Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
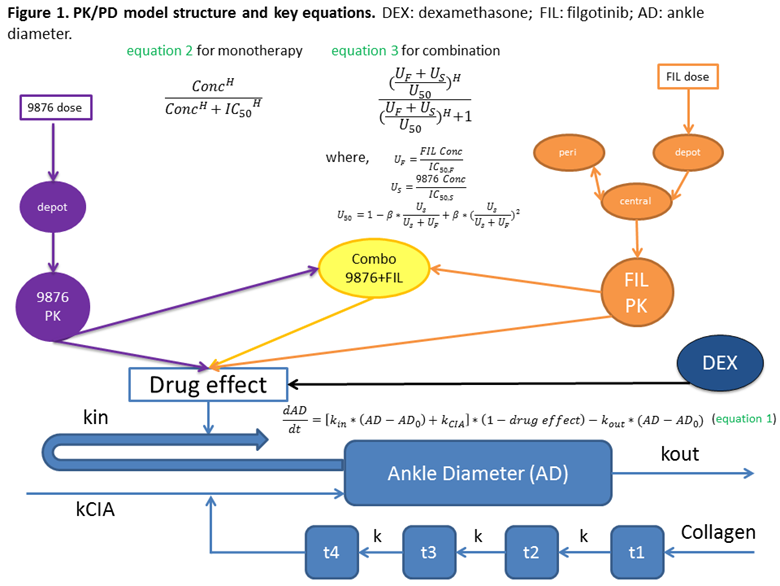
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL), a JAK1 inhibitor, and GS-9876, a SYK inhibitor, are currently being evaluated as once-daily monotherapy in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A preclinical study was conducted to compare the efficacy of FIL + GS-9876 in combination versus monotherapy of each agent in a rat collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. A semi-mechanistic pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model was developed to 1) characterize the exposure (plasma concentration)-response (ankle diameter) relationship following mono- and combination therapy, and 2) provide a quantitative assessment of PD interaction between the two drugs.
Methods: Monotherapy (FIL at 3 doses1,3,or 5 mg/kg, QD or GS-9876 5 mg/kg BID) and the combination (FIL 1, 3 mg/kg QD and GS-9876 5mg/kg, BID) treatments were administered to CIA rats. FIL was co-administered with the active metabolite to reflect the PK profile in humans. Dexamethasone at 0.075 mg/kg QD was the positive control. Dosing was initiated at the peak of inflammation (day 17-20) and continued through the chronic disease phase until day 34. Population PK models were developed to characterize FIL and GS-9876 concentration versus time profiles. Disease progression, assessed as the change in ankle diameter over time, was described by equation 1 (indirect response model), and drug effect (monotherapy and combination) by equations 2 and 3 (Figure 1; Ref: Minto et al., 2000). The analysis was conducted using a nonlinear mixed-effects modeling approach (NONMEM 7.3) and R v3.3.2 was used for processing/visualizing data.
Results: The model adequately described the PK of FIL/GS-9876 and the exposure-response relationship, following monotherapy and combination therapy. The results indicated a dose/exposure dependent reduction in ankle paw diameter following FIL monotherapy. Furthermore, a synergistic effect on efficacy was observed (based on an estimated β value >1) following treatment with the combination compared with either agent alone. Simulations (of various dose levels) indicated an exposure dependent increase in efficacy following combination treatment, with a plateau at doses ≥ FIL 3 mg/kg QD + GS-9876 5 mg/kg BID.
Conclusion: The PK/PD model demonstrated a synergistic interaction between FIL and GS-9876, thereby suggesting the utility of simultaneously targeting the JAK and SYK receptor pathways for RA. Furthermore, the model provides a quantitative framework for screening various drug combinations (of two or more drugs) in CIA rats and may help in selecting efficacious combinations for clinical assessment.
References: Minto, Charles F., et al. "Response surface model for anesthetic drug interactions." The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 92.6 (2000): 1603-1616.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Meng A, Di Paolo J, Sharma S, Mathias A. A Quantitative Framework for Evaluating Drug Combination Treatment in Rat Collagen-Induced-Arthritis Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-quantitative-framework-for-evaluating-drug-combination-treatment-in-rat-collagen-induced-arthritis-model/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-quantitative-framework-for-evaluating-drug-combination-treatment-in-rat-collagen-induced-arthritis-model/