Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
– Background/Purpose: The NIH indexes (of activity and chronicity) were proposed by Austin et al., in 1984. At the moment, there are therapies which can modify the histology of lupus nephritis; therefore, the markers of prognosis in the kidney biopsy may have different hazard ratios to the described by Austin et al.
– Methods: We evaluated all the patients in whom a kidney biopsy was performed. DKF was defined as a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of ≤ 60 ml/min/m2 in two determinations in the follow-up. Histology was graded from 0-3 for glomerular or tubular abnormalities weighted by the intensity of damage. Factors associated with the development of DKF according to the different factors were evaluated through Kaplan-Meier curves and multivariate Cox regression analysis. Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate independent factors associated with the development of DKF. Independent factors in the multivariate analysis were used to construct the new index using the hazard ratio of each variable. ROC curves for survival (Heagerty et al, 2000) were used to evaluate the performance of the new index in comparison with the activity and chronicity indexes.
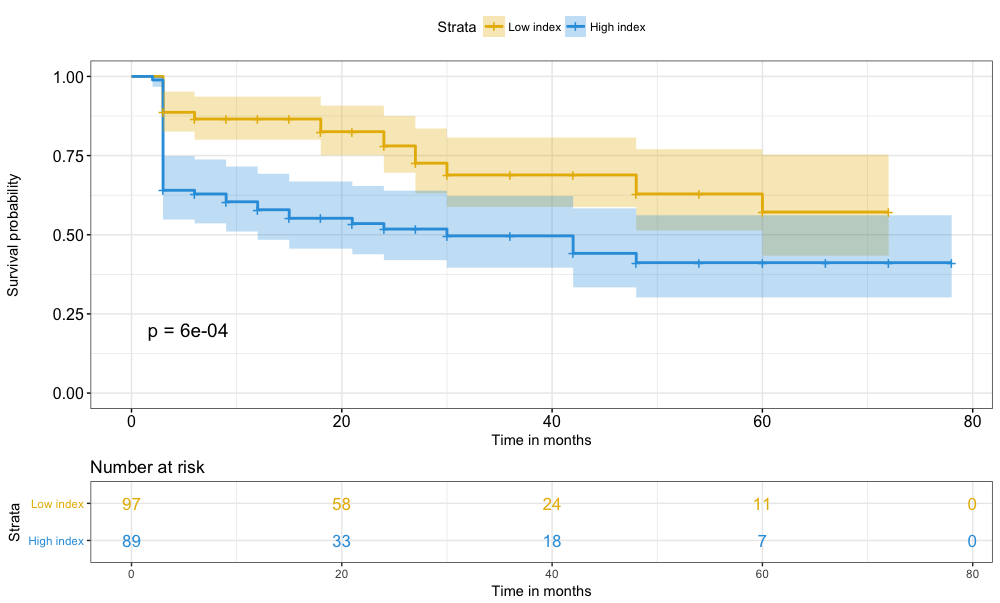
– Results: We have followed 186 patients with LN and kidney biopsy, 143 (76.9%) women, mean age at kidney biopsy was 29.7 ± 12.9 years; classes of LN were: 78 patients (41.3%) class IV, 31 (16.4%) class V, 23 (12.2%) class III/V, 23 (12.2%) class IV/V, 19 (10.1%) class III, and other classes 12 patients; 135 patients (79.5%) have a minimum follow-up of 12 months. Table 1 shows the results of the univariate and the final multivariate model that was used to develop the new index. ROC curves showed AUC for detecting DKF at 12 moths for activity, chronicity and our new index of 0.59, 0.70 and 0.74 respectively. Figure 1 shows the survival according two groups: low index (new index lower than the median) and high index.
Table1.
|
Histological feature
|
Univariate HR (CI)
|
Univariate p-value
|
Multivariate HR (CI)
|
Multivariate p-value
|
|
Glomerular abnormalities
|
|
|||
|
Cellular proliferation |
1.06 (0.88-1.28) |
0.547 |
NA |
NA |
|
Karyorrhexis |
0.94 (0.72-1.13) |
0.364 |
NA |
NA |
|
Cellular crescents |
1.09 (0.96-1.22) |
0.364 |
NA |
NA |
|
Hyaline thrombi |
0.91 (0.70-1.17) |
0.453 |
NA |
NA |
|
Leukocyte infiltration |
1.23 (0.97-1.57) |
0.059 |
NA |
NA |
|
Glomerular sclerosis |
1.64 (1.33-2.03) |
< 0.001 |
1.48 (1.14-1.91) |
0.003 |
|
Fibrous crescents |
1.68 (1.27-2.21) |
< 0.001 |
1.35 (0.99-1.82) |
0.051 |
|
Tubulointerstitial abnormalities
|
|
|||
|
Interstitial cell infiltration |
1.34 (1.17-1.55) |
< 0.001 |
1.41 (1.02-1.94) |
0.038 |
|
Interstitial fibrosis |
1.30 (0.97-1.75) |
0.162 |
NA |
NA |
|
Tubular atrophy |
1.35 (1.05-1.74) |
0.025 |
NA* |
NA* |
* Tubular atrophy was no included in the final model.
– Conclusion: We suggest predicting the risk of DKF with glomerular sclerosis, fibrous crescents, and interstitial cell infiltration. Maybe the other histological characteristics could be modified by the new therapies.
Figure 1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinez-Martinez MU, Vallín Orozco CE, Martínez-Galla D, Abud-Mendoza C. A New Histological Index for Predicting a Decline in Kidney Function in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. a Mexican Cohort Study of 186 Patients with a Kidney Biopsy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-histological-index-for-predicting-a-decline-in-kidney-function-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-a-mexican-cohort-study-of-186-patients-with-a-kidney-biopsy/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-histological-index-for-predicting-a-decline-in-kidney-function-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-a-mexican-cohort-study-of-186-patients-with-a-kidney-biopsy/