Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Measuring severity of interstitial lung disease (ILD) usually depends on the extent or pattern of imaging findings on computed tomography (CT) and the parameters of pulmonary function test. Krebs von den Lungen 6 (KL-6) is a sialylated glycoprotein mainly expressed on the surface membrane of type II pneumocytes and bronchiolar epithelial cells (1). Serum level of KL-6 had been reported to be associated with presence or outcome of ILD associated with connective tissue diseases (CTD-ILD) (2-4). We aimed to evaluate KL-6 as a potential biomarker reflecting severity of CTD-ILD.
Methods: Study population was a retrospective cohort of 464 Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic sclerosis (SSc), inflammatory myositis (IM), Sjogren¡¯s syndrome (SS), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had concurrent ILD or not. Serum concentration of KL-6 (U/mL) was measured by Nanopia KL-6 assay (SEKISUI MEDICAL, Tokyo), using latex enhanced immunoturbidimetric assay method. Temporally nearest CT and PFT results were collected within 2 years from each serum sampling. Semi-quantitative grade of ILD extent (grade 1: 0-25%, grade 2: 26-50%, grade 3: 51-75%, grade 4: 76-100%) was evaluated by CT scan. Student t-test and Pearson¡¯s coefficient (PC) were applied to evaluate the correlation of KL-6 level and severity of ILD.
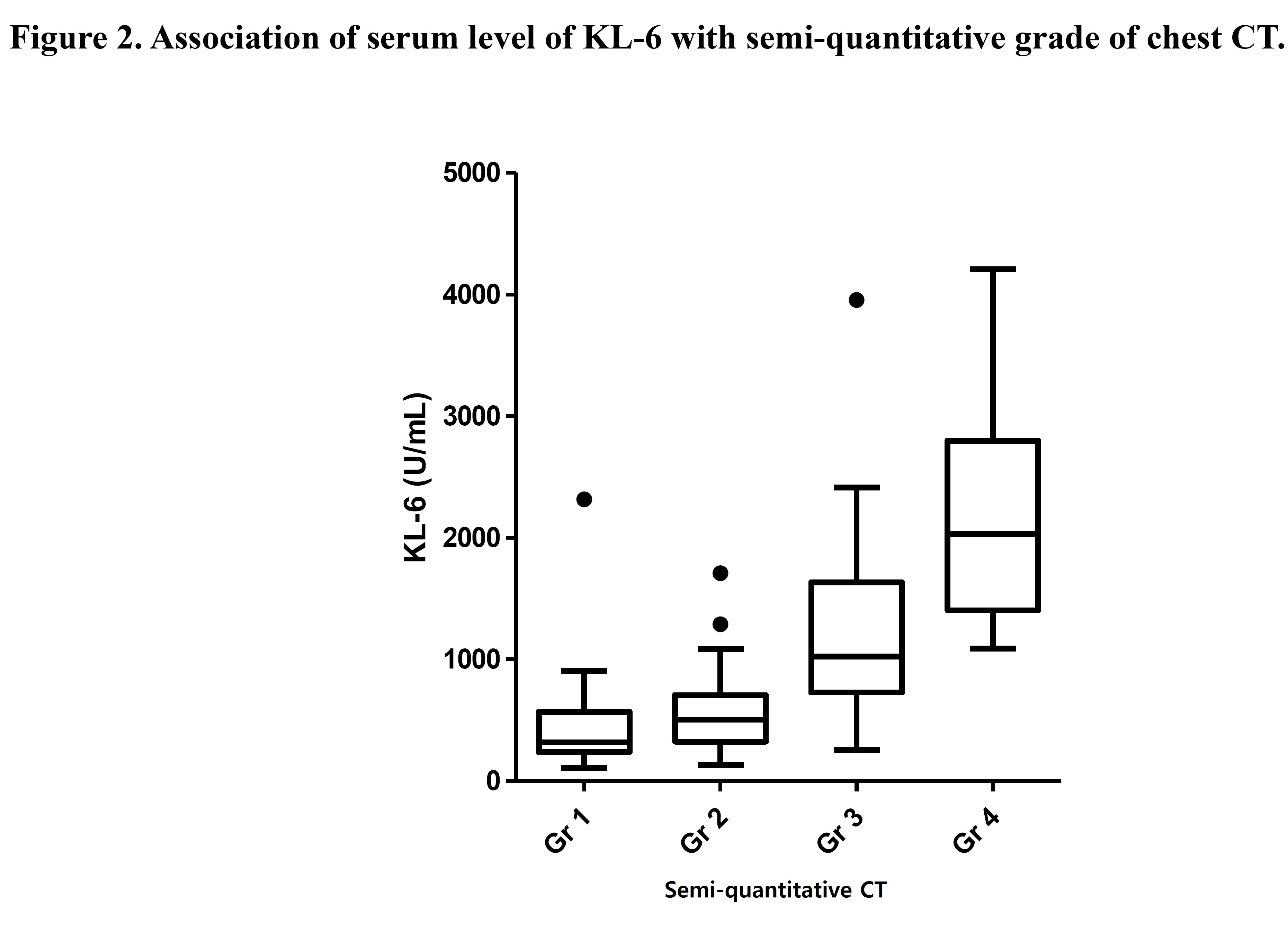
Results: The patients with CTD-ILD (n=162) had elevated serum level of KL-6 compared to CTD without ILD (n=302) (mean¡¾SEM, 737.9¡¾57.5 vs 238.2¡¾10.1U/mL, p<0.001) (Fig 1). In subgroup analysis, RA (544.6¡¾100.3 vs 241.7¡¾19.6, p<0.001), SSc (766.4¡¾103.7 vs 224.0¡¾26.3, p=0.002), IM (808.1¡¾99.8 vs 291.4¡¾33.1, p<0.001), and SS or SLE (914.1¡¾227.1 vs 215.0¡¾10.25, p<0.001) also had significant difference according to the presence of ILD. Semi-quantitative grade of ILD in CT scan was significantly proportional to KL-6 level except for grade 1 and 2 (Fig 2). Percent diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO%) and forced vital capacity (FVC%) had negative correlation with KL-6 level (PC=-0.587, p<0.001; PC=-0.399, p<0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: Serum levels of KL-6 were increased in CTD-ILD and had good correlation with CT grade, FVC, and DLCO. Higher serum level of KL-6 may reflect severity of CTD-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee JS, Lee EY, Park JK, Lee EB, Song YW. Serum KL-6 Level Reflects Severity of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Connective Tissue Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-kl-6-level-reflects-severity-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-connective-tissue-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-kl-6-level-reflects-severity-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-connective-tissue-disease/