Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a debilitating chronic disease with an unmet need for additional therapeutic approaches. Bioelectronic therapy (BET), such as electrical neurostimulation of the vagus nerve to activate innate protective neuro-immune reflexes, represents a novel means of treating diseases characterized by systemic inflammation. We performed a proof-of-concept study in RA patients using a marketed vagus nerve stimulation device at very low duty cycles (1-4 min/day), showing reduction of clinical disease activity, concomitant with reductions in TNF-α and IL-6 (PNAS 2016;113:8284). We have developed a novel advanced generation neurostimulation device, the MicroRegulator System, which is being evaluated in a first-in-man clinical study.
Methods:
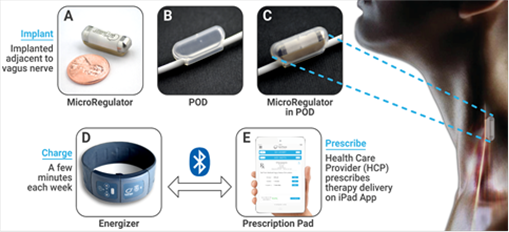
The MicroRegulator System is unique in that it is implanted directly on the vagus nerve as a single unit that contains an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), pulse generator with a wireless rechargeable battery, as well as a self-contained nerve-encapsulating cuff and electrodes that function without vagus nerve lead wires (Figure 1). Low power requirements allow for miniaturization of the device (< 2 cc). External components include an intermittently worn flexible collar that generates a radio frequency field for recharging and telemetry, as well as an iPad-based control device programming application.
Results:
The first-in-man study is a USA-based multi-centered double-blind trial, designed to look at safety and efficacy of the implanted MR system in refractory RA patients that have insufficient response to ≥ 2 biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs of ≥ 2 modes of action. This study is unique in its use of a neurosurgical sub-investigator paired with the rheumatologist to manage the first weeks of the study period. Implanted subjects, washed off biologics and on stable background of methotrexate, are randomized to 1 min of sham, QD, or QID stimulations for 12 weeks. Efficacy outcomes include standard RA clinical disease measures as well as quantitative MRI joint scoring, validated RA-specific biomarker panels, autonomic balance measurements and immune cell bioassays.
Conclusion:
A novel neurostimulation device has been developed and deployed in a first-in-man clinical study. BET, a non-pharmacological intervention, will potentially give rheumatologists a novel alternative means to treat RA, including those patients who have failed conventional treatments.
Figure 1. Schematic Representation of MicroRegulator System
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chernoff D, Levine Y, Peterfy C, Genovese MC. A First-in-Man Bioelectronic Therapy for Biologic-Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-first-in-man-bioelectronic-therapy-for-biologic-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-first-in-man-bioelectronic-therapy-for-biologic-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/