Background/Purpose:
Many RA patients have variable disease activity over time due to disease flare, reduction in efficacy of current medications and other disease mediating changes. Understanding these transitions and the factors associated with these transitions are important in the treatment of RA. Appropriate analytic models for estimating these transitions are needed.
Methods:
Modeling methods were explored for estimating transitions from various disease states defined by low, moderate and severe using CDAI. The framework needed to provide intuitive estimates of the probability of transitioning between states, stability using variable time intervals, allow repeated measures within patients, and a method of estimating associations of patient and treatment characteristics with transition probabilities. A Markov modeling framework was examined. To test the models we used RA patient disease activity data from the CORRONA RA registry and examined multiple visits per patient. There were over 160,000 visits from over 24,000 RA patients available for analysis.
Results:
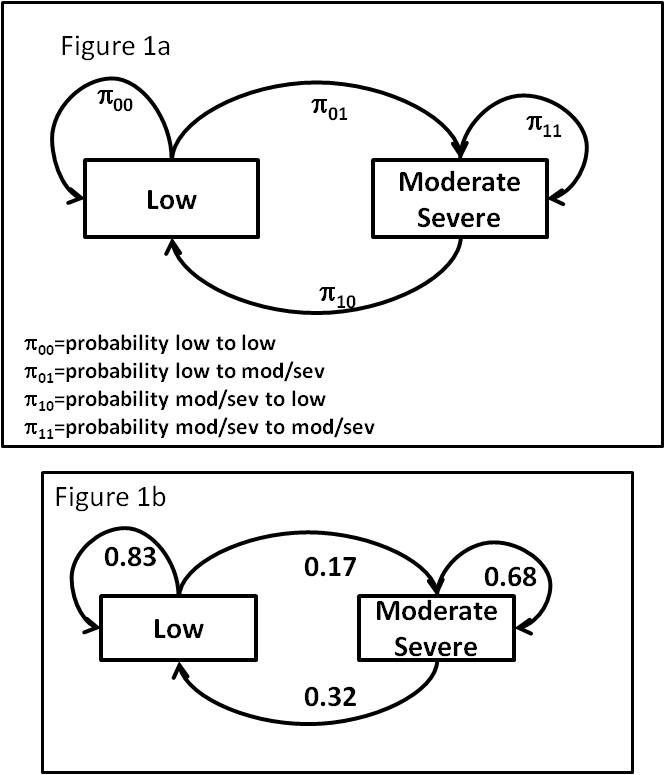
Starting with a simple transition model (Figure 1a), a first order Markov process was assumed and a logistic regression model that incorporates a single prior state produced stable estimates for variable time between visits. Transition probabilities differed by 0.07 for large differences in visit intervals, 3 mos vs 1 yr. A single logit equation can estimate the impact of the prior state (Yi,j-1), covariates (xij) associated with the transitions and test if different covariate associations are dependent on prior state:
![]() , where
, where ![]() . Figure 1b illustrates estimated transition probabilities.
. Figure 1b illustrates estimated transition probabilities.
The modeling framework is able to accommodate additional complexities. A multinomial logistic model provides estimates for more than two states. The models allow the use of higher order Markov processes to estimate the influence of disease state at earlier visits.
Conclusion:
Markov models and logistic or multinomial models of the transition probabilities provides a framework for analyzing patient disease states, the population transition probabilities and covariates associated with those transitions.
Disclosure:
G. W. Reed,
Corrona,
2,
University of Massachusetts Medical School,
3,
Corrona,
5,
Harvard Medical School,
;
A. S. Koenig,
Pfizer Inc,
3,
Pfizer Inc,
1;
K. C. Saunders,
Corrona,
3;
D. H. Collier,
Amgen Inc.,
1,
Amgen Inc.,
3;
J. M. Kremer,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Pfizer, HGS, UCB,
2,
Amgen, Abbott, Genentech, Pfizer ,
5,
Amgen, Abbott, BMS,
8,
Corrona,
4;
S. Kotak,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-methodology-for-estimating-disease-state-transitions-repeated-measures-markov-models-with-covariate-dependence/