Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: T Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Th17, a subset of CD4+ helper T cells, provides protection against pathogens and malignancies, but also promotes immune-mediated-inflammation in a range of disorders including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis. In our analysis of high throughput transcriptomic data, we identified aquaporin 3 (AQP3) as a novel gene in the promotion of Th17 differentiation and pathogenicity. AQP3 gene codes for a water channel protein highly expressed in the kidney and keratinocytes. Interestingly elevated AQP3 expression is reported in inflamed skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Elevated AQP3 was recently reported in a murine model of psoriasiform dermatitis but its importance in human psoriasis has not been examined. We investigated AQP3 expression in human psoriatic skin and analyzed the expression of AQP3 in human CD4+ T cells following cytokine exposure.
Methods:
To validate our initial in silico findings, we conducted in vitro experiments with human naive T cells. To investigate key inducers of AQP3 in CD4+ lymphocytes, we cultured naïve CD4+ T cells in the presence of IL1B, IL6, TGFB1, and IL23, alone, or in combination, and monitored IL17A, IL17F, and AQP3 mRNA expression levels by qPCR. We also analyzed AQP3 mRNA and protein levels in lesional and non-lesional skin from psoriasis patients compared to skin from healthy controls.
Results:
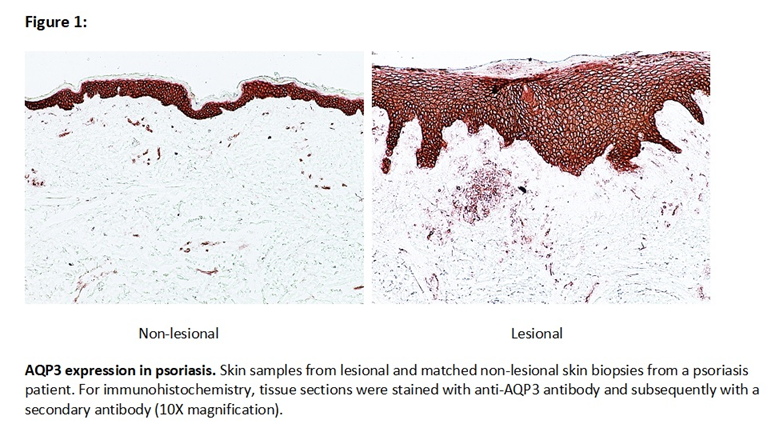
We found that AQP3 expression at 72 hours increased more than 7-fold in naive CD4+ T cells when cultured in the presence of Th17 differentiating conditions and correlated with IL-17A and IL-17F expression. When CD4+ lymphocytes were cultured in the presence of IL1B, IL6, and TGFB1 or TGFB3, a 5-fold increase in AQP3 was observed, but no increased expression was noted when cells were cultured with the individual cytokines. Interestingly, IL23 dramatically increased AQP3 expression in naive CD4+ T cells (more than 15-fold) when combined with IL1B, IL6, and TGFB1, but failed to do so when added alone. We also noted elevated mRNA (2.3 fold) and protein expression levels of AQP3 in lesional psoriatic skin compared to non-lesional skin (figure 1). Expression levels were highest in the epidermis but also noted in cells infiltrating the dermis.
Conclusion:
Expression of AQP3 was elevated in Th17 cells compared to naive CD4+ T cells. IL23 greatly augmented AQP3 expression in CD4+ T cells in the presence of IL1B, IL6, and TGFB1. In addition, AQP3 protein expression is increased in the cells infiltrating the dermis and keratinocytes in psoriasis, a Th17-related disorder. These data suggest that AQP3 may be a cellular marker of a pathogenic Th17 subset and may provide insights into disease pathogenesis with the potential to serve as a therapeutic target.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Paine A, Garcia-Hernandez MDLL, Korman BD, Duculan J, Suarez-Farinas M, Krueger JG, Ritchlin CT. Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) Protein Is Highly Expressed in Psoriatic Plaques and AQP3 Gene Expression Strongly Induced By IL-23 in CD4+ Th17 Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/aquaporin-3-aqp3-protein-is-highly-expressed-in-psoriatic-plaques-and-aqp3-gene-expression-strongly-induced-by-il-23-in-cd4-th17-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/aquaporin-3-aqp3-protein-is-highly-expressed-in-psoriatic-plaques-and-aqp3-gene-expression-strongly-induced-by-il-23-in-cd4-th17-cells/