Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster II: Co-morbidities and Complications
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has been shown to improve major outcomes like survival rates in other inflammatory diseases, like systemic lupus. The aim of our study was to assess currently available literature on the cardio-vascular impact of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in patients with RA.
Methods: We systematically searched literature (via Pubmed, Embase and abstracts from recent ACR and EULAR congresses) for studies evaluating the effects of HCQ, wether in monotherapy or in combination with other conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) on cardio-vascular outcomes or known risk factors for CVD in RA patients (lipid profiles, diabetes incidence, insulin resistance and incidence of CVD). A meta-analysis was performed with Review Manager Software, with random-effects models, whenever methodologically possible and relevant. Data were extracted by one investigator and independently checked by another.
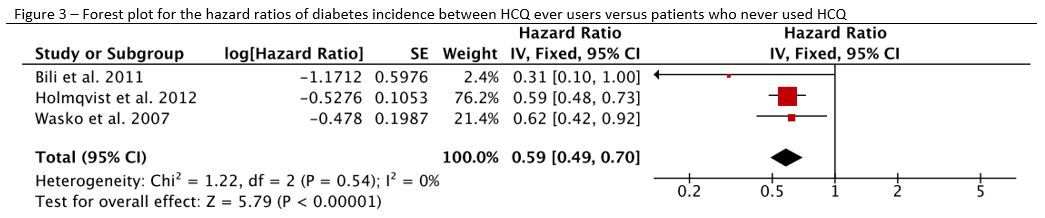
Results: The literature search revealed 213 articles and abstracts of potential interest, and further examination resulted in 13 studies fulfilling required criteria for preplanned analyses regarding the cardio-vascular impact of HCQ in RA. For lipid profiles, the mean difference (mg/dL) between HCQ users versus non-users was -9,82 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] -14.03; -5.60) for total-cholesterol (figure 1), -10.61 [-14.17;-7.04] for low-density-lipoprotein, +4.13 [2.22;6.04] for high-density-lipoprotein, and -19.15 [-27.20; -11.10] for triglycerides (figure 2); with respectively a decrease (mg/dL) of -13.15 [-20.96; -5.34], -12.35 [-20.14; -4.36], 1.67 [-0.96, 4.31] and -12.54 [-28.94; 3.86] after HCQ initiation. Diabetes incidence was reduced in “HCQ ever users” versus “patients who never used HCQ” with a hazard-ratio of 0.59 [0.49; 0.70] (figure 3). In addition, HCQ seems to decrease insulin resistance and incidence of cardio-vascular events but data were too scarce for meta-analysis.
Conclusion: Beside its limited efficacy on disease activity, this study supports the benefit of HCQ on metabolic profile and to a lesser extent on cardio-vascular events of patients with RA, suggesting its usefulness in combination with other csDMARD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rempenault C, Barnetche T, Morel J, Lukas C, Gaujoux-Viala C, Combe B, Hua C. Metabolic and Cardio-Vascular Benefits of Hydroxychloroquine in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/metabolic-and-cardio-vascular-benefits-of-hydroxychloroquine-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/metabolic-and-cardio-vascular-benefits-of-hydroxychloroquine-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/