Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Vasculitis Poster II: Behҫet’s Disease and IgG4-Related Disease
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Neurological involvement (NBD) is a rare complication of BD. Although NBD is not common in the course of BD, it is related with significant mortality and morbidity. We aimed to evaluate disease course and outcome of NBD patients registered in Hacettepe University Vasculitis Center (HUVAC) prospective database starting from October 2014.
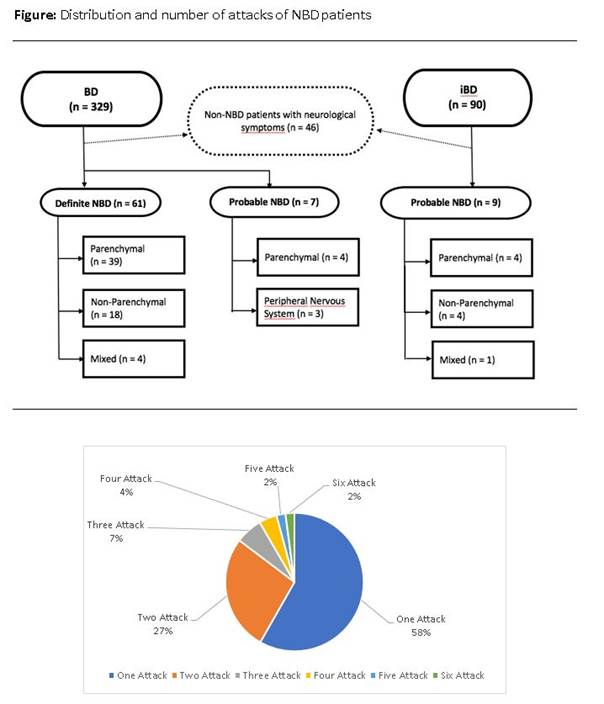
Methods: Totally, 456 patients were recorded as BD and 329 of them had fulfilled International Study Group (ISG) criteria. Ninety patients who did not meet criteria were considered to have incomplete BD after a review of an experienced rheumatologist. Altogether, 419 patients with complete or incomplete BD were included in this study.
One hundred and seventeen patients with neurological complaints/symptoms were retrospectively evaluated. Forty-six patients who did not meet definite or probable NBD ICR criteria were excluded from the study. In final analysis, 77 NBD patients (61 definite, 16 possible) were included.
Results: Demographic and clinical features of BD patients with and without neurological involvement are summarized in Table. Neurologic involvement of BD is seen more frequently in patients with eye involvement (Table). Distribution of patients having parenchymal, non-parenchymal and mixed NBD are 47 (61%), 22 (28.5%), 5 (6.5%), respectively. Median time period between diagnosis for BD and parenchymal NBD is 5.7 years (IQR=11). Brainstem is the most frequently affected parenchymal area (72.9%), followed by white matter and diencephalon (64.6%, 37.5%). Twelve (25.5%) patients had spinal cord involvement. Fifty-eight percent of patients with acute onset parenchymal disease had only one attack. Corticosteroids (IV pulse: in 75.5% and oral in 90%), cyclophosphamide (57.1%), interferon (79%) and Anti-TNF agents (%23.5) were the most frequently preferred treatment options for parenchymal NBD. Ten, twenty and thirty year survival rates was 97.4%, 89.6% and 89,6% in NBD and 100%, 99.7% and 98.8% in non-NBD group, respectively (log rank p<0.001). Nine deaths were observed in all patients with NBD whereas no death was observed in patients with non-parenchymal NBD.
Conclusion: Neurologic involvement was seen median 5 years after BD diagnosis and these patients had more eye involvement compared to non-NBD group. Over half of patients had just one attack and no death was seen in non-parenchymal group. Interferon-alpha and anti-TNF agents were used in majority of patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bolek EC, Sari A, Armagan B, Erden A, Kilic L, Kalyoncu U, Tuncer MA, Kiraz S, Karadag O. Clinical Features and Disease Course of Neurologic Involvement in Behcet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-and-disease-course-of-neurologic-involvement-in-behcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-and-disease-course-of-neurologic-involvement-in-behcets-disease/