Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is an inflammatory arthropathy due to the deposition of uric acid (monosodium urate: MSU) crystals in synovial tissue. MSU leads to activate nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and following IL-1beta secretion via caspase-1 activation in human monocytes. Synthesis of mature IL-1beta is a 2-step processes. In the 1st step, microbial-derived signals (binding of bacterial products such as LPS) up-regulate pro-IL-1beta, resulting in synthesis of pro-IL-1beta. However, priming signals for NLRP3 infammasome pathway had not been completely elucidated in sterile inflammatory arthritis including gout. In this study, we investigated the role of TNF-alpha on MSU-mediated IL-1beta induction in human neutrophils.
Methods: Venous peripheral blood was collected from healthy volunteers. Human neutrophils were stimulated with MSU (200 µg/ml), in the presence or absence of TNF-alpha priming (2 to 50 ng/ml). The cellular supernatants were analyzed for IL-1beta, IL-18 and caspase-1 by ELISA. Pro-IL-1beta mRNA expressions in human neutrophils were analyzed by real-time PCR.
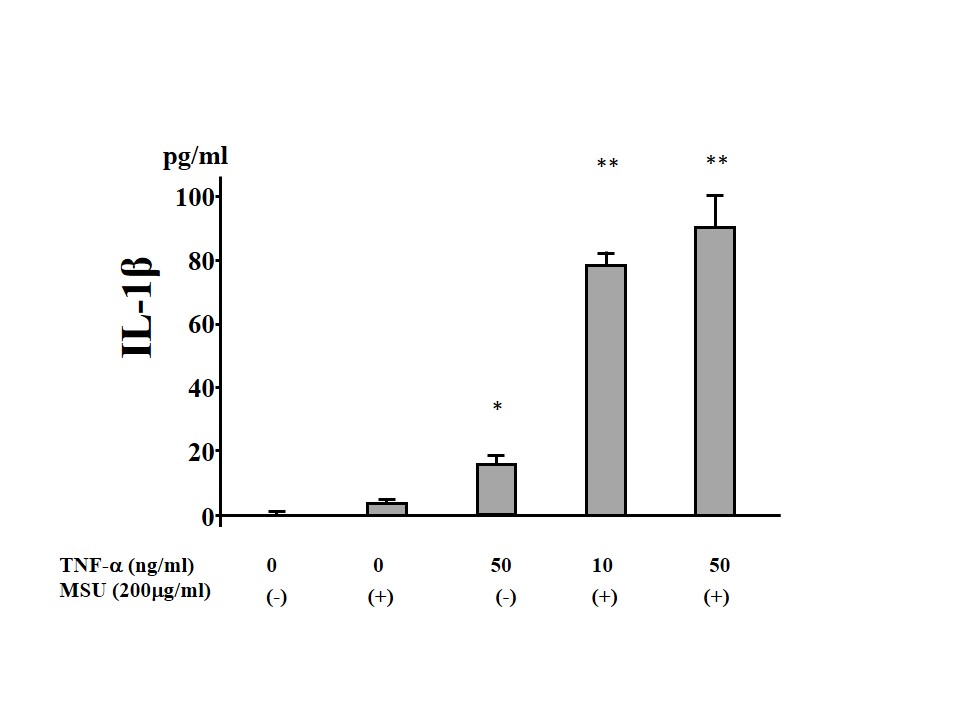
Results: TNF-alpha stimulation induced pro-IL-1beta mRNA expression, however, MSU stimulation alone did not induce pro-IL-1beta mRNA expression in neutrophils. TNF-alpha alone or MSU stimulation did not result in efficient IL-1beta secretion. Whereas MSU stimulation to TNF-alpha-primed neutrophils resulted in a marked IL-1beta (Figure 1) as well as IL-18 secretion. TNF-alpha-primed neutrophils secreted cleaved caspase-1 (p20) with MSU stimulation.
Conclusion: These results indicate that priming of human neutrophils with TNF-alpha promotes uric acid-mediated NLRP-3 activation and IL-1beta secretion in the absence of microbial stimulation, that provide new insights into the neutrophils-mediated inflammatory processes in gouty arthritis.
Figure 1. MSU induces IL-1beta synthesis from TNF-alpha-pretreated neutrophils.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sato S, Yashiro M, Asano T, Koga T, Suzuki E, Kobayashi H, Watanabe H, Migita K. TNF-α Potentiates Uric Acid-Induced Interleukin-1β Secretion in Human Neutrophils [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tnf-%ce%b1-potentiates-uric-acid-induced-interleukin-1%ce%b2-secretion-in-human-neutrophils/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tnf-%ce%b1-potentiates-uric-acid-induced-interleukin-1%ce%b2-secretion-in-human-neutrophils/