Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: XmAb5871 is a humanized anti-CD19 antibody Fc-engineered for increased affinity to FcgRIIb. Co-ligation of CD19 and FcgRIIb inhibits B lineage cells key to SLE pathogenesis. This Phase 2 study was designed to minimize background medications and placebo responses to improve interpretation of a small trial in a complex, heterogenous disease.
Methods: SLE patients were enrolled with moderate to severe, non-organ threatening disease, which was ameliorated during screening with >/= 160 mg of IM Depo-Medrol. Improvement was required before randomization, defined by SLEDAI decrease ≥4 points or ≥1 grade decrease in ≥1 BILAG A or B score. All immunosuppressive drugs were withdrawn except antimalarials or up to 10 mg/day prednisone or equivalent. Subjects were randomized to IV XmAb5871 (5 mg/kg) or placebo and given Depo-Medrol 80 mg IM on Days 1 and 15. Study treatments were every 14 days for up to 16 doses until Day 225 or loss of improvement (LOI), defined as SLEDAI increase of ≥4 points OR new BILAG A or B, with investigator agreement of significance. At LOI, patients could receive standard of care and withdraw. The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects with no LOI by Day 225 in the efficacy evaluable group, defined as those who completed Day 225, had LOI, or discontinued due to a drug-related adverse event. Those who dropped out for other reasons were excluded from this analysis.
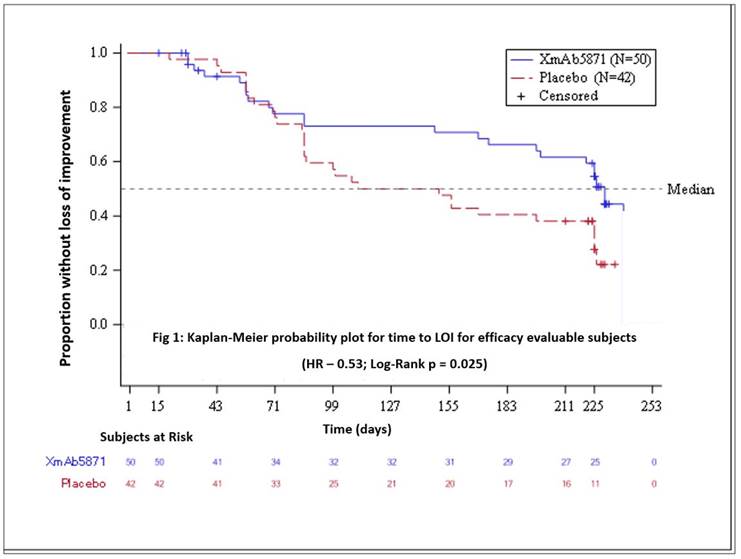
Results: 104 patients (99 female) were randomized. Median age was 44.5 years (20-65). XmAb5871-treated subjects stayed in the study longer receiving more infusions than the placebo group – 6.9 months vs 3.6 months and 15 vs 8.5, respectively. Six XmAb-treated patients were withdrawn for infusion-related events. 10 patients terminated from the placebo arm vs 2 from the XmAb5871-treated arm with exclusion from the efficacy evaluable population. These exclusions led to higher placebo response rates compared to the ITT population.
|
Table 1: Primary and Secondary Endpoints: Maintenance of Improvement |
||||||
|
|
Efficacy Evaluable Population |
Intent to Treat Population |
||||
|
|
XmAb5871 |
Placebo |
p value |
XmAb5871 |
Placebo |
p value |
|
% Response at Day 225 |
42 |
28.6 |
0.181 |
40.4 |
23.1 |
0.06 |
|
% Response at Day 169 |
58 |
40.5 |
0.11 |
57.7 |
34.6 |
0.02 |
|
1Primary Endpoint |
||||||
The most common AEs in XmAb5871-treated patients were transient, infusion-related gastrointestinal side effects during the 1st or 2nd infusion. There were 8 SAEs in 7 XmAb-treated subjects, 5 in 4 placebo patients, no opportunistic infections, and no deaths. Major organ flares: Placebo: 2 nephritis, 1 enteritis, 1 systemic flare; XmAb5871: 1 pneumonitis. All were treated and stabilized. Infection rate was low compared to other SLE trials; one pneumonia occurred in an XmAb5871-treated patient.
Conclusion: XmAb5871 was well-tolerated, infection rate was low, flares were similar to other lupus trials. Preliminary data from this small trial supports further evaluation of XmAb5871 in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Merrill JT, June J, Koumpouras F, Machua W, Khan MF, Askanase A, Khosroshahi A, Sheikh S, Foster PA, Zack DJ. Top-Line Results of a Phase 2, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Reversible B Cell Inhibitor, XmAb®5871, in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/top-line-results-of-a-phase-2-double-blind-randomized-placebo-controlled-study-of-a-reversible-b-cell-inhibitor-xmab5871-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/top-line-results-of-a-phase-2-double-blind-randomized-placebo-controlled-study-of-a-reversible-b-cell-inhibitor-xmab5871-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/