Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: To estimate the incidence and age and sex patterns of subjects having had osteoarthritis (OA)-related surgical treatment.
Methods: The Skåne Health Care Register (SHCR) is a legislative, mandatory register based on physicians’ International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 10 diagnostic codes and the classification of health care procedures and surgical codes according to KKÅ97. The register covers all in- and outpatient health care in southern Sweden (total population 1.3 million). For the year 2011 we identified patients ≥35 years of age having had the hip replacement and a main diagnosis of hip OA (M16) or having the knee replacement or other knee surgery (arthroscopic or endoscopic exploration of the joint, synovectomy, excision of meniscus or articular cartilage or other surgery of synovial membrane of the knee) in conjunction with the main diagnosis of knee OA (M17) or derangement of meniscus due to old tear or injury (M23.2), which we consider probable OA. We obtained annual cumulative incidence of OA-related surgery in 2011 by cross referencing with the population register to include all residents (aged ≥35) of Skåne by the 31st Dec 2010. To obtain estimates of the annual cumulative incidence of OA-related knee or hip surgery among all known knee or hip OA patients we used the point prevalence of knee and hip OA by the 31st Dec 2011 based on the SHCR register data from years 1999-2011.
Results: The annual incidence of OA-related knee replacement in the population aged ≥35 was 18.6 per 10,000 persons (95%CI: 17.6; 19.6), 16.1 for men and 21.0 for women. The annual incidence of other OA-related knee surgery in the population was 11.8 per 10,000 persons (95%CI: 11.0; 12.6), 14.6 for men and 9.2 for women. The 2011 incidence of OA-related hip replacement in the population was 19.3 per 10,000 persons (95%CI 18.3; 20.3), 11.7 for men and 16.1 for women. The annual incidence of OA-related knee and hip replacement in the population ≥65 years of age was 35 and 37 per 10,000 persons respectively.
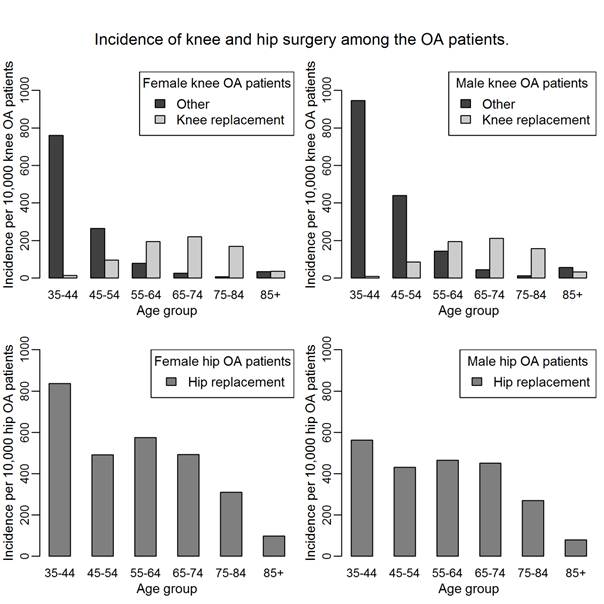
The incidence of OA-related knee replacement surgery among known prevalent knee OA patients aged ≥35 was 156 per 10,000 cases and peaked at age 65-74 years. The incidence of OA-related hip replacement among known prevalent hip OA patients was 359 per 10,000 cases and peaked at age 35-44 years. (Figure)
Conclusion: The present high incidence of OA-related surgeries in those aged ≥65 together with the estimated increased prevalence of hip and knee OA in next decades warrants great concerns for the future burden on the health care system. Efficient conservative treatment options should be sought.
Figure. The annual incidence of osteoarthritis-related knee and hip joint surgery among the OA-cases.
Disclosure:
A. Turkiewicz,
None;
I. F. Petersson,
None;
L. E. Dahlberg,
None;
M. Englund,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-osteoarthritis-related-knee-and-hip-joint-surgery-in-southern-sweden/