Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Palindromic rheumatism (PR) (transient acute attacks of articular and/or periarticular inflammation) may progress to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). How often early RA (ERA) patients report joint symptoms that come and go prior to diagnosis and how RA presentation may differ in this patient subset is uncharacterized. This study compared ERA patients who did versus did not report a history of transient episodes of joint inflammation preceding RA diagnosis.
Methods: Data were from patients with early classifiable or suspected RA according to their rheumatologist (symptoms <1 year; 83% met 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria) enrolled in the Canadian Early ArThritis CoHort (CATCH) in 2017 to 2018 who completed a new baseline questionnaire on prior inflammatory joint symptoms that “come and go”. Chi-square and t-tests were used to compare baseline sociodemographic and RA characteristics in ERA patients with versus without a reported history of prior palindromic symptoms. Simple, and multivariable logistic regression with backward selection (p<0.1) were used to identify age and sex-adjusted predictors of palindromic symptoms among baseline ERA characteristics.
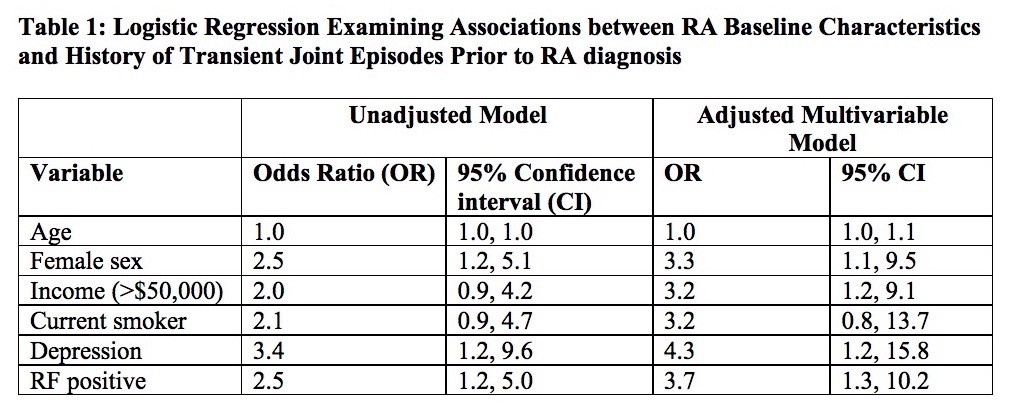
Results: 154 ERA patients were included; 66% were female and mean (sd) age was 54 (15) years. 83 (54%) patients reported having any previous joint pain and swelling prior to current episode; 65 (42%) endorsed prior episodic joint pain and swelling, of whom 31 (48%) reported transient joint symptoms for over six months. Patients reporting previous palindromic symptoms were more often female, RF positive, ACPA positive, had more comorbidities, and lower CRP, swollen joints, and baseline DAS28 (p<0.05). Univariate predictors of palindromic symptoms included female sex, RF positivity, higher income, comorbid OA, back/spine problems, and depression, higher rheumatic disease comorbidity index, and lower swollen joint count, CRP, DAS28, and physician global assessment of disease activity (p<0.1). In multivariable regression, RF positivity, depression, and higher income remained significant predictors of prior palindromic symptoms (p<0.05). Smoking was potentially associated with an average 3-fold increase in prior palindromic symptoms, though the relationship was not statistically significant in adjusted models (Table 1).
Conclusion: ERA patients commonly self-reported experiencing transient episodes of inflammatory arthritis prior to being diagnosed with RA; however, whether these symptoms were actual PR cannot be confirmed. ERA patients who endorsed having joint symptoms that come and go prior to RA diagnosis were more likely RF positive with higher income and more comorbidities at ERA cohort entry, but median time to RA onset was not different.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ellingwood L, Schieir O, Bartlett SJ, Bessette L, Hitchon CA, Boire G, Hazlewood G, Keystone EC, Tin D, Thorne C, Bykerk VP, Pope JE. Characterizing Palindromic Symptoms in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-palindromic-symptoms-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-palindromic-symptoms-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort-study/