Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc) carries a high morbidity and mortality, predominantly due to internal organ involvement. The purpose of this study was to investigate the time to event of new onset of visceral organ involvement and all-cause mortality in early dcSSc participants in an ongoing US multicenter registry (Prospective Registry of Early Systemic Sclerosis [PRESS]).
Methods: Inclusion criteria include a diagnosis of dcSSc and a disease duration of ≤ 2 years calculated from the date of onset of first non-Raynaud’s phenomenon symptom. Organ involvement was defined as new involvement or worsening during follow up visits— 1) absolute increase in mRSS of ≥ 4 units or 20%, 2) an absolute decline of FVC % of ≥ 10%; 3) PH on RHC; 4) LVEF of ≤ 45% on echo; 4) scleroderma renal crisis; or 5) all-cause mortality. We reported number of participants experiencing organ involvement during the course of the study via frequency tables and characterized the distribution of events through plots of the cumulative proportion of participants experiencing each event by time. Confidence intervals in the cumulative proportion plots were derived via bootstrap method.
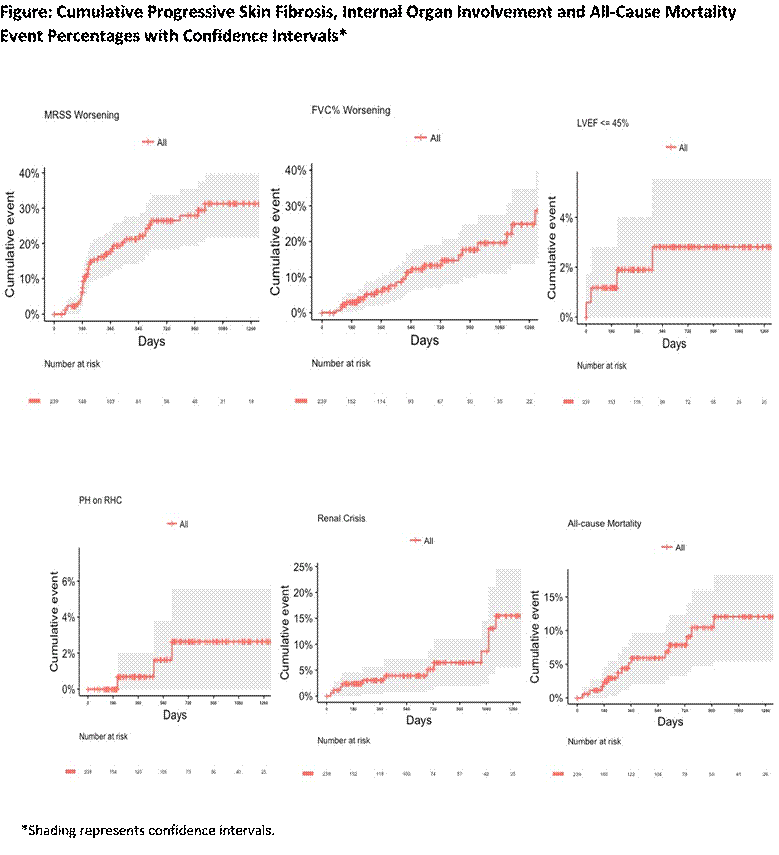
Results: The cohort consisted of 239 participants from 11 US SSc centers at baseline with median follow-up of 414 days (IQR=112-922 days). The baseline mean age for the cohort was 50.1 years, disease duration was 1.3 years, HAQ-DI score was 0.82, 71.1% were female, and 76.2% were white. In this cohort, 199 (83.3%) were treated with immunomodulatory therapies during the course of the study (82.0% during the first year) including 63.2% on mycophenolate mofetil, 20.9% on methotrexate, 5.0% on cyclophosphamide, 3.3% on D-penicillamine, 16.3% on hydroxychloroquine, and 2.1% on azathioprine (percentage is greater than 82.0% as some participants were on multiple therapies at a single time-point and/or during the study). Survival function plots showed that 75 of 231 (32.5%) participants showed progressive skin fibrosis, 27 of 192 (14.1%) showed ≥ 10% worsening of FVC%, 4 of 199 (2.0%) showed LVEF of ≤ 45%, 12 of 239 (5.0%) had new onset scleroderma renal crisis, 5 of 239 (2.1 %) had PH on RHC, and 14 of 239 (5.9%) died during the course of the study (Figure); 11 of the 14 deaths were considered to be related to SSc.
Conclusion: Despite immunomodulatory therapy, a high proportion of early dcSSc patients experience worsening of mRSS and lung function and mortality within 2 years of dcSSc diagnosis. There are ongoing vascular-predominant complications over the course of the disease, consistent with published literature [1]. This data supports an ongoing need to identify novel therapies for dcSSc.
1. Nihtyanova SI. Arthritis & rheumatology. 2014.
ADDIN EN.REFLIST
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Homer K, Brennan B, Assassi S, Bernstein EJ, Castelino FV, Domsic RT, Gordon JK, Hant FN, Hinchcliff M, Shah AA, Shanmugam V, Steen VD, Berrocal VJ, Hemmrich M, Frech TM, Khanna D. Progressive Skin Fibrosis, Internal Organ Involvement and All-Cause Mortality in an Early Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis United States Multicenter Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/progressive-skin-fibrosis-internal-organ-involvement-and-all-cause-mortality-in-an-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis-united-states-multicenter-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/progressive-skin-fibrosis-internal-organ-involvement-and-all-cause-mortality-in-an-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis-united-states-multicenter-registry/