Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: 3S082 ACR Abstract: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases I: MRI & CT (863–868)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue diseases (CTD-PAH), particularly PAH associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-PAH), has a poor prognosis compared with other PAH. The pathogenesis of CTD-PAH is complex, comprising not only pulmonary arteriopathy but also venous and interstitial involvements. In addition, recent studies have shown that right ventricular (RV) dysfunction is more pronounced in CTD-PAH than in other PAH despite similar or even lower pulmonary arterial (PA) pressure in CTD-PAH patients. The present study aimed to precisely evaluate RV function, including RV-PA coupling by combining cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and right heart catheterization (RHC) and to analyze its prognostic value in CTD patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH).
Methods: This is a single center retrospective analysis comprising 84 CTD patients, including SSc, systemic lupus erythematosus, and mixed connective tissue disease, who underwent both CMR and RHC from January 2008 to March 2018. End-systolic elastance (Ees, mPAP/RV end-systolic volume index), pulmonary arterial elastance [Ea, (mPAP-PAWP)/SV index], and Ees/Ea were calculated as load-independent parameters of RV systolic function, RV afterload, and RV-PA coupling metrics, respectively. The prognostic value of each parameter was evaluated by area under the ROC curves (AUCs) and Kaplan-Meier curves.
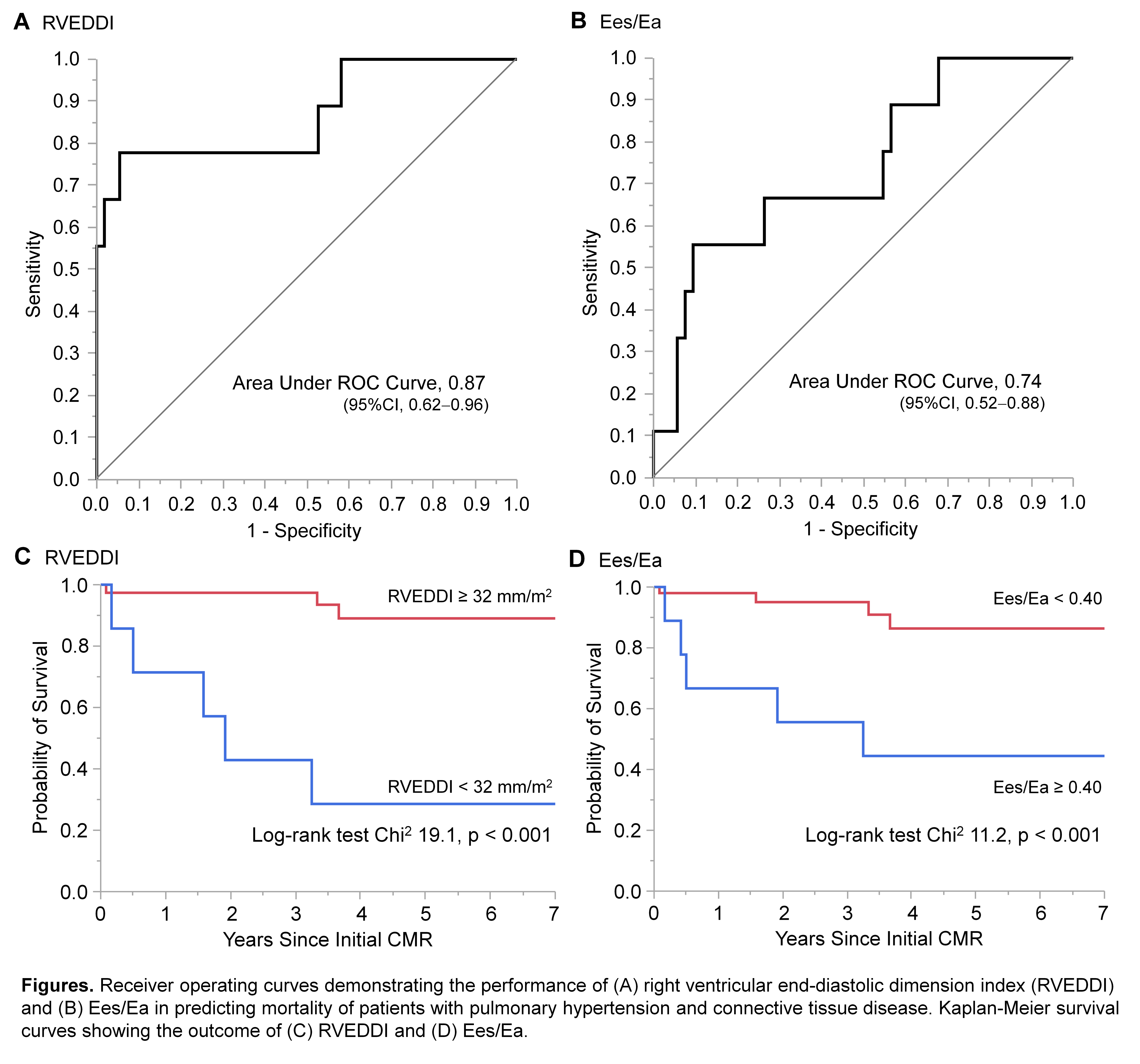
Results: Of 84 patients, 54 had PAH, 11 had non-PAH PH due to left heart disease, severe interstitial lung disease (ILD) and venous thromboembolic disease, and 19 did not have PH. Nine patients deceased during a median follow-up period of 25 months. In patients with PH (n=65), RV end-diastolic dimension (RVEDDI) and Ees/Ea strongly predicted the mortality with AUC of 0.87 and 0.74, respectively (Figure A and B). The 2-year overall survival rate was significantly lower in patients with either RVEDDI of >32 mm/m2 or Ees/Ea of <0.40 compared with other patients (62% vs 98%, p<0.001) (Figure C and D). Notably, 2-year survival of patients with both RVEDDI of >32 mm/m2 and Ees/Ea of <0.40 was only 20%. In multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analyses using propensity score to control confounding factors including age, sex, PAH, SSc, and ILD, RVEDDI still significantly predicted the mortality (hazards ratio 11.1, 95% confidence interval 1.82-70.6). In SSc-PAH patients (n=24), compared with other CTD-PAH patients, RVEDDI was significantly higher (p=0.004), and Ees was significantly lower (p=0.013), indicating RV impairment in systolic function as well as diastolic function.
Conclusion: RV dimension and RV-PA coupling, which can be evaluated by combining CMR and RHC, strongly predicted the prognosis of CTD patients with PH. More pronounced impairment of these parameters observed in SSc-PAH patients is consistent with the less favorable outcome of those patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abe N, Kato M, Nakamura H, Noguchi A, Fujieda Y, Oku K, Bohgaki T, Amengual O, Yasuda S, Atsumi T. Combining Cardiac Magnetic Resonance and Right Heart Catheterization to Evaluate Right Ventricular Function for the Prognosis Prediction in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases and Pulmonary Hypertension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combining-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-and-right-heart-catheterization-to-evaluate-right-ventricular-function-for-the-prognosis-prediction-in-patients-with-connective-tissue-diseases-and-pulmonary-hyper/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combining-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-and-right-heart-catheterization-to-evaluate-right-ventricular-function-for-the-prognosis-prediction-in-patients-with-connective-tissue-diseases-and-pulmonary-hyper/