Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a heterogeneous disease with diverse clinical and radiographic manifestations. A number of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles have been found to be associated with PsA.1 HLA-C*06:02 is associated with severe skin disease and a late onset, milder musculoskeletal phenotype; HLA-B*27:05 with entheseal-based disease, severe musculoskeletal disease, enthesitis, symmetric sacroiliitis (SI) and mild psoriasis; HLA-B*08:01 with synovial-based disease, asymmetric SI, joint deformity, joint fusion and dactylitis while HLA-B*38:01/39:01 is associated with more axial involvement and joint damage progression.2 Our hypothesis is that in each of these distinct genetic groups and perhaps as a consequence of the inflammatory events that occur following MHC-peptide interaction, a different pattern of inflammation involving diverse systemic molecules and mediators may be unleashed which in turn determines clinical phenotype and possibly therapeutic response. Our objective is to identify whether there are differences in cytokine expression between groups of patients with specific combinations of HLA genotypes and clinical features.
Methods: Patients with a diagnosis of PsA, fulfilling the CASPAR criteria, aged >18 years were clinically assessed, 10 patients from each of the 4 defined HLA groups. We included a fifth distinct clinical group, Arthritis Mutilans (AM), which as yet has no defined genotype. Serum samples were obtained. Cytokine Strategy: 50 individual patient samples (10 per group) and 5 reference pools (each pool consists of 50 samples) were subjected to in-house developed and validated multiplexed immunoassays to measure 47 cytokines using the Luminex xMAP. Analysis was performed in the Laboratory for Translational Immunology, UMC, Utrecht, The Netherlands. Data were analysed by 5-parametric curve fitting using BIO-Plex Manager software version 6.1.1.
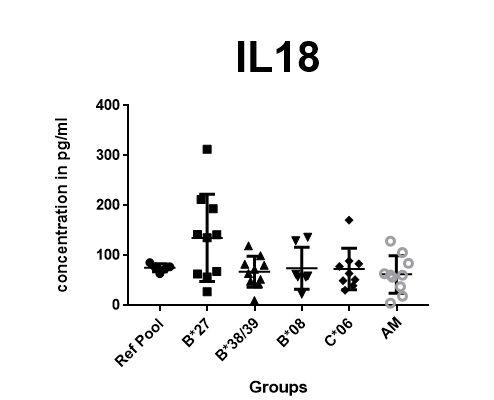
Results: Forty-seven cytokines were analysed in each individual sample (n=50). Four samples were excluded because of cross reaction. Fourteen cytokines were excluded because they were out of reference range (either above or below). Twelve cytokines were excluded as their coefficient of variation (CV) was > 20%. On analysis of the remaining 21, only 1 cytokines (IL18) was differentially expressed among the 5 groups, Figure1. IL18 was elevated in the HLA-B*27 group, with statistically significant difference between B*27 and AM (P<0.256, CI ̵ 135.6 to ̵ 9.982) and between B*27 and B*38/39 (P<0.0320, CI ̵ 129.3 to ̵ 6.524).
Figure 1 showing result IL18 cytokine in different group
Conclusion: IL18 was found to be elevated in HLA B*27 group. IL18 was significantly different between HLA B*27 group and AM and HLA B*38/39 group. Further analysis with a larger cohort is needed. References: 1. Winchester R, et al. A&R64:1134-44, 2012 2. Haroon M, et al. ARD75:155-162, 2016
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Elmamoun M, de Jager W, de Roock S, Haroon M, Winchester R, Pennington SR, FitzGerald O. Cytokine Expression in Groups of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Characterised By Specific HLA Genotypes and Clinical Features [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cytokine-expression-in-groups-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-characterised-by-specific-hla-genotypes-and-clinical-features/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cytokine-expression-in-groups-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-characterised-by-specific-hla-genotypes-and-clinical-features/