Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Voclosporin (VCS) is a novel CNI intended for use in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as lupus nephritis. VCS’s unique structure allows for less pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic variability and a potentially improved safety profile compared with other CNIs. The AURA study enrolled 265 subjects in over 20 countries using low (23.7 mg BID) or high dose VCS (39.5 mg BID) in addition to MMF 2g/day and steroids in active lupus nephritis (LN). 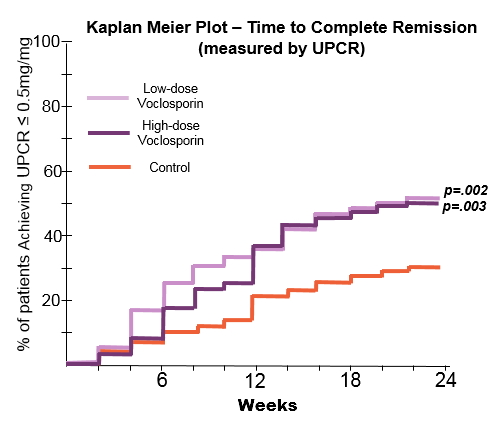
Methods: Entry criteria: renal biopsy within 6 months (Class III/V LN, ISN/RPS); UPCR≥1.5 (III/IV) or ≥2.0 mg/mg (V); serologic evidence of active LN; and eGFR >45ml/min. The steroid protocol was 20-25 mg (Day 1) with taper to 5 mg (Week 8), and 2.5 mg (Week 16-24). 24 week objectives included: Complete Remission (CR) defined as a urine protein/creatinine ratio (UPCR) of ≤0.5 mg/mg using first morning void with an eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min without a decrease of ≥20%; time to CR, Partial Remission (PR: 50% reduction in proteinuria) and time to PR.
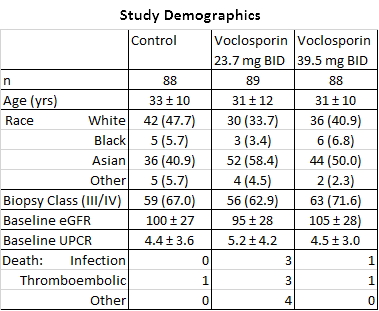
Results: The groups were generally well-balanced for age, gender and race, with a trend to higher proteinuria and lower eGFR data in the low dose VCS arm. The trial met its primary endpoint with superior CR rates in the low dose arm (OR: 2.03, p=0.045). There was a statistically significant improvement in time to CR and time to PR in both treatment arms (P<.01). A mean reduction in serum creatinine was seen in both arms (0.2 mg/dL low, 0.1 high; p<.001). BP did not vary by group. Over 90% of subjects experienced at least one adverse event; the most common being infectious (56.2% low, 63.6% high and 50.0% control), GI disorders (41.6% low, 52.3% high and 36.4% control). More serious adverse events occurred in the voclosporin groups (25.8% low, 25.0% high, 15.8% control), and were consistent with those observed in LN patients. Most deaths occurred in the first 2 months and were: low dose (infection-3, ARDS-2, thrombotic-3, cardiac tamponade, pulmonary hemorrhage), high dose (infection, PE) and control (CVA). All were considered unrelated to drug exposure by the investigators.
Conclusion: The AURA study is the first global LN study to meet its primary end point, Response rate was rapid; increasing CR in the VCS arms was seen by week 6. This study demonstrated the positive additive effects of VCS, despite the rigorous steroid taper (mean steroid dose 4 mg at Week 16). Adverse events were higher in the VCS treatment arms, consistent with increased immunosuppression. The overall mortality rate was similar to other recent LN trials (ALMS 3.8%, ALLURE 4.7%, BELONG 3.7%), with a higher mortality rate in the lowdose group. These promising data will be used to plan subsequent studies of voclosporin in LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dooley MA, Pendergraft W III, Ginzler EM, Olsen NJ, Tumlin J, Rovin BH, Houssiau FA, Wofsy D, Isenberg DA, Solomons N, Huizinga R. Speed of Remission with the Use of Voclosporin, MMF and Low Dose Steroids: Results of a Global Lupus Nephritis Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/speed-of-remission-with-the-use-of-voclosporin-mmf-and-low-dose-steroids-results-of-a-global-lupus-nephritis-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/speed-of-remission-with-the-use-of-voclosporin-mmf-and-low-dose-steroids-results-of-a-global-lupus-nephritis-study/
