Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Diagnosis and Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Discontinuation of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) therapy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is attributable to various reasons. Above all, adverse event (AE) and insufficient response (IR) are principal and crucial. In this study, we investigate association between covariates including rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity and discontinuation of TNFi therapy due to AE and IR using COX proportional hazard analysis. Additionally, multiple imputation analysis for COX proportional hazard regression was performed. This approach is becoming increasingly popular for handling missing data. Excluding participants who have one or more missing values, a so-called complete case analysis can introduce selection bias as participants who have complete data may be different to those with missing data.
Methods: This study included patients enrolled in the Tsurumai Biologic Communication Registry which comprises Nagoya University and 18 affiliated institutions in Japan. We assessed relationships between individual characteristic components and patient outcomes using multiple imputation method for COX proportional hazard model. All analyses were conducted in R version 3.5.0.
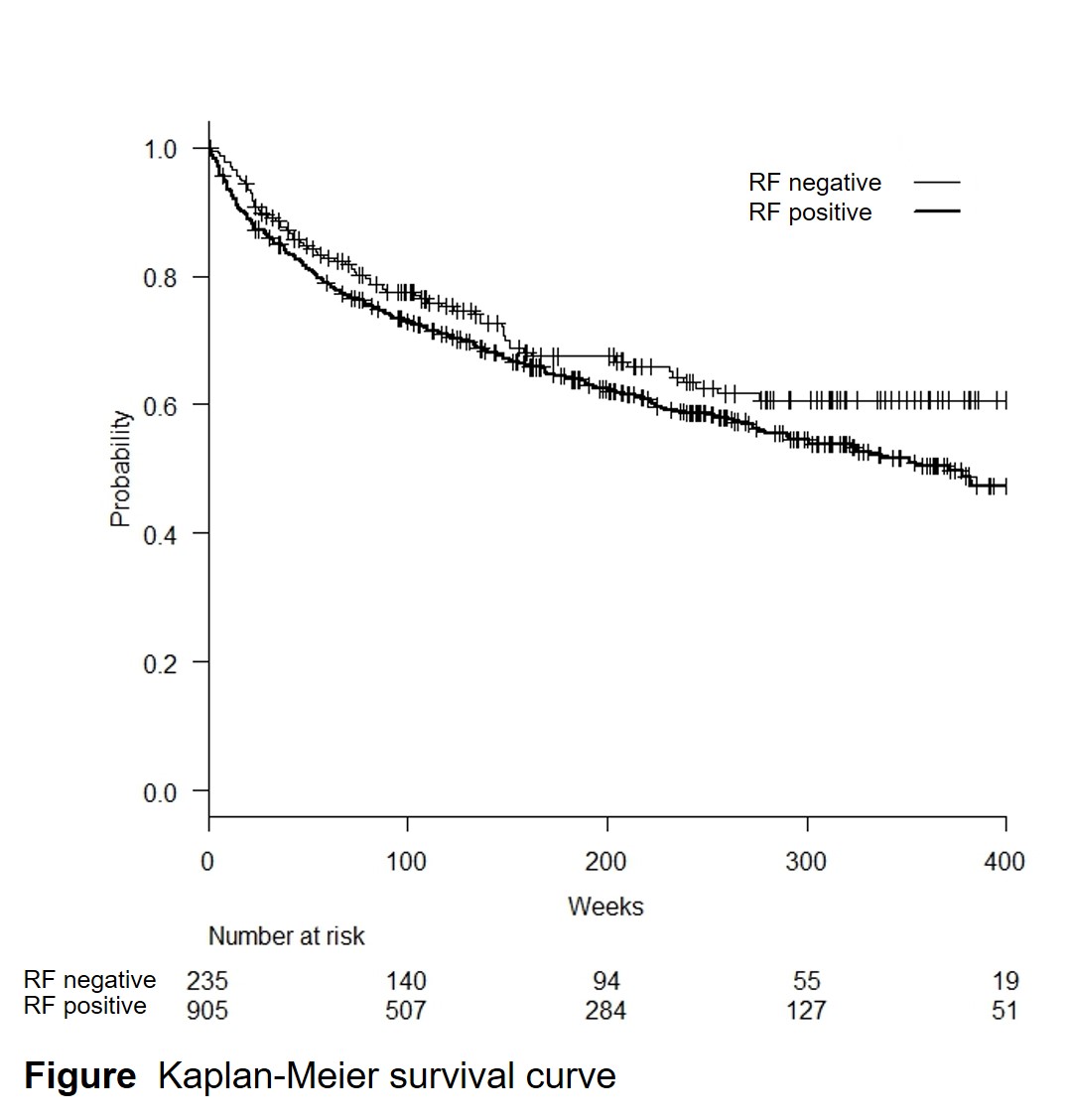
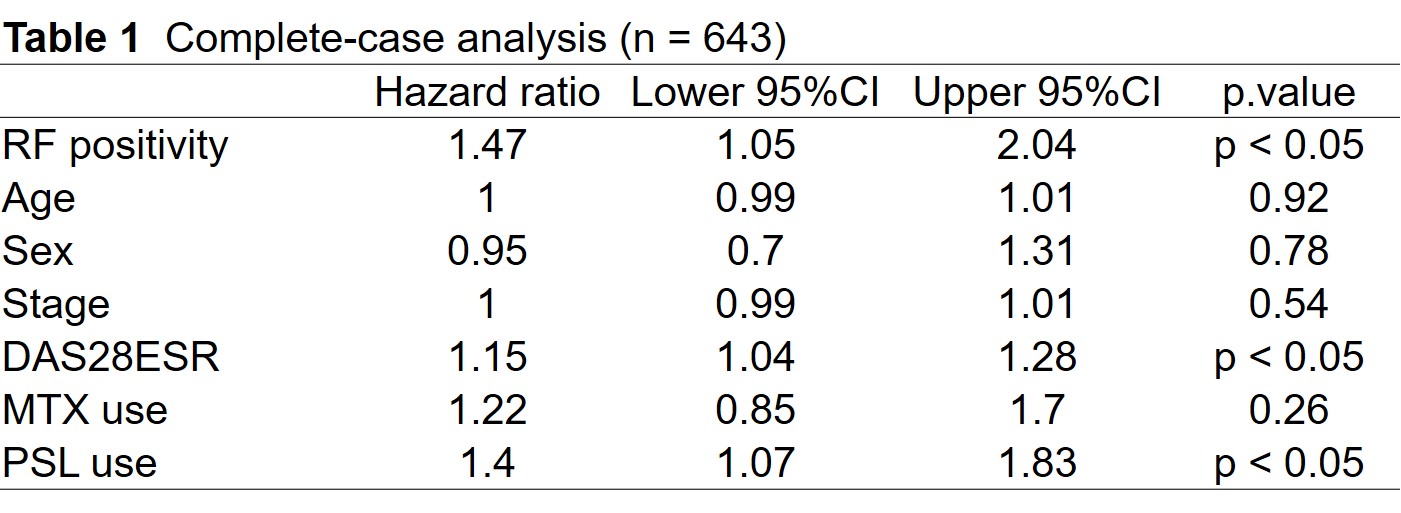
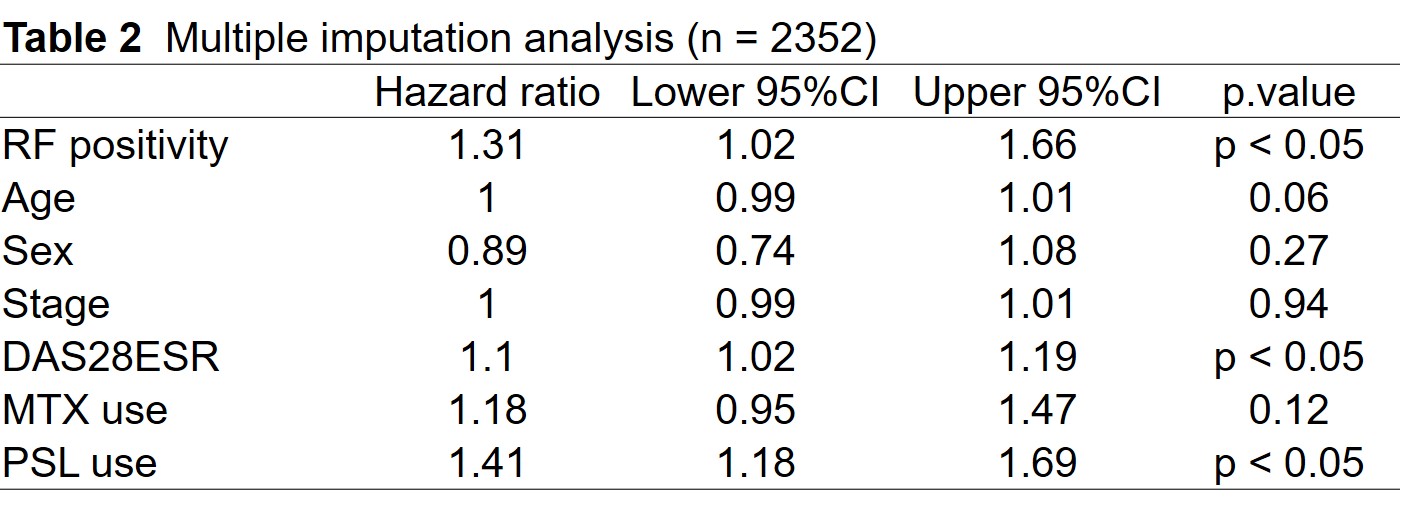
Results: There was a higher crude discontinuation rate in RF positive patients than in RF negative patients using Kaplan-Meier survival curve and log-rank test (P < 0.05; Figure). The difference was significant in COX proportional hazard analysis adjusting for baseline characteristics including age, sex, stage, das28 using erythrocyte sedimentation rate at baseline, methotrexate use, and prednisolone use (n = 643, HR = 1.47, P < 0.05; Table 1), and multiple imputation method for COX proportional hazard model (n = 2352, HR = 1.31, P < 0.05; Table 2).
Conclusion: Using multiple imputation method for COX proportional hazard regression, we demonstrated that RF positivity is related with higher discontinuation rate of TNFi therapy due to AE and IR on bio-naïve RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogawa Y, Takahashi N, Kojima T, Ishiguro N. Rheumatoid Factor Positivity Is Related with Higher Discontinuation Rate of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy Due to Adverse Event and Insufficient Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multiple Imputation Method for COX Proportional Hazard Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-positivity-is-related-with-higher-discontinuation-rate-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-therapy-due-to-adverse-event-and-insufficient-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multiple-i/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-positivity-is-related-with-higher-discontinuation-rate-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-therapy-due-to-adverse-event-and-insufficient-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multiple-i/