Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The identification of peripheral blood markers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) may facilitate an earlier diagnosis and provide insight regarding the pathogenesis of this severe disease complication. Antibodies directed against citrullinated fibrinogen (AhFibA) and the α36-50Cit and β60-74Cit peptides exhibiting its immunodominant epitopes are associated with radiographic damages in RA but have not been yet studied in RA-ILD. The aim of this study was to characterize the profile of anti-α36-50Cit and anti-β60-74Cit subfamilies of AhFibA in RA-ILD.
Methods: Anti-CCP2, AhFibA and their anti-α36-50Cit and anti-β60-74Cit subfamilies were assayed by ELISA in a population of RA-ILD (n=75), RA-noILD (n=75) patients and in a control group of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patients (n=75). RA was diagnosed according to ACR 1987 and/or ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria. ILD status was assessed with High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) in all the patients.
Results: Using a 98.5% specificity level, anti-CCP2, AhFibA and their anti-α36-50Cit and anti-β60-74Cit subfamilies were detected in 66%, 65%, 36% and 62% of RA patients, respectively whereas they were not detected in the majority of IPF patients (1%) (Table 1). No significant difference was observed for the sensibility of the different antibodies for the identification of ILD among RA patients. Anti-CCP2, AhFibA and anti-β60-74Cit titers were significantly lower in RA-ILD patients compared to RA-noILD patients (Table 1) whereas there was a trend for higher anti-α36-50Cit autoantibodies (P=0.145; ns). Within AhFibA positive RA patients, anti-α36-50Cit were more frequently observed in those having ILD (66% vs 33, P=0.013). In addition, anti-α36-50Cit antibody titers correlated with those of AhFibA only in RA-ILD patients (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Specific qualitative and quantitative profiles of anti-α36-50Cit and anti-β60-74Cit autoantibodies subfamilies of AhFibA are associated with the occurrence of ILD in the context of RA.
|
|
RA-ILD (n=75) |
RA-noILD (n=75) |
IPF (n=75) |
P value |
|
Positivity (n,%) – AhFibA – anti-β60-74Cit – anti-α36-50Cit |
. 46 (61.3) 43 (57.3) 31 (41.3) |
. 53 (70.6) 51 (68.0) 23 (30.7) |
. 1 (1.3) 1 (1.3) 2 (2.6) 1 (1.3) |
. ns ns ns ns |
|
Titers, – anti CCP2 (U/mL) – AhFibA (DO) – anti-β60-74Cit (ΔDO) – anti-α36-50Cit-fib (ΔDO) |
. 327 (5-30669) 0.34 (0.00-2.02) 0.18 (0.00-3.45) 0.02 (0.00-3.3) |
. 378 (5-36582) 0.60 (0.00-2.66) 0.51 (0.00-4.64) 0.01 (0.00-3.14) |
. 5 (5-539) 0.00 (0.00-0.53) 0.00 (0.00-0.11) 0.00 (0.00-0.09) |
. 0.028 0.025 0.047 ns |
|
Positivity among AhFibA+ (n, %) – anti-β60-74Cit – anti-α36-50Cit |
n=43 32 (74.4) 26 (60.4) |
n=54 46 (85.2) 18 (33.3) |
n=1 0 0 |
. 0.21 0.013 |
Table 1. Distribution of different autoantibodies in the 3 groups (RA-ILD, RA-noILD, IFP). Positivity rate is expressed in number of patients (%), Titers are expressed as median (min-max).
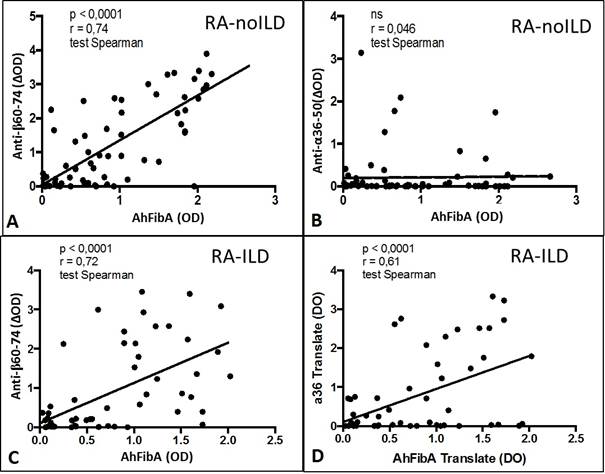 Figure 1. Correlation between AhFibA titers with anti-β60-74Cit or anti-α36-50Citautoantibody titers in RA-noILD population (A and B) and in RA-ILD population (C and D).
Figure 1. Correlation between AhFibA titers with anti-β60-74Cit or anti-α36-50Citautoantibody titers in RA-noILD population (A and B) and in RA-ILD population (C and D).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Juge PA, Nogueira L, Serre G, Flipo RM, Wemeau-Stervinou L, Schaeverbeke T, Dromer C, Adam-Marchand S, Boissier MC, Nunes H, Borie R, Crestani B, Dieude P. Specific Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Profiles Are Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Related Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/specific-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies-profiles-are-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/specific-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies-profiles-are-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-interstitial-lung-disease/
