluster of CD14–CD16–CD11c+(Figure 2; orange circle). RA t-SNE showed a decrease of canonical DC subsets (yellow ellipses) and the appearance of five clusters with some DC features that did not fit accepted definitions (Figure 2a-e)
Conclusion: We found extensive alterations in the DC compartment in RA, including a significant decrease in the major CD1c+ subset and the emergence of anomalous HLA-DR+ non-lymphoid cells with antigen-presenting potential that are candidate DC subsets. The novel subsets included one resembling CD14+ monocyte-derived DC, a subset of which also expressed CD1c in addition to plasmacytoid markers; CD303 and CD123. The remaining populations were distinguished by combinations of CCR2, CD11c, CD123 and CD172a (SIRPα). The association of adverse measures of cardiac function with changes of the DC compartment, including decreases of CD1c+ mDC, emphasize their potential clinical significance.

Table 1 – Enumeration and expression of DR and CCR2 Expression in DC subsets in RA
Red circles: monocyte populations. Yellow: DC populations. A small homogenous population of CD14-CD16-CD11c+ cells without DC characteristics is shown in orange.
Classical monocytes: CD14+CD16+
Intermediate monocytes: CD14+CD16+
Nonclassical monocytes: CD14-CD16+
CD1c+ cDC: CD11c+CD1c+
CD141+ cDC: CD11c+ CD141+
pDC: 11c-CD303+
Red circles: monocyte populations. Yellow: DC populations. Orange: DR+ cells which do not conform to standard DC paradigms but express partial DC markers.
a- CD14+ CD1c+ CD141+ CD172a+ CD123+- b- CD14-CD16- 11c+ c- CD14-CD16- CD172a+ d- CD123+ e- CD14- CD16- CD45RA+-
Classical monocytes: CD14+CD16+
Intermediate monocytes: CD14+CD16+
Nonclassical monocytes: CD14-CD16+
CD1c+ cDC: CD11c+CD1c+
CD141+ cDC: CD11c+ CD141+
pDC: 11c-CD303+
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Geier C, Giles J, Gibor G, Bathon J, Winchester R. In Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Decreases in Conventional Dendritic Cell Lineages Are Associated with Adverse Measures of Myocardial Function and Expansions of Anomalous HLA-DR+ Myeloid Subsets [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-decreases-in-conventional-dendritic-cell-lineages-are-associated-with-adverse-measures-of-myocardial-function-and-expansions-of-anomalous-hla-dr-myeloid-subsets/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-decreases-in-conventional-dendritic-cell-lineages-are-associated-with-adverse-measures-of-myocardial-function-and-expansions-of-anomalous-hla-dr-myeloid-subsets/