Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment II
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC) improved the signs and symptoms of AS in 2 Phase 3 studies (MEASURE 1 and 2).1,2 Here, we present interim results through 104 weeks (wks) from the MEASURE 3 study (NCT02008916), the first Phase 3 study assessing efficacy and safety of subcutaneous (SC) maintenance therapy with 300 or 150 mg SEC following intravenous (IV) loading.
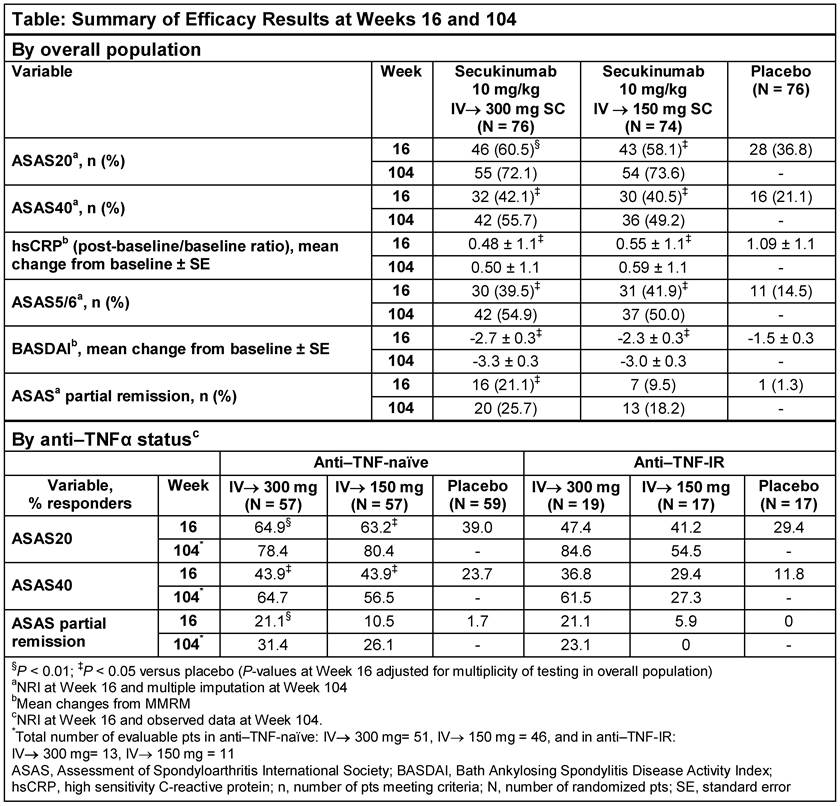
Methods: 226 patients (pts) were randomized to IV SEC 10 mg/kg (baseline, Wks 2 and 4) followed by SC SEC 300 or 150 mg every 4 wks (IV→300/150 mg), or matched placebo (PBO). At Wk 16, PBO pts were re-randomized to SC SEC 300 or 150 mg. Primary endpoint was ASAS20 response rate at Wk 16. Secondary endpoints included ASAS40, hsCRP, ASAS 5/6, BASDAI and ASAS partial remission (PR). Non-responder imputation through Wk 16 and multiple imputation for binary variables and mixed-effect model for continuous variables through Wk 104 were used. Analyses by prior anti-TNF therapy use (anti–TNF-naïve and -inadequate response or intolerance [IR]) were pre-specified and reported as observed at Wk 104. Efficacy results at Wk 104 are reported for pts originally randomized to SEC. Safety analyses included all pts who received ≥1 dose of SEC.
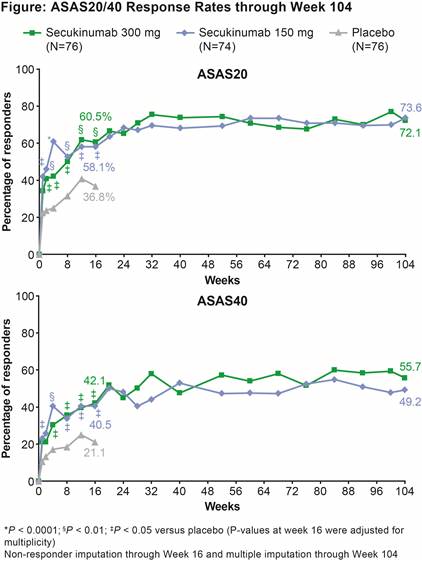
Results: 84.2% (64/76; SEC IV→300 mg) and 77.0% (57/74; SEC IV→150 mg) pts completed 104 wks of treatment. ASAS20 response rate was significantly greater at Wk 16 (primary endpoint) in SEC IV→300 mg and IV→150 mg groups vs PBO. All secondary endpoints were met at Wk 16, except ASAS PR in the IV→150 mg group. Improvements achieved with SEC in all clinical endpoints at Wk 16 were sustained through Wk 104 (Table and Figure). ASAS20/40 and ASAS PR responses by anti–TNF status are shown in Table. At Wk 104, response rates on more stringent clinical endpoints (e.g. ASAS PR) were higher with the 300 mg dose, particularly in the smaller group of anti–TNF-IR pts. Safety profiles of both SEC doses were similar through Wk 104 (mean±SD exposure: 633.8±165.4 days [300 mg] and 644.5±135.4 days [150 mg]). Exposure-adjusted incidence rates over the entire treatment period in the combined group of SEC doses for Candida infections, serious infections/infestations, and uveitis were 1.0, 1.0, and 0.3 per 100 pt-years, respectively. No cases of inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, were reported.
Conclusion: SEC (300 and 150 mg) provided rapid and significant improvements in the signs and symptoms of active AS, with responses sustained through 104 wks. SEC was well-tolerated with a safety profile consistent with previous reports.
References: 1. Braun J, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;1–8; 2. Marzo-Ortega H, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2017;doi: 10.1002/acr.23233
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pavelka K, Kivitz AJ, Dokoupilova E, Blanco R, Maradiaga M, Tahir H, Slade A, Wang Y, Rohrer S, Porter B. Secukinumab Provides Sustained Improvements in the Signs and Symptoms of Active Ankylosing Spondylitis: 2-Year Results from a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-the-signs-and-symptoms-of-active-ankylosing-spondylitis-2-year-results-from-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-the-signs-and-symptoms-of-active-ankylosing-spondylitis-2-year-results-from-a-phase-3-study/