Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment - Poster III: Biomarkers and Nephritis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
A panel of autoantibodies in combination with C4d-bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs, EC4d and BC4d) has been established as a sensitive and specific testing method for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The purpose of this study was to prospectively establish the performance characteristics of this testing method in an independent cohort of SLE subjects relative to subjects with diseases other than SLE.
Methods:
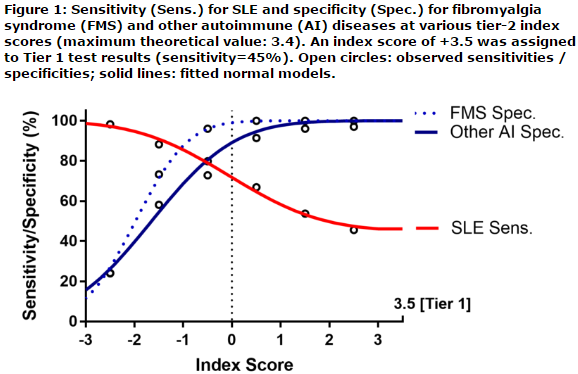
This cross-sectional prospective diagnostic validation study enrolled consented adult subjects at 12 sites across the USA. Venous blood was collected and transported overnight to a CAP-accredited reference clinical laboratory. The testing logic relied on two consecutive Tiers. In Tier 1, positivity for any of 4-lupus specific markers (inclusive of anti-dsDNA as confirmed by Crithidia, anti-Smith, and EC4d or BC4d levels above the 99th percentile of a control group) resulted a Tier-1 positive test assessment. All Tier-1 negative results were analyzed in a Tier 2, to yield a Tier-2 index score. This Tier-2 index score was inclusive of an ANA component, a CB-CAPs component (as component for complement activation), and a third component composite of autoantibodies for diseases other than SLE. Tier 2 positive test results (index score ≥0.1) were combined with Tier 1 positive test results to yield the overall two-tiered positive test results. Negative test results all presented with an index score lower than 0.1. All testing personnel were blinded to disease diagnosis throughout the study. Test performances in this independent validation cohort were assessed using sensitivity, specificity, positive (+) and negative (-) likelihood ratio (LR) the later reported with confidence intervals (CI).
Results:
A total of 476 adult subjects inclusive of 184 subjects with SLE (all meeting the 1982 ACR criteria revised in 1997), 215 subjects with auto-immune rheumatic and non-rheumatic diseases (inclusive of 77 subjects with autoimmune thyroiditis or hepatitis, 107 subjects with rheumatoid arthritis and 31 subjects with other rheumatic diseases) and a group of 77 subjects with primary fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) were enrolled. Tier 1 yielded 45% sensitivity for SLE and 98% specificity in distinguishing SLE from other diseases (LR+: 24.6 [CI95%: 10.1-59.5]), LR-: 0.56 [CI95%: 0.49-0.64]). Tier 2 yielded 48% sensitivity and 91% specificity in distinguishing SLE from other diseases (LR+: 5.6 [CI95%: 3.6-8.8], LR-: 0.56 [CI95%: 0.46-0.69]). All together the performance characteristics of the two-tiered diagnostic method yielded 72% sensitivity for SLE and 90% specificity in distinguishing SLE from other diseases (LR+: 7.0 [CI95%: 4.9-10.0], LR-: 0.32 [CI95: 0.25-0.40]).
Conclusion:
These data indicate that a panel of autoantibodies in combination with C4d-bound complement activation products is sensitive and specific for SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wallace DJ, Ramsey-Goldman R, Askanase AD, Manzi S, Ahearn J, Furie R, Weinstein A, Putterman C, Massarotti E, Collins C, Kalunian K, Arriens C, Silverman SL, Reddy S, Chitkara P, Ibarra C, Barken D, Alexander R, Conklin J, Dervieux T. Prospective Validation of a Panel of Autoantibodies in Combination with C4d-Bound Complement Activation Products for the Differential Diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prospective-validation-of-a-panel-of-autoantibodies-in-combination-with-c4d-bound-complement-activation-products-for-the-differential-diagnosis-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prospective-validation-of-a-panel-of-autoantibodies-in-combination-with-c4d-bound-complement-activation-products-for-the-differential-diagnosis-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/