Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: TARC, also known as chemokine ligand 17 (CCR17), is expressed in the thymus and is produced by dendritic cells, endothelial cells, keratinocytes and fibroblasts. TARC has affinity as a ligand for CCR4 and CCR8, which are predominantly expressed by Th2 cells. High serum concentration of TARC is determined in allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis and bronchial asthma. Several studies have reported frequent atopic symptoms among patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). We investigated the role of TARC as a biomarker in IgG4-RD, in which Th2 cytokines associate in disease states.
Methods: We evaluated the serum concentration of TARC from 26 IgG4-RD patients, 22 healthy controls (HC) by ELISA. We also analyzed the correlations between TARC concentration and clinical parameters. To investigate the biological effect of TARC toward pathogenesis in IgG4-RD, in vitro induction of plasmablasts from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in patients with IgG4-RD by TARC was evaluated.
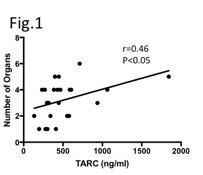
Results: We found that the serum concentration of TARC in the IgG4-RD was significantly higher than HC (IgG4-RD mean 493.9 ng/mlCHC mean 262.0 ng/mlCp<0.001). ROC curve for TARC distinguish IgG4-RD from HC, the cutoff value 296.5 ng/ml (sensitivity 80.8%, specificity 72.7%). Serum concentration of TARC from IgG4-RD positively correlated with number of organ involvement (Fig. 1) whereas showed the correlation neither with serum IgG4 nor eosinophil number in peripheral blood. In addition, no difference in TARC concentration was found among IgG4-RD patients with or without atopic symptoms. TARC in vitro clearly induced the formation of plasmablasts from patients with IgG4-RD (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: Collectively, our data suggest that TARC is an essential Th2 cytokine in patients with IgD4-RD. TARC may be involved in the development of IgG4-RD through an aberrant induction of plasmablasts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Umeda M, Origuchi T, Kawashiri S, Koga T, Ichinose K, Endo Y, Tsuji S, Takatani A, Igawa T, Shimizu T, Fukui S, Sumiyoshi R, Nishino A, Iwamoto N, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Kawakami A. Thymus and Activation-Regulated Chemokine (TARC) As Biomarker for IgG4-Related Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/thymus-and-activation-regulated-chemokine-tarc-as-biomarker-for-igg4-related-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/thymus-and-activation-regulated-chemokine-tarc-as-biomarker-for-igg4-related-disease/